m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT05674
|
[1] | |||
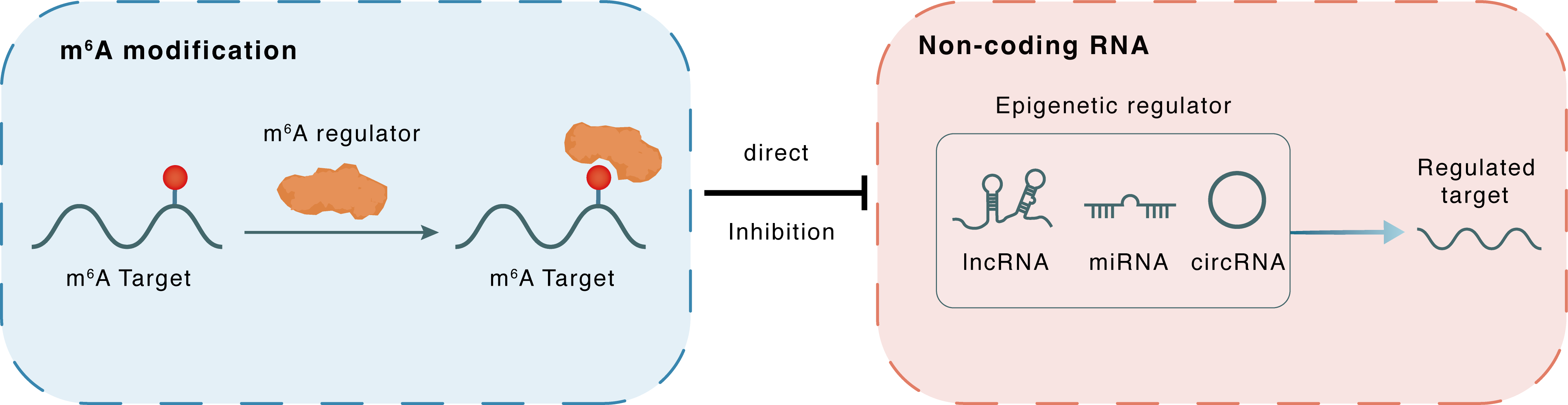 m6A modification
miR-93-5p
miR-93-5p
HNRNPA2B1
m6A modification
miR-93-5p
miR-93-5p
HNRNPA2B1
 : m6A sites
Direct
Inhibition
Non-coding RNA
miR-93-5p
FRMD6
lncRNA miRNA circRNA : m6A sites
Direct
Inhibition
Non-coding RNA
miR-93-5p
FRMD6
lncRNA miRNA circRNA
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins A2/B1 (HNRNPA2B1) | READER | |||
| m6A Target | hsa-miR-93-5p | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-93-5p | microRNA | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | FERM domain containing 6 (FRMD6) | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | m6A → ncRNA | Inhibition | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | m6A regulators directly modulate the functionality of ncRNAs through specific targeting ncRNA | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | Activation of the HNRNPA2B1/ hsa-miR-93-5p/FERM domain containing 6 (FRMD6) axis facilitates prostate cancer progression in an m6A-dependent manner | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Prostate cancer | ICD-11: 2C82 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | ||||
| Cell migration | |||||
| Cell invasion | |||||
| In-vivo Model | Male four-week-old BALB/C nude mice were inoculated subcutaneously in the right axilla with 1×106 HNRNPA2B1 knockout or negative control DU145 cells. Xenograft tumor growth was recorded weekly by measuring the width (W) and length (L) of the tumor with vernier calipers and calculating the tumor volume (V, mm3) using the formula V = W2 × L × 0.52. Xenograft tumors were harvested and weighed five weeks after cell injection. | ||||
Full List of Potential Compound(s) Related to This m6A-centered Crosstalk
| 2C82: Prostate cancer | 1 Compound(s) Regulating the Disease | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| CC-94676 | Phase 1 | [2] | ||
| External Link | ||||
References