m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00291)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
IGF1
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Browse Drug
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | DKO-1 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: METTL3 knockdown DKO-1 cell
Control: DKO-1 cell
|
GSE182382 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -2.21E+00 p-value: 2.40E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| Representative RIP-seq result supporting the interaction between IGF1 and the regulator | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
| Regulation | logFC: 6.27E+00 | GSE60213 |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | The long-lived endocrine mutants - Snell dwarf, growth hormone receptor deletion and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A knockout - all show increases in the N6-adenosine-methyltransferases (METTL3/14) that catalyze 6-methylation of adenosine (m6A) in the 5' UTR region of select mRNAs. In addition, these mice have elevated levels of YTHDF1, which recognizes m6A and promotes translation by a cap-independent mechanism. Augmented translation by cap-independent pathways facilitated by m6A modifications contribute to the stress resistance and increased healthy longevity of mice with diminished GH and Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF1) signals. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ageing-related disease | ICD-11: 9B10-9B60 | ||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | DNA repair and mitochondrial stress | |||
| In-vitro Model | Mouse fibroblasts (Major cellular components of loose connective tissue) | |||
Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL14 | ||
| Cell Line | BMDM | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: METTL14 knockout mice BMDM
Control: Wild type mice BMDM
|
GSE153512 | |
| Regulation |
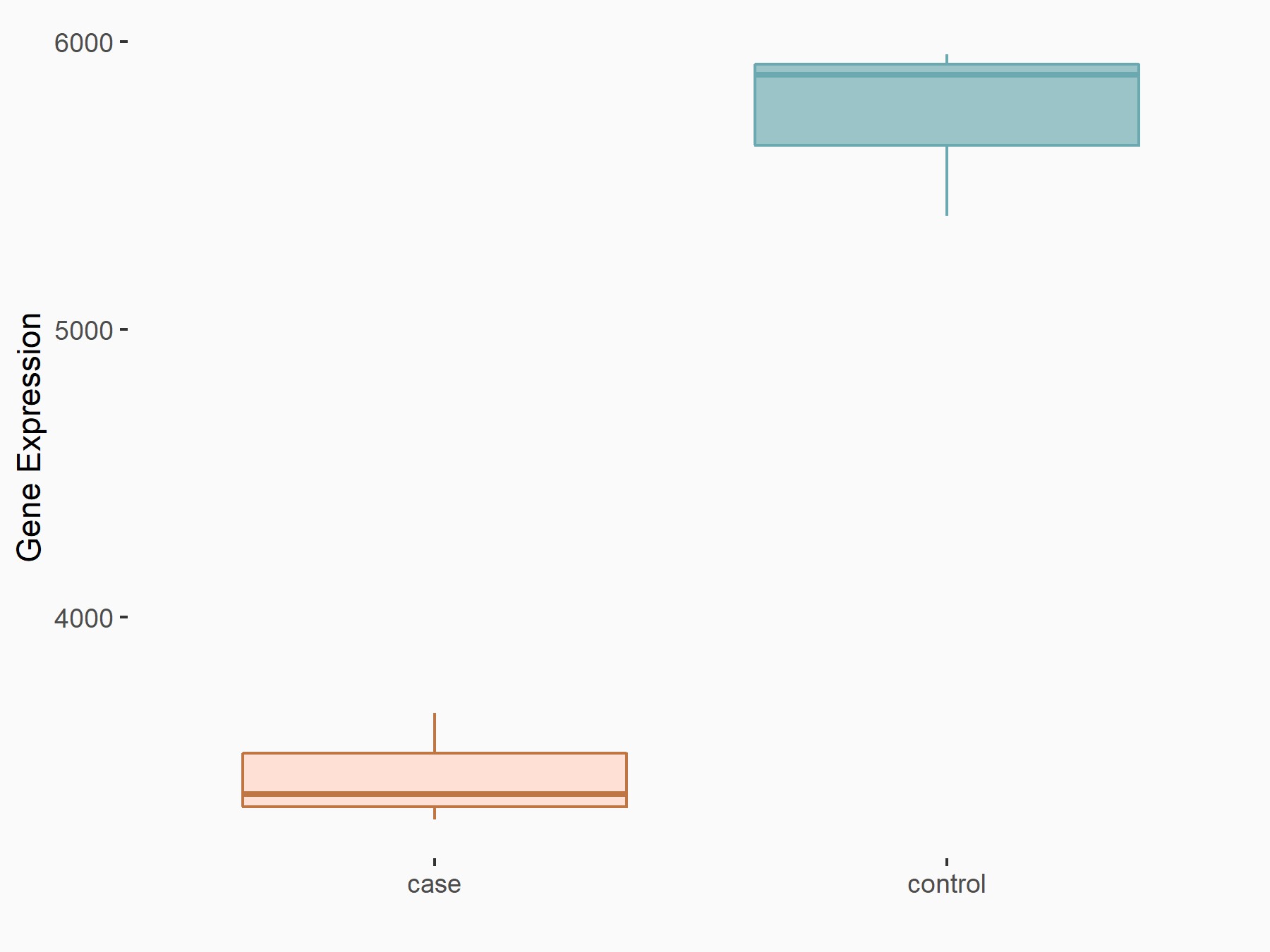  |
logFC: -7.37E-01 p-value: 4.88E-20 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | The long-lived endocrine mutants - Snell dwarf, growth hormone receptor deletion and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A knockout - all show increases in the N6-adenosine-methyltransferases (METTL3/14) that catalyze 6-methylation of adenosine (m6A) in the 5' UTR region of select mRNAs. In addition, these mice have elevated levels of YTHDF1, which recognizes m6A and promotes translation by a cap-independent mechanism. Augmented translation by cap-independent pathways facilitated by m6A modifications contribute to the stress resistance and increased healthy longevity of mice with diminished GH and Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF1) signals. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ageing-related disease | ICD-11: 9B10-9B60 | ||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | DNA repair and mitochondrial stress | |||
| In-vitro Model | Mouse fibroblasts (Major cellular components of loose connective tissue) | |||
YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) [READER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by YTHDF1 | ||
| Cell Line | AGS cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shYTHDF1 AGS
Control: shNC AGS
|
GSE166972 | |
| Regulation |
  |
logFC: -1.17E+00 p-value: 4.12E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | The long-lived endocrine mutants - Snell dwarf, growth hormone receptor deletion and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A knockout - all show increases in the N6-adenosine-methyltransferases (METTL3/14) that catalyze 6-methylation of adenosine (m6A) in the 5' UTR region of select mRNAs. In addition, these mice have elevated levels of YTHDF1, which recognizes m6A and promotes translation by a cap-independent mechanism. Augmented translation by cap-independent pathways facilitated by m6A modifications contribute to the stress resistance and increased healthy longevity of mice with diminished GH and Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF1) signals. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ageing-related disease | ICD-11: 9B10-9B60 | ||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | DNA repair and mitochondrial stress | |||
| In-vitro Model | Mouse fibroblasts (Major cellular components of loose connective tissue) | |||
Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 (IGFBP3) [READER]
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Overexpression of IGFBP3 induced apoptosis and enhanced cisplatin response in vitro and confirmed that the suppression is in part by blocking Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF1) signaling. IGFBP3 is effective in lung cancer cells with high IGF1 signaling activity and imply that relevant biomarkers are essential in selecting lung cancer patients for IGF1-targeted therapy. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | NCI-H460 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 |
| HCC2429 | Lung non-small cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5132 | |
| In-vivo Model | Paired littermates of F2 (Igfbp3+/+:KrasG12D/+ and Igfbp3-/-:KrasG12D/+) were sacrificed ranging from ages 4 to 7 months. After preliminary analysis of F2 mice, we sacrificed 5-month-old Igfbp3+/+:KrasG12D/+ and Igfbp3-/-KrasG12D/+ mice that had been backcrossed to S129 background for representative analysis. The lung tissue was immediately removed after the mice were sacrificed and visible pleural nodules were counted directly. | |||
Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Overexpression of IGFBP3 induced apoptosis and enhanced cisplatin response in vitro and confirmed that the suppression is in part by blocking Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF1) signaling. IGFBP3 is effective in lung cancer cells with high IGF1 signaling activity and imply that relevant biomarkers are essential in selecting lung cancer patients for IGF1-targeted therapy. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| Target Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 (IGFBP3) | READER | ||
| Responsed Drug | Cisplatin | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | NCI-H460 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 |
| HCC2429 | Lung non-small cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5132 | |
| In-vivo Model | Paired littermates of F2 (Igfbp3+/+:KrasG12D/+ and Igfbp3-/-:KrasG12D/+) were sacrificed ranging from ages 4 to 7 months. After preliminary analysis of F2 mice, we sacrificed 5-month-old Igfbp3+/+:KrasG12D/+ and Igfbp3-/-KrasG12D/+ mice that had been backcrossed to S129 background for representative analysis. The lung tissue was immediately removed after the mice were sacrificed and visible pleural nodules were counted directly. | |||
Ageing-related disease [ICD-11: 9B10-9B60]
| In total 2 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | The long-lived endocrine mutants - Snell dwarf, growth hormone receptor deletion and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A knockout - all show increases in the N6-adenosine-methyltransferases (METTL3/14) that catalyze 6-methylation of adenosine (m6A) in the 5' UTR region of select mRNAs. In addition, these mice have elevated levels of YTHDF1, which recognizes m6A and promotes translation by a cap-independent mechanism. Augmented translation by cap-independent pathways facilitated by m6A modifications contribute to the stress resistance and increased healthy longevity of mice with diminished GH and Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF1) signals. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ageing-related disease [ICD-11: 9B10-9B60] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | DNA repair and mitochondrial stress | |||
| In-vitro Model | Mouse fibroblasts (Major cellular components of loose connective tissue) | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | The long-lived endocrine mutants - Snell dwarf, growth hormone receptor deletion and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A knockout - all show increases in the N6-adenosine-methyltransferases (METTL3/14) that catalyze 6-methylation of adenosine (m6A) in the 5' UTR region of select mRNAs. In addition, these mice have elevated levels of YTHDF1, which recognizes m6A and promotes translation by a cap-independent mechanism. Augmented translation by cap-independent pathways facilitated by m6A modifications contribute to the stress resistance and increased healthy longevity of mice with diminished GH and Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF1) signals. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ageing-related disease [ICD-11: 9B10-9B60] | |||
| Target Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 1 (YTHDF1) | READER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | Nucleotide excision repair | hsa03420 | ||
| Cell Process | DNA repair and mitochondrial stress | |||
| In-vitro Model | Mouse fibroblasts (Major cellular components of loose connective tissue) | |||
Cisplatin
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [2] | |||
| Response Summary | Overexpression of IGFBP3 induced apoptosis and enhanced cisplatin response in vitro and confirmed that the suppression is in part by blocking Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF1) signaling. IGFBP3 is effective in lung cancer cells with high IGF1 signaling activity and imply that relevant biomarkers are essential in selecting lung cancer patients for IGF1-targeted therapy. | |||
| Target Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 (IGFBP3) | READER | ||
| Responsed Disease | Lung cancer | ICD-11: 2C25 | ||
| Pathway Response | MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | NCI-H460 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0459 |
| HCC2429 | Lung non-small cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5132 | |
| In-vivo Model | Paired littermates of F2 (Igfbp3+/+:KrasG12D/+ and Igfbp3-/-:KrasG12D/+) were sacrificed ranging from ages 4 to 7 months. After preliminary analysis of F2 mice, we sacrificed 5-month-old Igfbp3+/+:KrasG12D/+ and Igfbp3-/-KrasG12D/+ mice that had been backcrossed to S129 background for representative analysis. The lung tissue was immediately removed after the mice were sacrificed and visible pleural nodules were counted directly. | |||
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00291)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: 2OMSITE000074 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102398897-102398898:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | CTTGGGAGAAGGCTTAGAATAAAAGATGTAGCACATTTTGC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | Nm-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337514.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: Nm_site_1477 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 26 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014676 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102401284-102401285:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | ATCTGCCAGCTGTGTCATGGACTCACCACTGTGTGACCTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_3882535; ENST00000337514.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204810 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014677 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102401306-102401307:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TTTTCTCATGGAAGAAATGAACATCTGCCAGCTGTGTCATG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337514.10; rmsk_3882535 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204811 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014678 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102401378-102401379:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CTGGCGAGTCCAGAGAGGAAACTGTGGAATGGAAAAAGCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337514.10; rmsk_3882535 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204814 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014679 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102401399-102401400:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AGTCCACTGATGCAAATTGGACTGGCGAGTCCAGAGAGGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337514.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204816 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014680 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102401426-102401427:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCTTCCAAGAGGAACTTCAGACACAAAAGTCCACTGATGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337514.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204818 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014681 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102401433-102401434:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AGTTATGCCTTCCAAGAGGAACTTCAGACACAAAAGTCCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337514.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204819 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014682 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102401489-102401490:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CAAGGGGAAGGGTACTGAAAACACCATCCATTTGGGAAAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337514.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204821 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014683 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102402355-102402356:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCAATGAAATACACAAGTAAACATTCCAACATTGTCTTTAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000481539.1; ENST00000337514.10; ENST00000644491.1; ENST00000392904.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204823 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014684 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102402425-102402426:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GTTACCTGTTAAACTTTGGAACACCTACCAAAAAATAAGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000644491.1; ENST00000481539.1; ENST00000337514.10; ENST00000392904.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204825 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014685 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102402433-102402434:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CTGCACGAGTTACCTGTTAAACTTTGGAACACCTACCAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000481539.1; ENST00000392904.5; ENST00000644491.1; ENST00000337514.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204826 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014686 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102402501-102402502:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GAACTACAGGATGTAGGAAGACCCTCCTGAGGAGTGAAGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392904.5; ENST00000481539.1; ENST00000644491.1; ENST00000424202.6; ENST00000337514.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204827 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014687 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102402519-102402520:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AGGGAGTGCAGGAAACAAGAACTACAGGATGTAGGAAGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000644491.1; ENST00000392904.5; ENST00000392905.7; ENST00000424202.6; ENST00000337514.10; ENST00000481539.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204828 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014688 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102402525-102402526:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AAGTAGAGGGAGTGCAGGAAACAAGAACTACAGGATGTAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000424202.6; ENST00000337514.10; ENST00000392904.5; ENST00000392905.7; ENST00000644491.1; ENST00000481539.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204829 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014689 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102417596-102417597:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CCTAGAAAGCGCAAAGAAAGACAGTGGCAAAAATGAAAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337514.10; ENST00000392905.7; ENST00000644491.1; ENST00000392904.5; ENST00000307046.8; ENST00000424202.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204830 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014690 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102417649-102417650:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TTAGAGAATCTCGCTAAGAAACATGGAGAAAACGGAAAAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000307046.8; ENST00000392905.7; ENST00000392904.5; ENST00000424202.6; ENST00000644491.1; ENST00000337514.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204831 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014691 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102417766-102417767:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GGATGATGAGAGAGGAGCAGACAGCAAGAATGAAAAGCAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392905.7; ENST00000307046.8; ENST00000424202.6; ENST00000392904.5; ENST00000644491.1; ENST00000337514.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204832 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014692 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102417800-102417801:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | ATGAAGGACAGGAGGATTAAACAGACAGAGGCAAGGATGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392904.5; ENST00000337514.10; ENST00000307046.8; ENST00000424202.6; ENST00000392905.7; ENST00000644491.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204833 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014693 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102417813-102417814:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GCAAAAAAGGAAAATGAAGGACAGGAGGATTAAACAGACAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000337514.10; ENST00000307046.8; ENST00000424202.6; ENST00000644491.1; ENST00000392904.5; ENST00000392905.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204834 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014694 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102417912-102417913:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | GAGGGGAACAGAAGGAGGGGACAGAAGCAAGTCTGCAGATC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000307046.8; ENST00000392904.5; ENST00000392905.7; ENST00000337514.10; ENST00000424202.6; ENST00000644491.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204835 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014695 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102417925-102417926:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AAGACACATCCAGGAGGGGAACAGAAGGAGGGGACAGAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000392904.5; ENST00000337514.10; ENST00000307046.8; ENST00000644491.1; ENST00000392905.7; ENST00000424202.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204836 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014696 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102417942-102417943:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GAAGGAAAGGTTGGCCAAAGACACATCCAGGAGGGGAACAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000307046.8; ENST00000392905.7; ENST00000392904.5; ENST00000644491.1; ENST00000337514.10; ENST00000424202.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204837 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014697 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102417977-102417978:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GCCCCCATCTACCAACAAGAACACGAAGTCTCAGAGAAGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000307046.8; ENST00000392905.7; ENST00000337514.10; ENST00000392904.5; ENST00000644491.1; ENST00000424202.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204838 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014698 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102419516-102419517:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GCCACACCGACATGCCCAAGACCCAGAAGGTAAGCCCACCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000644491.1; ENST00000307046.8; ENST00000337514.10; ENST00000392905.7; ENST00000424202.6; ENST00000392904.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204839 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014699 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102419645-102419646:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GCAGTCGGAGGGCGCCTCAGACAGGCATCGTGGATGAGTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000644491.1; ENST00000307046.8; ENST00000392904.5; ENST00000392905.7; ENST00000337514.10; ENST00000424202.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204840 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014700 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102475659-102475660:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TCTTCAGTTCGTGTGTGGAGACAGGGGCTTTTATTTCAGTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000424202.6; ENST00000644491.1; ENST00000392905.7; ENST00000307046.8; ENST00000337514.10; ENST00000392904.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204841 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE014701 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:102475715-102475716:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | ACCAGCTCTGCCACGGCTGGACCGGAGACGCTCTGCGGGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000424202.6; ENST00000644491.1; ENST00000392905.7; ENST00000307046.8; ENST00000337514.10; ENST00000392904.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_204842 | ||
References