m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00792)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
KRT7-AS
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | HUVEC cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL3 HUVEC cells
Control: shScramble HUVEC cells
|
GSE157544 | |
| Regulation |
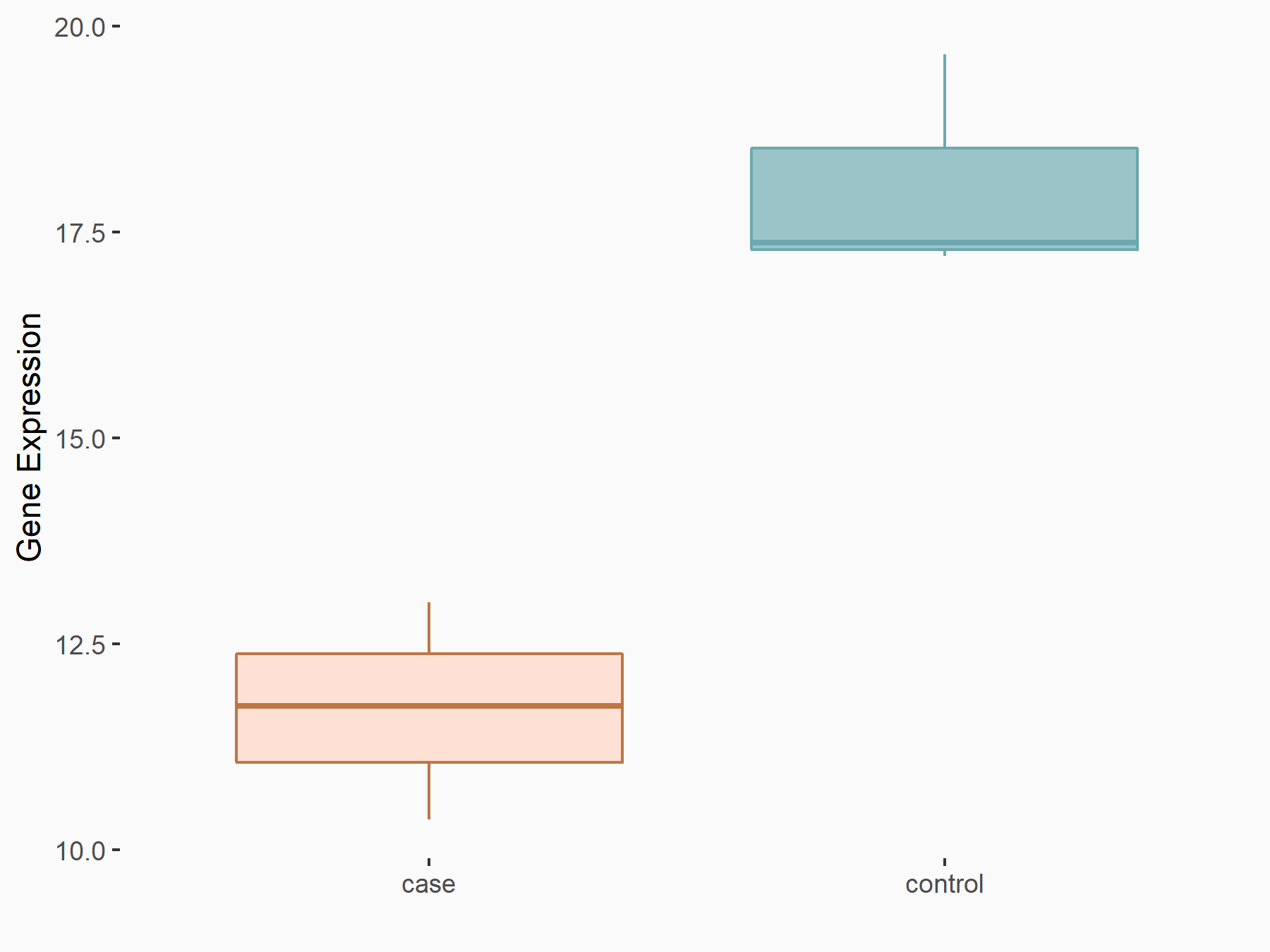 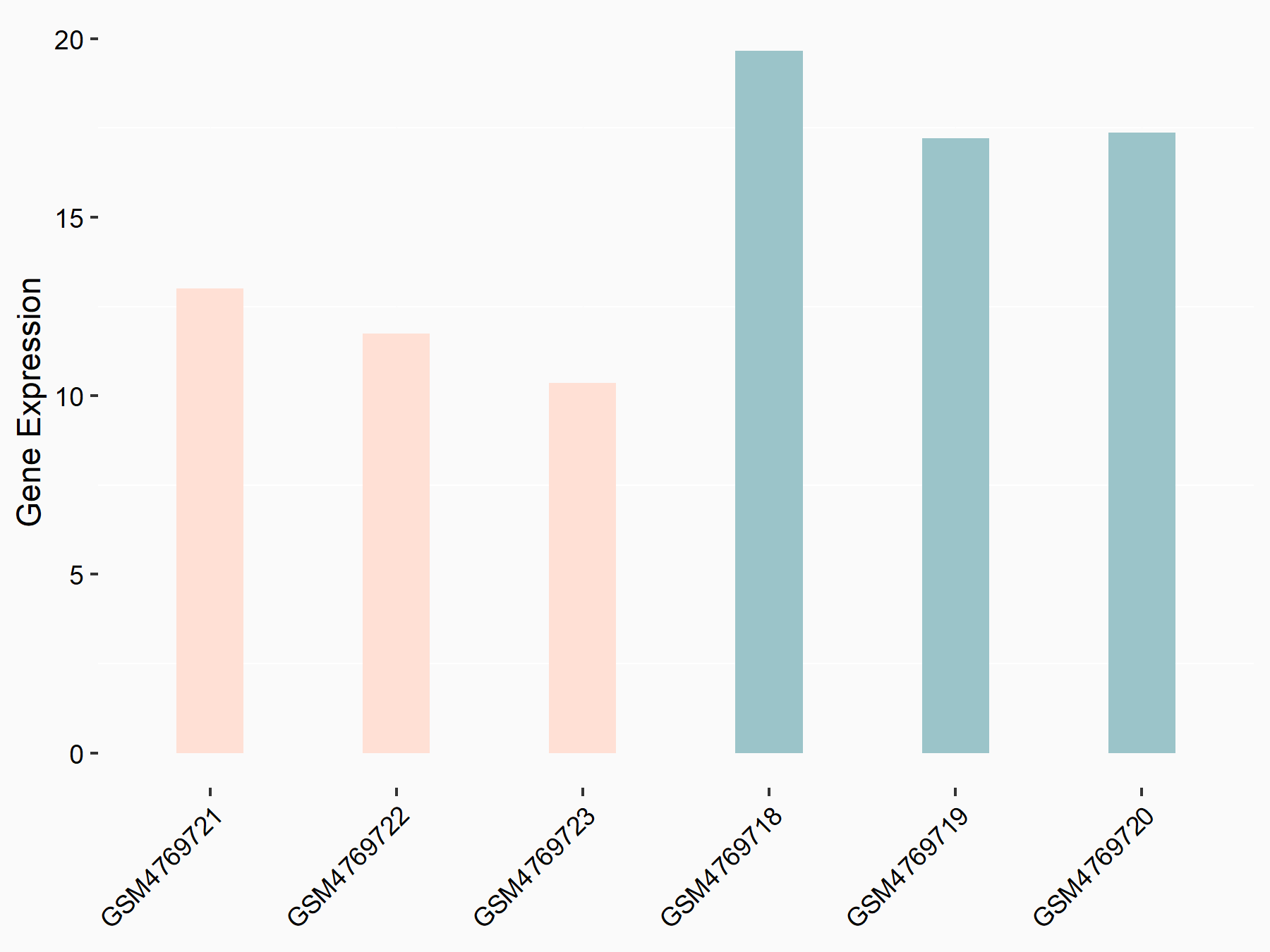 |
logFC: -5.89E-01 p-value: 3.54E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| Representative RIP-seq result supporting the interaction between KRT7-AS and the regulator | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
| Regulation | logFC: 8.95E+00 | GSE60213 |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Specifically, increased METTL3 methylated KRT7-AS at A877 to increase the stability of a KRT7-AS/KRT7 mRNA duplex via IGF2BP1/HuR complexes. m6A promotes breast cancer lung metastasis by increasing the stability of a KRT7-AS/KRT7 mRNA duplex and translation of KRT7. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer | ICD-11: 2C60 | ||
| Cell Process | Lung Metastasis | |||
| In-vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| In-vivo Model | First, subcutaneous transplanted model was used to evaluate the growth of BT-549LMF3 and BT-549 cells. Cells (5 × 106 per mouse, n = 5 for each group) were diluted in 200 ul PBS + 200 ul Matrigel (BD Biosciences) and subcutaneously injected into immunodeficient female mice. Second, subcutaneous transplanted model was used to evaluate the metastasis potential of BT-549LMF3 and BT-549 cells. Cells (5 × 106 per mouse, n = 5 for each group) were diluted in 200 ul PBS + 200 ul Matrigel (BD Biosciences) and subcutaneously injected into immunodeficient female mice. Third, the in vivo lung metastasis model was established by injecting with BT-549, BT-549LMF3, FTO stable BT-549LMF3, sh-METTL3 BT-549LMF3, and sh-KRT7 BT-549LMF3 stable cells (1 × 106 per mouse, n = 5 for each group). | |||
Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Specifically, increased METTL3 methylated KRT7-AS at A877 to increase the stability of a KRT7-AS/KRT7 mRNA duplex via IGF2BP1/HuR complexes. m6A promotes breast cancer lung metastasis by increasing the stability of a KRT7-AS/KRT7 mRNA duplex and translation of KRT7. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Lung Metastasis | |||
| In-vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1092 | |
| In-vivo Model | First, subcutaneous transplanted model was used to evaluate the growth of BT-549LMF3 and BT-549 cells. Cells (5 × 106 per mouse, n = 5 for each group) were diluted in 200 ul PBS + 200 ul Matrigel (BD Biosciences) and subcutaneously injected into immunodeficient female mice. Second, subcutaneous transplanted model was used to evaluate the metastasis potential of BT-549LMF3 and BT-549 cells. Cells (5 × 106 per mouse, n = 5 for each group) were diluted in 200 ul PBS + 200 ul Matrigel (BD Biosciences) and subcutaneously injected into immunodeficient female mice. Third, the in vivo lung metastasis model was established by injecting with BT-549, BT-549LMF3, FTO stable BT-549LMF3, sh-METTL3 BT-549LMF3, and sh-KRT7 BT-549LMF3 stable cells (1 × 106 per mouse, n = 5 for each group). | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
Non-coding RNA
m6A Regulator: Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05565 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | KRT7-AS | |
| Regulated Target | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 7 (KRT7) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m6A → ncRNA | |
| Disease | Breast cancer | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00792)
| In total 6 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE012509 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:52245263-52245264:- | [2] | |
| Sequence | CAGAGAATCCTAAGGGTTAAACACATAGGTTTGGATATCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_3791110; ENST00000546686.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_189110 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE012513 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:52245680-52245681:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GGATGAATGTCAAGCCCCAAACCCCACGGAGCCCTAGAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; GSC-11; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000546686.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_189114 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE012514 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:52245863-52245864:- | [2] | |
| Sequence | GAAGCCGCACACACAAAGGGACTGTTATCATTTCAACCTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000546686.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_189115 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE012515 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:52246192-52246193:- | [2] | |
| Sequence | CATGAAGAATGTGCTATCAGACTCCCCCATTCCAGCCTCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000546686.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_189116 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE012516 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:52246231-52246232:- | [2] | |
| Sequence | ATGAAGGCCCAGCTGCATAGACAGAGGTGGCATGCGGTTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000546686.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_189117 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE012517 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr12:52247239-52247240:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TCTGGTACGATGCCTAAGGAACTCAGACGGAAGAGGCCTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | MT4; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000546686.1; rmsk_3791116 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_189118 | ||
References