m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT03230
|
[1] | |||
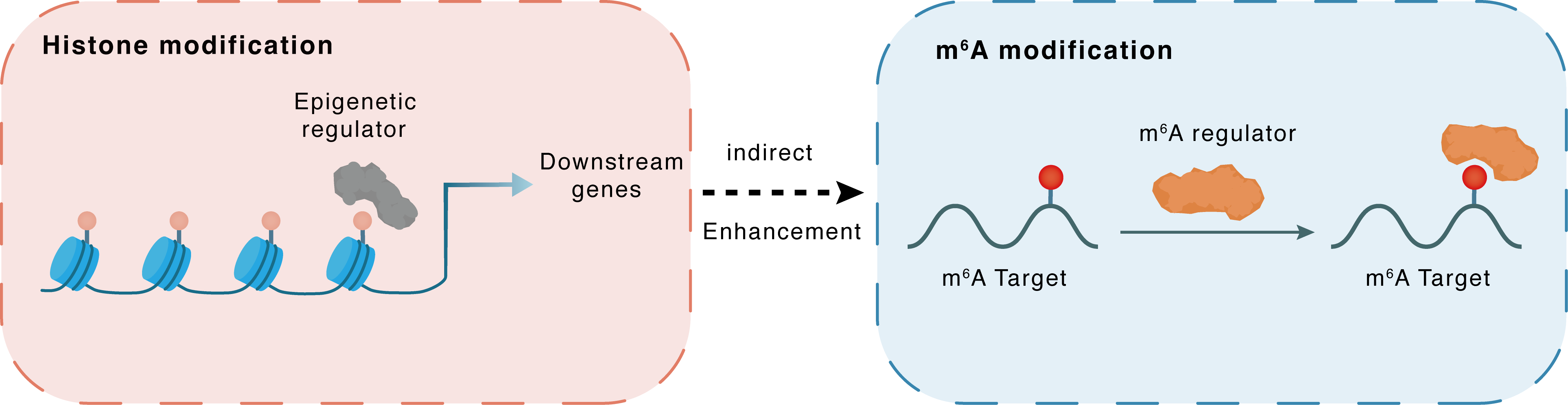 Histone modification
H3K4me3
PHF20
METTL14
Indirect
Enhancement
m6A modification
HOXA13
HOXA13
IGF2BP3
Histone modification
H3K4me3
PHF20
METTL14
Indirect
Enhancement
m6A modification
HOXA13
HOXA13
IGF2BP3
 : m6A sites : m6A sites
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3) | READER | |||
| m6A Target | Homeobox protein Hox-A13 (HOXA13) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Histone modification (HistMod) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | PHD finger protein 20 (PHF20) | READER | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | View Details | |||
| Downstream Gene | METTL14 | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | Histone modification → m6A | Enhancement | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | histone modification indirectly regulates m6A modification through downstream signaling pathways | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | PHF20 elevated METTL14 expression by enhancing the enrichment of Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) on its promoter, and METTL14 strengthened Homeobox protein Hox-A13 (HOXA13) m6A methylation to maintain HOXA13 mRNA stability through IGF2BP3. In conclusion, PHF20 elevates METTL14 expression by enhancing H3K4me3 enrichment on its promoter and enhances HOXA13 mRNA stability via IGF2BP3-mediated m6A modification, thus facilitating HOXA13 expression and eventually inducing osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. | ||||