m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT02110
|
[1] | |||
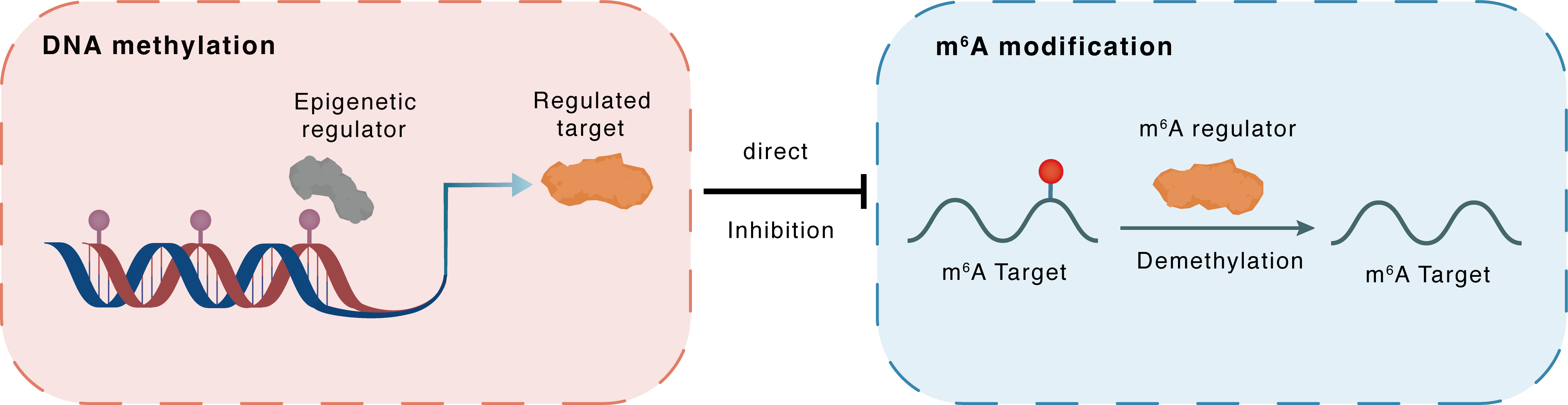 DNA methylation
Epigenetic Regulator
ALKBH5
Direct
Inhibition
m6A modification
ATG12
ATG12
ALKBH5
Demethylation
DNA methylation
Epigenetic Regulator
ALKBH5
Direct
Inhibition
m6A modification
ATG12
ATG12
ALKBH5
Demethylation
 : m6A sites : m6A sites
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | ERASER | |||
| m6A Target | Ubiquitin-like protein ATG12 (ATG12) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | DNA methylation (DNAMeth) | ||||
| Regulated Target | RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | DNA methylation → m6A | Inhibition | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | DNA methylation directly impacts m6A modification through modulating the expression level of m6A regulator | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | Folic acid reduces the expression of ALKHB5 via promoter DNA hypermethylation. Decreased ALKBH5 causes increased m6A modification and increased expression of Ubiquitin-like protein ATG12 (ATG12) in a demethylase activity-dependent manner, thereby promoting autophagy and preventing hepatic steatosis. | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease | ICD-11: DB92.Z | |||
| Cell Process | Cell autophagy | ||||
| Lipid metabolism | |||||
Full List of Potential Compound(s) Related to This m6A-centered Crosstalk
| DB92: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | 12 Compound(s) Regulating the Disease | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| Epeleuton | Phase 2 | [2] | ||
| Synonyms |
(S,5Z,8Z,11Z,13E,17Z)-Ethyl 15-hydroxyicosa-5,8,11,13,17-pentaenoate; 15(S)-HEPE-EE; 15(S)-HYDROXY-(5Z,8Z,11Z,13E,17Z)-EICOSAPENTAENOIC ACID ETHYL ESTER; 1667760-39-5; 5,8,11,13,17-Eicosapentaenoic acid, 15-hydroxy-, ethyl ester, (5Z,8Z,11Z,13E,15S,17Z)-; AKOS040748327; CHEMBL5095178; Epeleuton; Epeleuton [INN]; FA9BPX1T6V; UNII-FA9BPX1T6V
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
| IMM-124E | Phase 2 | [3] | ||
| External Link | ||||
| TVB-2640 | Phase 2 | [4] | ||
| Synonyms |
FASN-IN-2; 1399177-37-7; 4-(1-(4-Cyclobutyl-2-methyl-5-(5-methyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3- yl)benzoyl)piperidin-4-yl)benzonitrile; US8871790, 480; CHEMBL3661754; SCHEMBL12488853; BDBM137084; BCP30428; EX-A3643; s9714; ZINC150188638; HY-112829; CS-0066310; TVB2640; TVB 2640;FASN-IN-2; US8871790, 152; 4-(1-(4-Cyclobutyl-2-methyl-5-(3-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)benzoyl)piperidin-4-yl)benzonitrile; 4-(1-(4-cyclobutyl-2-methyl-5-(5-methyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)benzoyl)piperidin-4-yl)benzonitrile; 4-[1-[4-cyclobutyl-2-methyl-5-(5-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)benzoyl]piperidin-4-yl]benzonitrile
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
| Vupanorsen | Phase 2 | [5] | ||
| Synonyms |
IONIS-ANGPTL3-LRx; AKCEA-ANGPTL3-LRx
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
| ZED1227 | Phase 2 | [6] | ||
| Synonyms |
(2E,6S)-7-((1-(2-((2-Ethylbutyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl)-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-3-pyridinyl)amino)-6-(((1-methyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)carbonyl)amino)-7-oxo-2-heptenoic acid methyl ester; (2E,6S)-7-[[1-[2-[(2-Ethylbutyl)amino]-2-oxoethyl]-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-3-pyridinyl]amino]-6-[[(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)carbonyl]amino]-7-oxo-2-heptenoic Acid Methyl Ester; 1542132-88-6; 2-Heptenoic acid, 7-((1-(2-((2-ethylbutyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl)-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-3-pyridinyl)amino)-6-(((1-methyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)carbonyl)amino)-7-oxo-, methyl ester, (2E,6S)-; 2-Heptenoic acid, 7-[[1-[2-[(2-ethylbutyl)amino]-2-oxoethyl]-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-3-pyridinyl]amino]-6-[[(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)carbonyl]amino]-7-oxo-, methyl ester, (2E,6S)-; AKOS040742843; BDBM50245478; CHEMBL4081588; CS-0015432; EX-A7845R; GLUTAMINASE; GTPL12802; HY-19359; Methyl (2E,6S)-7-((1-(2-((2-ethylbutyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl)-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-3-pyridinyl)amino)-6-(((1-methyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)carbonyl)amino)-7-oxo-2-heptenoate; Methyl (2E,6S)-7-[[1-[2-[(2-ethylbutyl)amino]-2-oxoethyl]-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-3-pyridinyl]amino]-6-[[(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)carbonyl]amino]-7-oxo-2-heptenoate; Methyl (E,6S)-7-((1-(2-(2-ethylbutylamino)-2-oxo-ethyl)-2-oxo-3-pyridyl)amino)-6-((3-methylimidazole-4-carbonyl)amino)-7-oxo-hept-2-enoate; methyl (E,6S)-7-[[1-[2-(2-ethylbutylamino)-2-oxoethyl]-2-oxopyridin-3-yl]amino]-6-[(3-methylimidazole-4-carbonyl)amino]-7-oxohept-2-enoate; methyl (S,E)-7-((1-(2-((2-ethylbutyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)amino)-6-(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-5-carboxamido)-7-oxohept-2-enoate; MS-29784; SCHEMBL16735736; SCHEMBL16751074; T4SR539YKF; TAK-227; UNII-T4SR539YKF; ZED1227; ZED-1227
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
| PXL-770 | Phase 2 | [7] | ||
| External Link | ||||
| ASP9831 | Phase 2 | [8] | ||
| External Link | ||||
| Netoglitazone | Phase 2 | [9] | ||
| Synonyms |
Isaglitazone; Netoglitazone [USAN]; MCC 555; MCC-555; RWJ-241947; Netoglitazone (USAN/INN); 5-((6-((2-fluorophenyl)methoxy)-2-naphthalenyl)methyl)-2,4-thiazolidinedione; 5-({6-[(2-fluorobenzyl)oxy]naphthalen-2-yl}methyl)-1,3-thiazolidine-2,4-dione; 5-[[6-[(2-fluorophenyl)methoxy]naphthalen-2-yl]methyl]-1,3-thiazolidine-2,4-dione
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
| RG-125 | Phase 1 | [10] | ||
| Synonyms |
AZD4076
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
| GSK-677954 | Discontinued in Phase 2 | [11] | ||
| Synonyms |
SCHEMBL2065429
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
| KD-3020 | Preclinical | [11] | ||
| External Link | ||||
| RIPA-56 | Investigative | [12] | ||
| Synonyms |
1956370-21-0; N-benzyl-N-hydroxy-2,2-dimethylbutanamide; CHEMBL4092421; GTPL9643; SCHEMBL17874088; EX-A4338; BDBM50229025; MFCD30738006; s6511; ZINC616570725; CS-6266; compound 92 [WO2016101885]; compound 56 [PMID: 27992216]; HY-101032; C(C1=CC=CC=C1)N(C(C(CC)(C)C)=O)O; A1-28956
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| External Link | ||||
References