m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT05954
|
[1] | |||
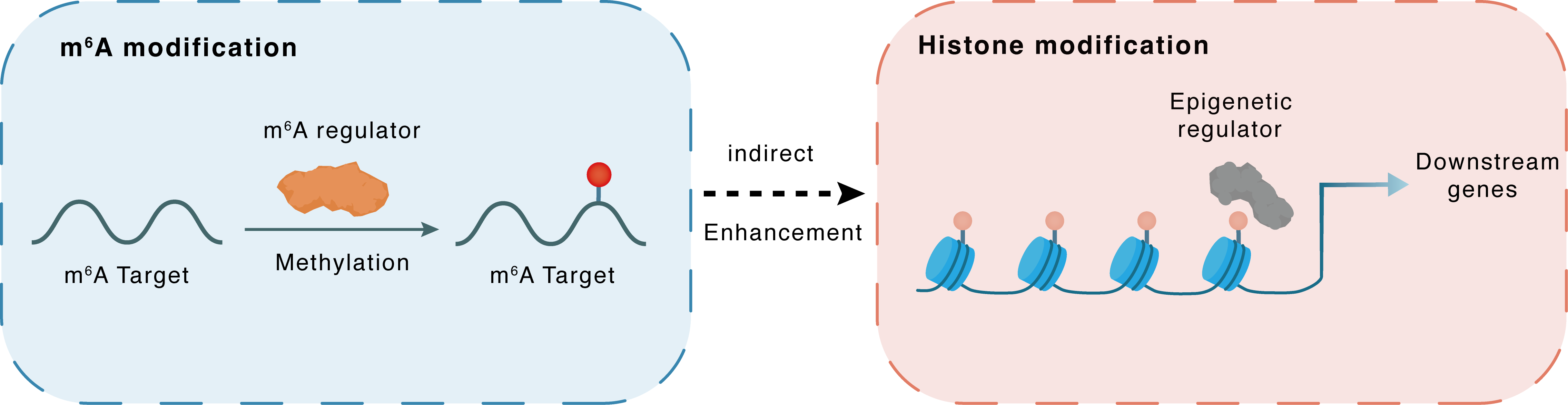 m6A modification
caRNAs
caRNAs
RBM15
Methylation
m6A modification
caRNAs
caRNAs
RBM15
Methylation
 : m6A sites
Indirect
Enhancement
Histone modification
H3K27me3
PRC2
Downstream Gene : m6A sites
Indirect
Enhancement
Histone modification
H3K27me3
PRC2
Downstream Gene
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | RNA-binding motif protein 15 (RBM15) | WRITER | |||
| m6A Target | Chromatin-associated RNAs (caRNAs) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Histone modification (HistMod) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) | WRITER | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | m6A → Histone modification | Enhancement | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | m6A modification indirectly regulates histone modification through downstream signaling pathways | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | RBFOX2 can recruit RBM15, an MTC component, to facilitate methylation of Chromatin-associated RNAs (caRNAs). RBM15 also physically interacts with YTHDC1 and recruits polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) to the RBFOX2-bound loci for chromatin silencing and transcription suppression. PRC2, a key player in epigenetic regulation, is known to mediate the trimethylation of histone H3 on lysine 27 (Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3)). This modification is crucial for the establishment of a repressive chromatin state, effectively preventing the binding of transcriptional activators and thus suppressing gene expression at the loci targeted by RBFOX2 and its associated factors. RBFOX2/m6A/RBM15/YTHDC1/PRC2 axis plays a critical role in myeloid leukaemia. | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2B33.1 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell survival | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| Cell differentiation | |||||
| Cell invasion | |||||
| Apoptosis | |||||
| In-vivo Model | Sexually mature ICR mice, aged at least 10 weeks, were paired as one female and one male per cage to obtain pregnancies. The time of the vaginal plug sighting was denoted as day 0.5 of the pregnancy. The mice were divided into an FTO protein group and control group, with 10 pairs of mice in each group. Starting on day 0.5 of the pregnancy, mice in the FTO protein group were intraperitoneally injected daily with FTO protein (3.5 ng/kg), whereas those in the control group had daily intraperitoneal injections of equal volumes of saline. Female mice were euthanised on day 13.5 of the pregnancy (day 12.5-14.5), and the total numbers of normal and resorbed embryos were determined, along with the rate of embryo resorption. | ||||