m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT03027
|
[1] | |||
 m6A modification
SETD1A
SETD1A
METTL14
Methylation
m6A modification
SETD1A
SETD1A
METTL14
Methylation
 : m6A sites
Direct
Enhancement
Histone modification
H3K4me3
SETD1A
KLF1 : m6A sites
Direct
Enhancement
Histone modification
H3K4me3
SETD1A
KLF1
|
|||||
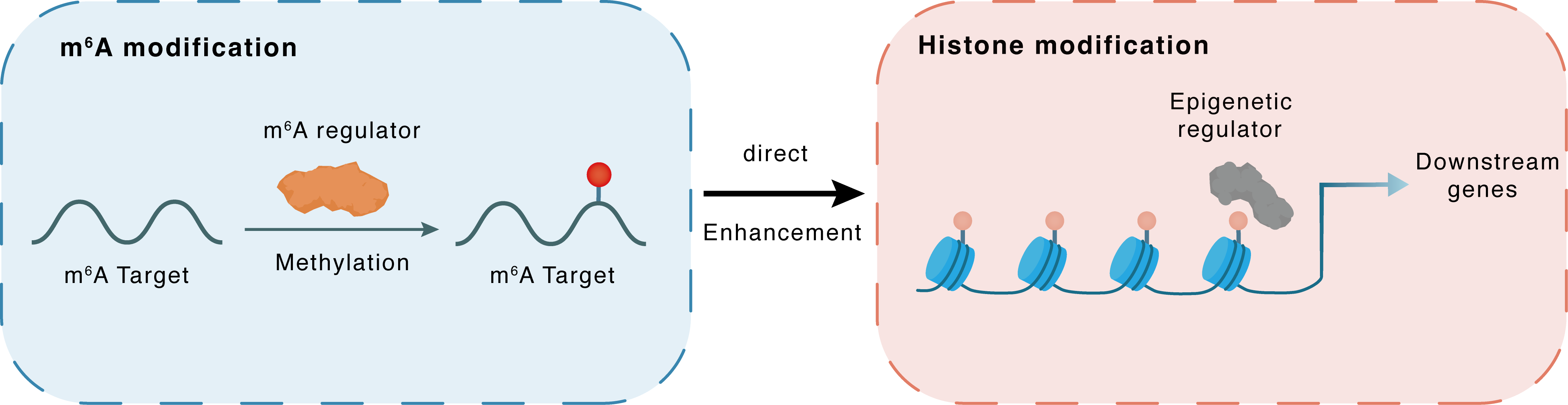
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | |||
| m6A Target | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD1A (SETD1A) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Histone modification (HistMod) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD1A (SETD1A) | WRITER | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | View Details | |||
| Downstream Gene | KLF1 | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | m6A → Histone modification | Enhancement | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | m6A modification impacts directly histone modification through modulating the expression level of histone-associated enzymes | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | Among validating hits are genes coding for the N6-methyladenosine (m6A) mRNA methyltransferase (MTase) complex, including, METTL14, METTL3, and WTAP. We demonstrate that m6A MTase activity promotes erythroid gene expression programs through selective translation of ~300 m6A marked mRNAs, including those coding for Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD1A (SETD1A), SETD1B and KTM2D. Remarkably, loss of m6A marks results in dramatic loss of Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) marks across key erythroid-specific KLF1 transcriptional targets | ||||
In-vitro Model |
HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| HEK293T | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0063 | ||