m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT05541
|
[1] | |||
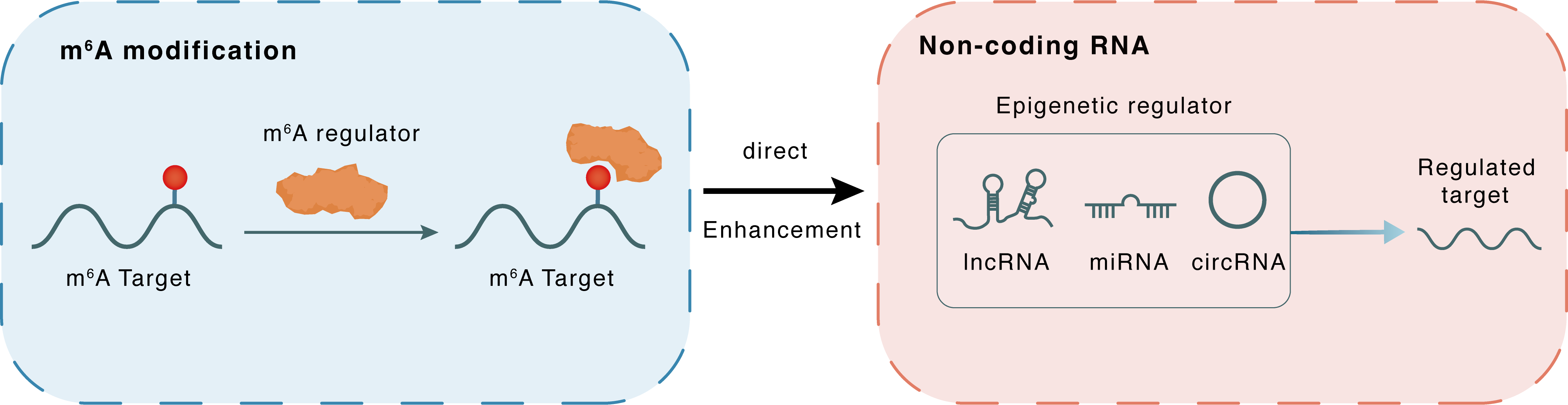 m6A modification
KCNQ1OT1
KCNQ1OT1
YTHDF2
m6A modification
KCNQ1OT1
KCNQ1OT1
YTHDF2
 : m6A sites
Direct
Enhancement
Non-coding RNA
KCNQ1OT1
HOXA9
lncRNA miRNA circRNA : m6A sites
Direct
Enhancement
Non-coding RNA
KCNQ1OT1
HOXA9
lncRNA miRNA circRNA
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) | READER | |||
| m6A Target | KCNQ1 opposite strand/antisense transcript 1 (KCNQ1OT1) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | KCNQ1 opposite strand/antisense transcript 1 (KCNQ1OT1) | LncRNA | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Homeobox A9 (HOXA9) | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | m6A → ncRNA | Enhancement | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | m6A regulators directly modulate the functionality of ncRNAs through specific targeting ncRNA | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | ALKBH5 mediates KCNQ1 opposite strand/antisense transcript 1 (KCNQ1OT1) expression via an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner and KCNQ1OT1 could directly bind to Homeobox A9 (HOXA9) to further regulate the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells. | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Laryngeal cancer | ICD-11: 2C23 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | ||||
| Cell migration | |||||
| Cell invasion | |||||
In-vitro Model |
HOK | Normal | Hexagrammos otakii | CVCL_YE19 | |
| Tu 212 | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_4915 | ||
| AMC-HN-8 | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_5966 | ||
| In-vivo Model | 1 × 106 (100 ul) cells of infected and uninfected by lentiviral were, respectively, injected subcutaneously into nude mice which divided randomly into scramble group and shKCNQ1OT1-1 group. | ||||