m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00734)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
STK4
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | Caco-2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL3 Caco-2 cells
Control: shNTC Caco-2 cells
|
GSE167075 | |
| Regulation |
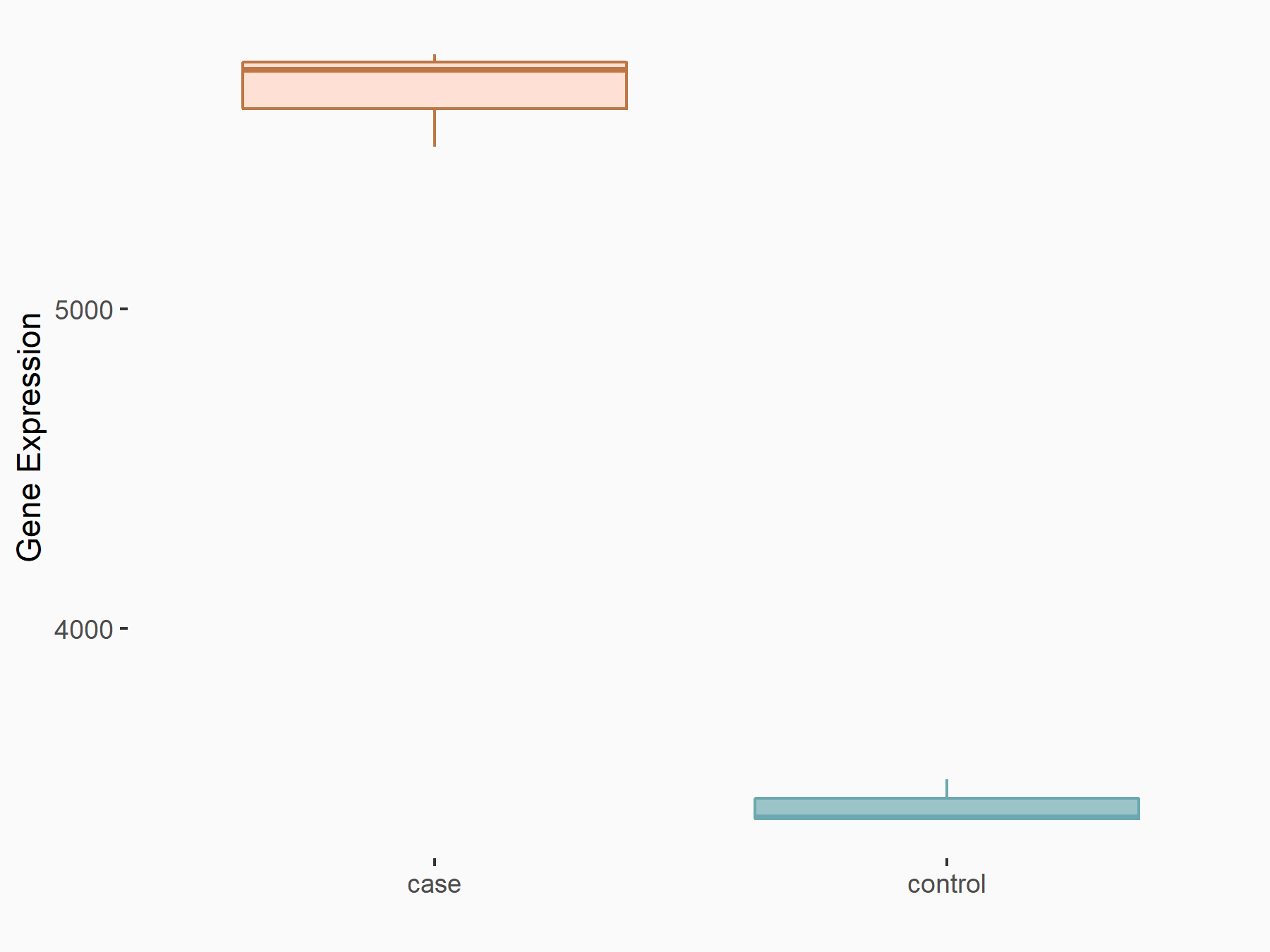  |
logFC: 7.22E-01 p-value: 1.68E-60 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| Representative RIP-seq result supporting the interaction between STK4 and the regulator | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
| Regulation | logFC: 1.45E+00 | GSE60213 |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Silencing METTL3 suppresses miR-222-3p expression and thus stimulates Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4 (STK4) expression, thereby repressing the malignancy and metastasis of Thyroid Carcinoma. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Thyroid Cancer | ICD-11: 2D10 | ||
Thyroid Cancer [ICD-11: 2D10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Silencing METTL3 suppresses miR-222-3p expression and thus stimulates Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4 (STK4) expression, thereby repressing the malignancy and metastasis of Thyroid Carcinoma. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Thyroid Cancer [ICD-11: 2D10] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00734)
| In total 43 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010644 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45045870-45045871:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | GGCTGGAGTGCAGTGGCCCAATCTCGGCTCACTGCAACCTC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87642 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010645 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45059437-45059438:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | GAAATAAGGGTTCCCTGAACACAAATACTGTGATACCAATT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87643 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010646 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45059475-45059476:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | ATTCTGCAACAGTCCATTTGATAACCAGGGTGACTACTGAG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87644 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010647 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45059477-45059478:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | TCTGCAACAGTCCATTTGATAACCAGGGTGACTACTGAGTG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87645 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010648 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45059478-45059479:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | CTGCAACAGTCCATTTGATAACCAGGGTGACTACTGAGTGA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87646 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010649 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45059481-45059482:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CAACAGTCCATTTGATAACCAGGGTGACTACTGAGTGACTG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87647 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010650 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45059554-45059555:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | TGGACAAAGGGATGATTCACATCCCAAGCGGGATAGAGCAG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87648 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010651 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45059560-45059561:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | AAGGGATGATTCACATCCCAAGCGGGATAGAGCAGGACAGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87649 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010652 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45059568-45059569:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | ATTCACATCCCAAGCGGGATAGAGCAGGACAGCGCAGGATT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87650 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010653 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45059578-45059579:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | CAAGCGGGATAGAGCAGGACAGCGCAGGATTTCATCATGCG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87651 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010654 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45061350-45061351:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | ACCCACAACCACCGAATATTAAATAGAAAATTCCAGAAATA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; rmsk_5131236 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87652 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010655 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45061354-45061355:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | ACAACCACCGAATATTAAATAGAAAATTCCAGAAATAAACA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; rmsk_5131236; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87653 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010656 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45061393-45061394:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | CAATTCATGAATTTTAAATTATGCGTCATCCTGAGTAGTAT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; rmsk_5131236 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87654 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010657 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45061419-45061420:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | CATCCTGAGTAGTATGAGGAAACCTTGTGCCATCCTGCTCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; rmsk_5131236; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87655 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010658 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45061430-45061431:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | GTATGAGGAAACCTTGTGCCATCCTGCTCCATCCTGCCTGG | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_5131236; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87656 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010659 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45061454-45061455:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | TGCTCCATCCTGCCTGGGACATGAATCATTGCTCTGTTCAG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5; rmsk_5131236; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87657 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010660 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45061457-45061458:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | TCCATCCTGCCTGGGACATGAATCATTGCTCTGTTCAGCAT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; rmsk_5131236 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87658 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010661 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45061458-45061459:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | CCATCCTGCCTGGGACATGAATCATTGCTCTGTTCAGCATA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; rmsk_5131236; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87659 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010662 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45061530-45061531:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | AGGCATCTTGGTTATCATAAAGACTGTTGTGGTATTGGTAT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; rmsk_5131236; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87660 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010663 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45065991-45065992:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | TTACTTAATAATGGCCCCAAAGCATAAGAGTTGTGATGCTG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8; rmsk_5131245; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87661 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010664 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45073089-45073090:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | TTTAGGACCTGTGATCCCAAAGATTACATTCTTAACTACCA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87662 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010665 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077456-45077457:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CTTGTCGCCCAGGCTGGAGTACAATGGCACGATCTTGGCTC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87663 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010666 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077459-45077460:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | GTCGCCCAGGCTGGAGTACAATGGCACGATCTTGGCTCACT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87664 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010667 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078228-45078229:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | TTTTTTTTTTTTTTTGAGACAGAGTCTCACTCTGTTGCCCA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87665 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010668 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078236-45078237:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | TTTTTTTGAGACAGAGTCTCACTCTGTTGCCCAGGCTGGAG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87666 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010669 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078298-45078299:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | CACTGCAACCTCCGCCTCCCAGGTTCAAGCAATTCTCCTGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87667 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010670 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078304-45078305:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | AACCTCCGCCTCCCAGGTTCAAGCAATTCTCCTGCCTCAGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87668 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010671 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078305-45078306:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | ACCTCCGCCTCCCAGGTTCAAGCAATTCTCCTGCCTCAGCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87669 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010672 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078309-45078310:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCGCCTCCCAGGTTCAAGCAATTCTCCTGCCTCAGCCTCCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87670 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010673 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078346-45078347:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | TCCCAGGTAGCTGCCACTACAGGTGCTGCACCACCACGCCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87671 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010674 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078371-45078372:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | CTGCACCACCACGCCCGGCTAATTTTTGTATTTTTAGTAGA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87672 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010675 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078466-45078467:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | CACCCGCCTCGGCCTCCCAAAGTGCTGGGATTACAGGCGTG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87673 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010676 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079027-45079028:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | ACCAGCCTGAGCAACATGGCAAAATCCCATCTCTACAAAAC | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_5131275; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87674 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010677 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079067-45079068:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | CATCAAAAAAAAAAAAAATTAGTCGGGCATGGTGGTGCACA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; rmsk_5131275; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87675 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010678 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079094-45079095:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | CATGGTGGTGCACACCTGTAATCCCAGCTTGTCAGGAGGCT | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_5131275; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87676 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010679 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079116-45079117:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCCAGCTTGTCAGGAGGCTGAAGTGGGAGGATCACCTGAGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_5131275; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87677 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010680 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079117-45079118:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCAGCTTGTCAGGAGGCTGAAGTGGGAGGATCACCTGAGCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; rmsk_5131275; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87678 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010681 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079129-45079130:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | GAGGCTGAAGTGGGAGGATCACCTGAGCCCAGGGAGGTCAA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; rmsk_5131275; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87679 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010682 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079134-45079135:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | TGAAGTGGGAGGATCACCTGAGCCCAGGGAGGTCAAGGATG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6; rmsk_5131275 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87680 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010683 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079143-45079144:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | AGGATCACCTGAGCCCAGGGAGGTCAAGGATGCAGTGAGCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6; rmsk_5131275 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87681 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010684 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079148-45079149:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | CACCTGAGCCCAGGGAGGTCAAGGATGCAGTGAGCCATGGT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8; rmsk_5131275 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87682 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010685 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079200-45079201:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | ACTCTAGCCTGGGTGACAGAATGAGACCCCGTCTCAAAAAA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8; rmsk_5131275 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87683 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE010686 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079203-45079204:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CTAGCCTGGGTGACAGAATGAGACCCCGTCTCAAAAAAAAA | ||
| Transcript ID List | rmsk_5131275; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_87684 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 132 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053101 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44966590-44966591:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGAGACGGTACAGCTGAGGAACCCGCCGCGCCGGTGAGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; H1B; H1A; fibroblasts; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000480745.5; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000487587.2; ENST00000488618.1; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533391 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053102 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44972113-44972114:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GATGAAGATAGTTTAACCAAACAACCAGAAGAAGTATTTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; hESC-HEK293T; CD4T; peripheral-blood; TIME; iSLK; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000480745.5; ENST00000488618.1; ENST00000487587.2; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533392 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053103 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44972146-44972147:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTATTTGATGTCTTAGAGAAACTTGGAGAAGGGTGAGTGTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; CD4T; peripheral-blood; TIME; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000480745.5; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000488618.1; ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000487587.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533393 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053104 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44972172-44972173:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGAAGGGTGAGTGTAAAGAAACTATAGGTAGGTCATTGGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; CD4T; peripheral-blood; TIME; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000488618.1; ENST00000487587.2; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000480745.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533394 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053105 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44972234-44972235:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAAGAAGCAGAAGGATATGAACCTTTCAGCATTGTTCTAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000487587.2; ENST00000480745.5; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000488618.1; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000474717.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533395 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053106 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44974393-44974394:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTGTTATTCTGACTGAATGAACCTAAGCAAGCCTCATTTAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | GM12878 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000487587.2; ENST00000480745.5; ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533396 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053107 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44974435-44974436:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TAGGAATATTTTGAAGGAAGACCTTCACTGCACTTCTTTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | GM12878 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000487587.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533397 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053108 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44974459-44974460:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCACTGCACTTCTTTTCCAAACATGTGACACAATGCTATTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | GM12878 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000487587.2; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533398 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053109 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44974810-44974811:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGAGGATGAATGGTTTGTGAACTCTCACTGACTTGTATCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; GM12878; Huh7; iSLK; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000487587.2; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533399 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053110 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44974820-44974821:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | TGGTTTGTGAACTCTCACTGACTTGTATCTTGTGAAATGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.28175 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000487587.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533400 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053111 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44974855-44974856:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AATGAGCTATGGCTAAAAAAACTGTTGGATTCTGGAGGCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; GM12878; LCLs; Huh7; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000487587.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533401 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053112 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44974936-44974937:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAGTAGAGCCAAAGCTCCAGACCAGGATGAGTGGAGAGCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; GM12878; Huh7; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000487587.2; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533402 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053113 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44975265-44975266:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGGGAATCAAGTTTTAAGGGACTTGCTTGTGAGTATGATTG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000487587.2; ENST00000474717.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533403 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053114 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44975458-44975459:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TGAGTGAGTGTATGAAGAGAACTTTCTAATATATAAGAATA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000487587.2; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000474717.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533404 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053115 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44975515-44975516:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTAAATATAAGGATATATAGACAGCTATGGACAAGGGATAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000487587.2; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533405 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053116 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44975525-44975526:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGATATATAGACAGCTATGGACAAGGGATAGGAAAGAAATC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000487587.2; ENST00000474717.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533406 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053117 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44975562-44975563:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AATCTAAATAATCAGCGGAGACTAAAGCATGCCTTATCCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000487587.2; ENST00000474717.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533407 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053118 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44975629-44975630:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCATGAAGTTGGGGGCTGGAACTCGGCTCTCCATCTGTGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000487587.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533408 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053119 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44975649-44975650:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ACTCGGCTCTCCATCTGTGAACTAAAGCTGAAATAAATTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000487587.2; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533409 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053120 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44976233-44976234:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | AATTGAAAGATAGAAATGAGACTGATCACAACATGCAGAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000474717.2; rmsk_5131050; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533410 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053121 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44976477-44976478:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | AGAATAGTAGACTGTTAAGGACAAAGGAAACCTTAAAAACT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000372806.8; rmsk_5131050; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533411 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053122 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44976706-44976707:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | AATGCCTTTGGATGGAAGTAACAATACCCAACAAACAGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533412 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053123 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44978459-44978460:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TAGGTCCTATGGCAGCGTATACAAAGCTATTCATAAAGAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533413 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053124 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44978479-44978480:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ACAAAGCTATTCATAAAGAGACCGGCCAGATTGTTGCTATT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000474717.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533414 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053125 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44978522-44978523:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCAAGTTCCTGTGGAATCAGACCTCCAGGAGATAATCAAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000474717.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533415 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053126 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44981866-44981867:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTATGGCAGTTATTTTAAGAACACAGACTTATGGATCGTTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533416 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053127 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44981872-44981873:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CAGTTATTTTAAGAACACAGACTTATGGATCGTTATGGAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533417 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053128 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44981930-44981931:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | GTATCTGATATCATTCGATTACGAAATAAAACGGTAGGTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.046785714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000474717.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533418 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053129 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44987167-44987168:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | TAGCTACAATATTACAATCAACTCTTAAGGGACTTGAATAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.595904762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000474717.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533419 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053130 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44987178-44987179:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTACAATCAACTCTTAAGGGACTTGAATACCTTCATTTTAT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533420 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053131 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44987208-44987209:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | CTTCATTTTATGAGAAAAATACACCGAGATATCAAGGCAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000474717.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533421 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053132 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44987245-44987246:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | CAGGAAATATTTTGCTAAATACAGAAGGACATGCAAAACTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533422 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053133 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44987253-44987254:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATTTTGCTAAATACAGAAGGACATGCAAAACTTGCAGATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000474717.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533423 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053134 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44987262-44987263:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AATACAGAAGGACATGCAAAACTTGCAGATTTTGGGGTAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000474717.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533424 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053135 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44995122-44995123:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGCGGAATACAGTGATAGGAACACCATTTTGGATGGCTCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533425 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053136 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44995180-44995181:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGGATACAACTGTGTAGCAGACATCTGGTCCCTGGGAATAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000474717.2; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533426 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053137 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44997186-44997187:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AGGCAATCTTCATGATTCCTACAAATCCTCCTCCCACATTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533427 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053138 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44997212-44997213:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTCCTCCCACATTCCGAAAACCAGAGCTATGGTCAGATAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533428 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053139 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:44997251-44997252:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AACTTTACAGATTTTGTGAAACAGTGTCTTGTAAAGAGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533429 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053140 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45000434-45000435:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGGAGTGTCAATACTGCGAGACTTAATTAATGAAGCCATGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533430 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053141 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45000462-45000463:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AATGAAGCCATGGATGTGAAACTGAAACGCCAGGAATCCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533431 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053142 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45000497-45000498:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | ATCCCAGCAGCGGGAAGTGGACCAGGACGATGAAGAAAACT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533433 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053143 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45000515-45000516:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGACCAGGACGATGAAGAAAACTCAGTGAGTGGCAGCCGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533434 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053144 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45001281-45001282:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TACTATGATTGAGCACGATGACACGTTGCCATCACAACTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533435 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053145 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45001294-45001295:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CACGATGACACGTTGCCATCACAACTGGGCACCATGGTGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533436 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053146 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45001343-45001344:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGGATGAGGAAGAGGAAGGAACTATGAAAAGTAAGGCTCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; LCLs; Huh7; Jurkat | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533437 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053147 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45024983-45024984:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGTTTTCAGGAAGGGATGAGACCATGCAGCCTGCGAAACCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; LCLs; Huh7; Jurkat | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533438 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053148 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45025000-45025001:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAGACCATGCAGCCTGCGAAACCATCCTTTCTTGAATATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; LCLs; Huh7; Jurkat | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533439 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053149 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45025024-45025025:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCCTTTCTTGAATATTTTGAACAAAAAGAAAAGGAAAACCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; LCLs; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533440 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053150 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45025041-45025042:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGAACAAAAAGAAAAGGAAAACCAGATCAACAGCTTTGGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; LCLs; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533441 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053151 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45025119-45025120:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAAAATACCACAGGATGGAGACTACGAGTTTGTAAGTAGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; hNPCs; Huh7; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533442 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053152 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45053088-45053089:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTGCTCTTTTCTTTCAGAAAACTAGCCAAGAACAGCAGTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HEK293T; hNPCs; Huh7; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533443 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053153 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45053099-45053100:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTTCAGAAAACTAGCCAAGAACAGCAGTCTGGAAAAGACAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; Huh7; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533444 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053154 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45053116-45053117:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGAACAGCAGTCTGGAAAAGACATATGTATCCAAAATTGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; Huh7; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533445 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053155 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45053143-45053144:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TATCCAAAATTGCCAGGGAAACCTGCTGTGTAGATACGCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533446 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053156 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45053172-45053173:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTAGATACGCTTTCTGAGAAACCACATGGTAAATGAATGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; H1A; H1B; A549; LCLs; MT4; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533447 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053157 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45075029-45075030:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCTTCTAGCTTAAGAGTTGGACAGTGGAGGACCTTCAGAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; A549; LCLs; MT4; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533448 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053158 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45075039-45075040:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TAAGAGTTGGACAGTGGAGGACCTTCAGAAGAGGCTCTTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; A549; LCLs; MT4; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533449 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053159 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45075066-45075067:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAAGAGGCTCTTGGCCCTGGACCCCATGATGGAGCAGGAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; fibroblasts; LCLs; MT4; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533450 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053160 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45075163-45075164:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GAGGCTAAGAAGAGACGGCAACAAAACTTCTGAGCAAGGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533451 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053161 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45075168-45075169:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TAAGAAGAGACGGCAACAAAACTTCTGAGCAAGGCCAGGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1B; H1A; hESCs; fibroblasts; LCLs; MT4; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533452 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053162 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45075295-45075296:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TCTCCACAGCACCTTTGTGAACTCAGGAATGTGCGCCAGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533453 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053163 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45075363-45075364:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CCATCTTGATGTGTGTATGTACATTGGTCAGGTATATTATC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533454 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053164 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45075410-45075411:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | GATTTATATTGGCGCTTTTAACTCAGAGTTTTAAACCCCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.590089286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533455 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053165 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45075424-45075425:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTTTTAACTCAGAGTTTTAAACCCCAGGAACAGAGACTCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; hNPCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; MM6; Huh7; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533456 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053166 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45075433-45075434:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CAGAGTTTTAAACCCCAGGAACAGAGACTCCTAGTTGAGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; hNPCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533457 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053167 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45075439-45075440:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTTAAACCCCAGGAACAGAGACTCCTAGTTGAGTGATAGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; CD8T; H1299; Huh7; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533458 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053168 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45075522-45075523:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | TCAATTGTTCTTTCTGGAAGACTTTTAAAAAAATATAAATA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; HeLa; A549; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000372801.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533459 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053169 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45075656-45075657:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TAAGATTATGGTACTGTGGAACATGAGGGCAGAGGACACCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533460 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053170 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45075671-45075672:+ | ||
| Sequence | GTGGAACATGAGGGCAGAGGACACCGGGAGGCTGTTAGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533461 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053171 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45075695-45075696:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | CGGGAGGCTGTTAGGGGGTCACTGAATCCCAGGAGCCAACC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.469291667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533462 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053172 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45075985-45075986:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCCCAGTGCCTTAAGAGGAGACATGATCTCTACCAGGGACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HEK293T; HeLa; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533463 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053173 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076003-45076004:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | AGACATGATCTCTACCAGGGACTCTCAGCAAACACGGGACT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34; HEK293T; HeLa; A549; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533464 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053174 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076014-45076015:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTACCAGGGACTCTCAGCAAACACGGGACTGTGTTCAGTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533465 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053175 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076021-45076022:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGACTCTCAGCAAACACGGGACTGTGTTCAGTCCACAAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533466 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053176 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076035-45076036:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CACGGGACTGTGTTCAGTCCACAAAGGAAAAGCGTTTTTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533467 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053177 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076083-45076084:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ATTGTTCATGTAAAAATCATACACGTGGCATGTTGCTCCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533468 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053178 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076111-45076112:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | CATGTTGCTCCACATTCCTTACACACAGGGGTAGAGGGGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533469 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053179 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076218-45076219:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | AAAGGATAAATGAATATTAGACTAAGATTTGTTTTCCAGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | BGC823 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533470 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053180 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076251-45076252:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTCCAGGAGGCTCAATCTGAACACACAGAATGTCAGAGCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T; BGC823 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533471 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053181 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076278-45076279:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GAATGTCAGAGCTGGAAGGGACTATAGAGATCATCTGATCT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; BGC823 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533472 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053182 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076325-45076326:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTTGTACGGATGATCGCAAAACTGAGGTGTAGAGAGGGGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533473 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053183 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076357-45076358:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AGAGGGGAATGGCCAAAATCACAAAGCAAGTTAGCGTTAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533474 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053184 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076482-45076483:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TTGGTTAATTGTTCCAGGGAACCTTGCTAACAGAAACTTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533475 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053185 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076497-45076498:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | AGGGAACCTTGCTAACAGAAACTTGCTCTTGCCTTGGCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533476 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053186 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076593-45076594:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TCAGCGAGTCCTTGAGCTCCACAACATCTACCAGATATAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533477 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053187 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076616-45076617:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | ACATCTACCAGATATAGCAGACAAGCACCCATGGAGGCAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533478 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053188 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076674-45076675:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | ATCAGAGGGCTTTGCAAAAGACAGCATAGAGCCATCTTCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533479 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053189 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076788-45076789:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TAATTGCTTTTGCTCCTGAAACCTGGGAATCAATGGAAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD34 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533480 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053190 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076938-45076939:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTATGTGGCGGATACGGAAAACAGAGGACAATTTGAGGATC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533481 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053191 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45076945-45076946:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCGGATACGGAAAACAGAGGACAATTTGAGGATCTTGCTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533482 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053192 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077036-45077037:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTGAGCTGGGTAGGCTCTAAACTTCACAATAACCCTGTGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533483 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053193 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077041-45077042:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CTGGGTAGGCTCTAAACTTCACAATAACCCTGTGACTTAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533484 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053194 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077184-45077185:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ACTATAGGGGGTCAATATTTACACAAAAAAGGAAAGTCACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533485 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053195 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077202-45077203:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTACACAAAAAAGGAAAGTCACAAGCCTGTTTAAAATGAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533486 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053196 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077244-45077245:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GACCACCTTTTCTTGCATAGACTAAATAACTCGAACTGGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533487 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053197 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077258-45077259:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GCATAGACTAAATAACTCGAACTGGCATTTTTAGGTTGGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533488 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053198 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077281-45077282:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GGCATTTTTAGGTTGGAAAGACAGCTGAATTAGTAGTTAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533489 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053199 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077327-45077328:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TAGCCAAGTAAGTTTTAAAAACCAAAGCATCCAGGATGCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533490 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053200 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077346-45077347:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AACCAAAGCATCCAGGATGCACACCCCTGCACCATTTGCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533491 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053201 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077456-45077457:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | CTTGTCGCCCAGGCTGGAGTACAATGGCACGATCTTGGCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533492 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053202 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077646-45077647:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TCCACCCGCCTCAGCCTCCCACACTGCTGGGATTACAGGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533493 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053203 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077702-45077703:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GGCCTCTCTTTCTTTTTTAAACAAAGAACTTTGCACTTGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533494 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053204 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077817-45077818:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | TAACTATTCTTGGGTCATGAACTTTGATCTGGAGTTTGTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533495 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053205 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077874-45077875:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCACCCAGCTTGCTGATCCAACAAAGTCTATTGCTTACCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533496 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053206 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077956-45077957:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGGATCAGAGAAATTTCCTGACAAGGTATATTTGTTTTCTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533497 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053207 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077980-45077981:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | GGTATATTTGTTTTCTAGTGACAGAAAGGCAAAGGAACAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533498 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053208 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45077996-45077997:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AGTGACAGAAAGGCAAAGGAACAAGTCCTAGTTGTTGTTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533499 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053209 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078028-45078029:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | TGTTGTTGTTGTTGTTGAATACTAAATTTAAGATATGTCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.53247619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533500 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053210 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078150-45078151:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTGTTCTCTGCCTTCAAGAAACAATGACCTGATTCTGTCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533501 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053211 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078428-45078429:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | ATTAGCCAGGTGGGTCTTGAACTCCTGACCTTGTGATCCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533502 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053212 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078632-45078633:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | ATTGGATGGATGAATGTTTGACGGGGAAGAGGAAGGGTAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.833690476 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8; rmsk_5131273 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533503 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053213 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078726-45078727:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | AGAACCAGTCATCTGAAGCAACTTAAGAATTGTAGCCTTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.595904762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533504 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053214 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078746-45078747:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | ACTTAAGAATTGTAGCCTTGACTCCTTGAGACTGTAGATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.28175 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533505 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053215 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078756-45078757:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | TGTAGCCTTGACTCCTTGAGACTGTAGATTTCGATCCAGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533506 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053216 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078825-45078826:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGAAATTTATACCATTTAAAACTCAGTAAGTCTTTTAAATA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533507 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053217 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078864-45078865:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TATCAGGAAGGAGAGAAGCGACATCATGATACATCCTATGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8; rmsk_5131274 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533508 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053218 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078874-45078875:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GAGAGAAGCGACATCATGATACATCCTATGGGTATTAAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8; rmsk_5131274 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533509 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053219 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45078954-45078955:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TAACAACTTCAACATCATAAACAAATTCCTTGAAAAATAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; rmsk_5131274; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533510 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053220 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079020-45079021:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AATAGATACCAGCCTGAGCAACATGGCAAAATCCCATCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; rmsk_5131275; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533511 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053221 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079306-45079307:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | GGTATTATTATCCTCATTTTACAGATGTGAAAATTGAGGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533512 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053222 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079466-45079467:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | AAGATTGCAGCTCCTTATTTACTAGAAAATTGTTCCTGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.494845238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533513 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053223 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079492-45079493:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | AAATTGTTCCTGCCCAATCTACATCTCCACCTCACCCCATC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533514 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053224 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079500-45079501:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | CCTGCCCAATCTACATCTCCACCTCACCCCATCTTTTCTTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.032470238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533515 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053225 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079524-45079525:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | CACCCCATCTTTTCTTAAGCACTATGTTTGTGTTTTTATCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.252583333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533516 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053226 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079570-45079571:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ATATTCATTGTCTTTGGAATACATGTTCTTGTTTGTGTTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533517 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053227 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079618-45079619:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | AATCTCTTTTACCAGCTTGCACTCGGACCAACTTGGAAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.252583333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533518 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053228 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079624-45079625:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTTTACCAGCTTGCACTCGGACCAACTTGGAAAAAAAAAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533519 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053229 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079665-45079666:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | CTTAAATGTTTTTGCTATGTACAGTTTAAAAATGTGAAGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000499879.6; ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533520 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053230 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079719-45079720:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | TTTTGTAAGAAAATCTAATAACACTGGCTTAAGTGCTGACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533521 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053231 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079802-45079803:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | AGGTCAGCAGTTTGTATGAGACATAGCTTCCTCCATTGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8; ENST00000499879.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533522 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE053232 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr20:45079948-45079949:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | AATAAACTGTCCTTTGGACCACAAACCCTTATTAACGAGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000372806.8 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_533523 | ||
References