m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT03236
|
[1] | |||
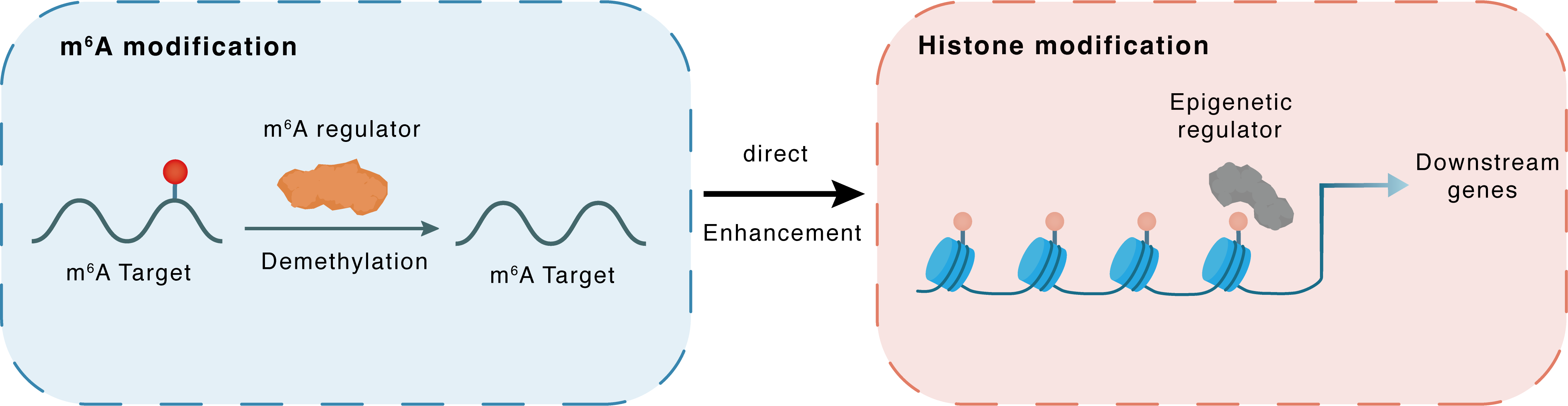 m6A modification
RBBP5
RBBP5
ALKBH5
Demethylation
m6A modification
RBBP5
RBBP5
ALKBH5
Demethylation
 : m6A sites
Direct
Enhancement
Histone modification
H3K4me3
RBBP5
GATA4 : m6A sites
Direct
Enhancement
Histone modification
H3K4me3
RBBP5
GATA4
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ERASER | |||
| m6A Target | Retinoblastoma-binding protein 5 (RBBP5) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Histone modification (HistMod) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Retinoblastoma-binding protein 5 (RBBP5) | WRITER | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | View Details | |||
| Downstream Gene | GATA4 | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | m6A → Histone modification | Enhancement | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | m6A modification impacts directly histone modification through modulating the expression level of histone-associated enzymes | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | KDM5B and Retinoblastoma-binding protein 5 (RBBP5), the components of H3K4 modifying enzyme complexes, are identified as downstream targets for ALKBH5 in cardiac-committed hESCs. Loss of function of ALKBH5 alters the expression of KDM5B and RBBP5 through impairing stability of their mRNAs, which in turn promotes the transcription of GATA4 by enhancing Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) at the promoter region of GATA4. | ||||