m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT03075
|
[1] | |||
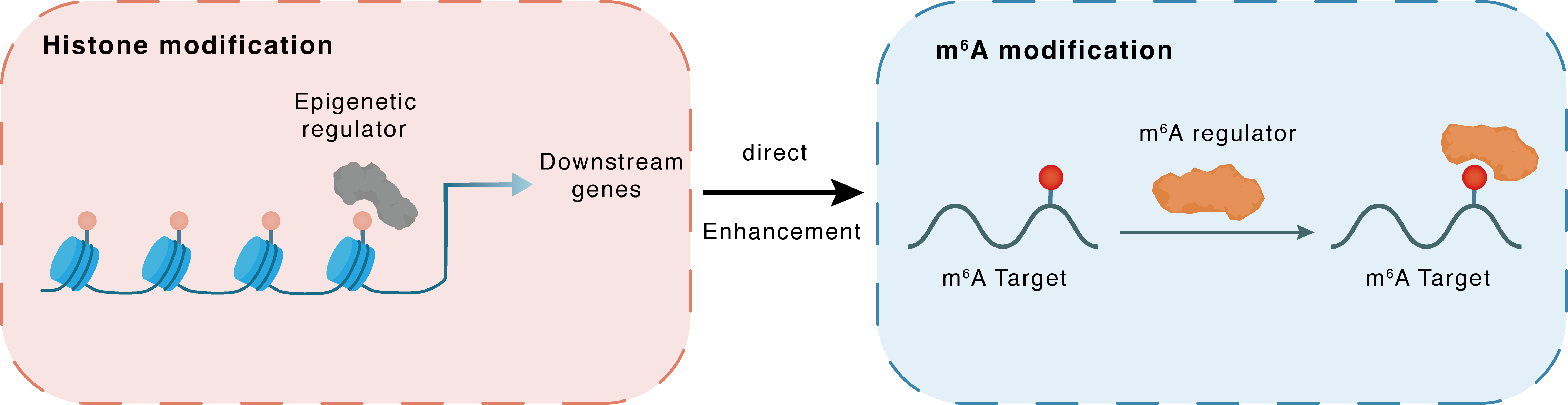 Histone modification
HNRNPA2B1
JMJD6
Downstream Gene
Direct
Enhancement
m6A modification
IFI16
IFI16
hnRNPA2B1
Histone modification
HNRNPA2B1
JMJD6
Downstream Gene
Direct
Enhancement
m6A modification
IFI16
IFI16
hnRNPA2B1
 : m6A sites : m6A sites
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins A2/B1 (HNRNPA2B1) | READER | |||
| m6A Target | Gamma-interferon-inducible protein 16 (IFI16) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Histone modification (HistMod) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Bifunctional arginine demethylase and lysyl-hydroxylase JMJD6 (JMJD6) | ERASER | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 (HNRNPA2B1) | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | Histone modification → m6A | Enhancement | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | histone modification directly impacts m6A modification through recruiting m6A regulator | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | the arginine demethylase JMJD6 promotes the demethylation of HNRNPA2B1 at Arg226 and activates its translocation to cytoplasm, which further magnifies the expression of CGAS, Gamma-interferon-inducible protein 16 (IFI16), and STING | ||||
In-vitro Model |
RAW 264.7 | Mouse leukemia | Mus musculus | CVCL_0493 | |
| HEK293 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0045 | ||
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||
| In-vivo Model | Hnrnpa2b1fl/fl and Hnrnpa2b1fl/flLyz2-Cre+ mice were infected with 1×108 plaque-forming units (PFU) of HSV-1 viruses intraperitoneally. Serum IFN-beta concentrations were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit. HSV-1 titers were determined by plaque assays using homogenates from brains of infected mice. | ||||