m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT05344
|
[1] | |||
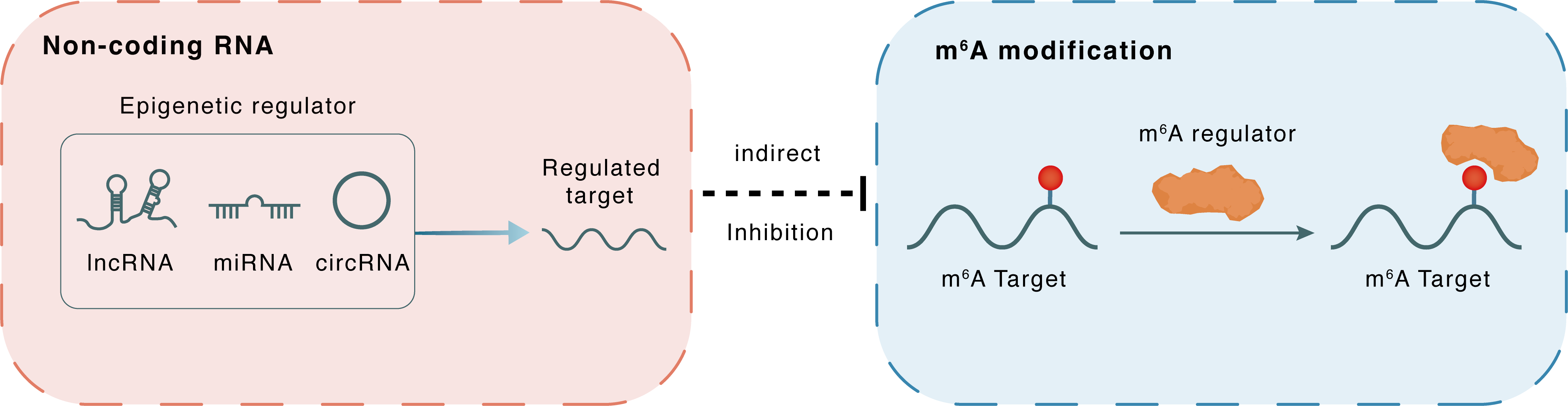 Non-coding RNA
miR-320d
METTL3
lncRNA miRNA circRNA
Indirect
Inhibition
m6A modification
KIF3C
KIF3C
IGF2BP1
Non-coding RNA
miR-320d
METTL3
lncRNA miRNA circRNA
Indirect
Inhibition
m6A modification
KIF3C
KIF3C
IGF2BP1
 : m6A sites : m6A sites
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) | READER | |||
| m6A Target | Kinesin-like protein KIF3C (KIF3C) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-320d | microRNA | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 3 (METTL3) | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | ncRNA → m6A | Inhibition | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | ncRNAs indirectly impacts m6A modification through downstream signaling pathways | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | Methyltransferase-like protein 3 (METTL3)-mediated m6A modification of Kinesin-like protein KIF3C (KIF3C)-mRNA promotes prostate cancer progression and is negatively regulated by hsa-miR-320d. METTL3 induced m6A modification on KIF3C, promoting the stabilization of KIF3C-mRNA by IGF2 binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1). | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Prostate cancer | ICD-11: 2C82 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell migration | ||||
| Cell invasion | |||||
| In-vivo Model | For the proliferation assays, C4-2B cells of KIF3C knockdown, negative control (1×106/200μl) were subcutaneously injected into BALB/c nude mice. The tumors were dissected and weighed (4-6 weeks old, male). | ||||
Full List of Potential Compound(s) Related to This m6A-centered Crosstalk
| 2C82: Prostate cancer | 1 Compound(s) Regulating the Disease | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| CC-94676 | Phase 1 | [2] | ||
| External Link | ||||
References