m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00582)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
APOE
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
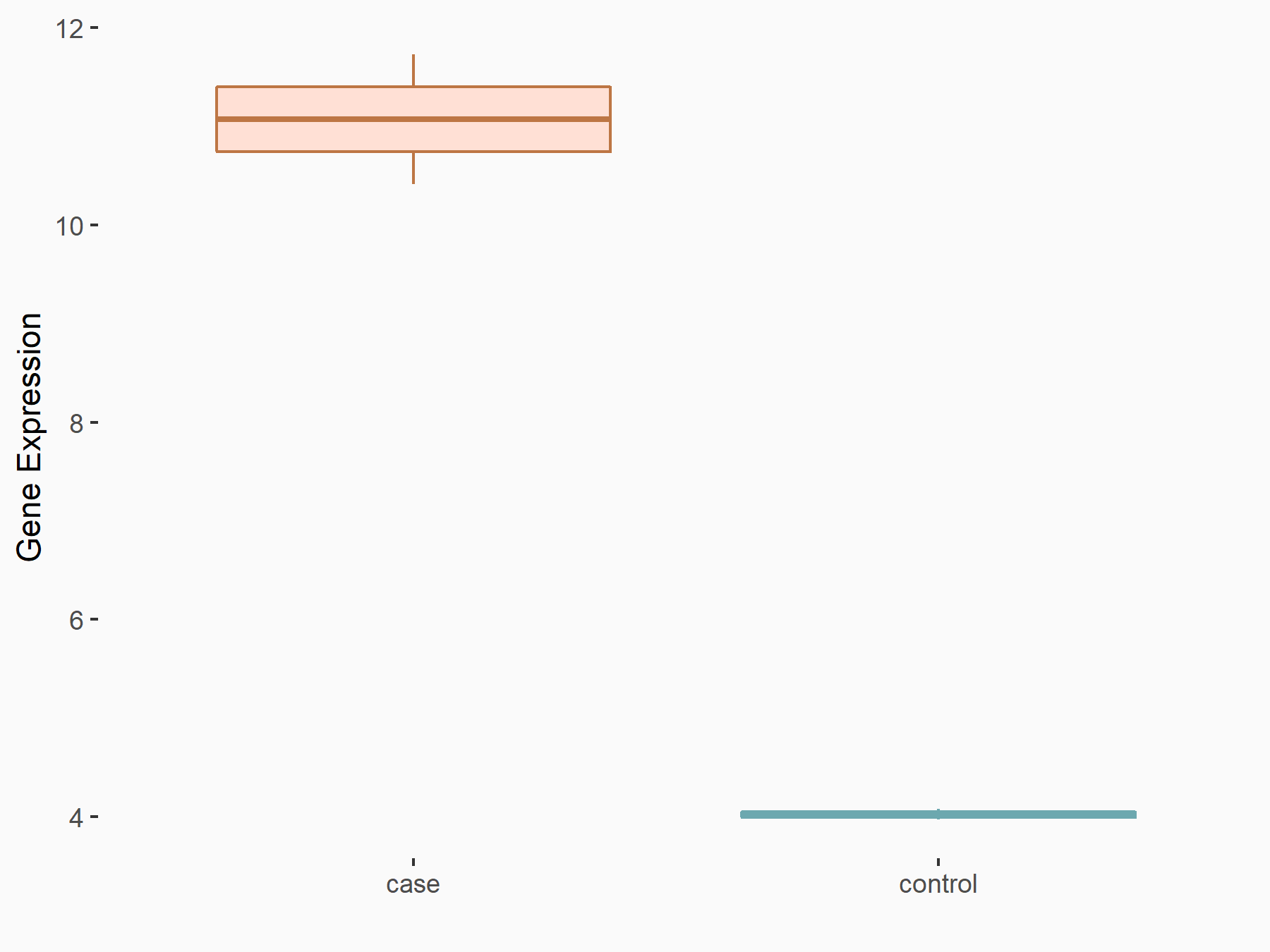 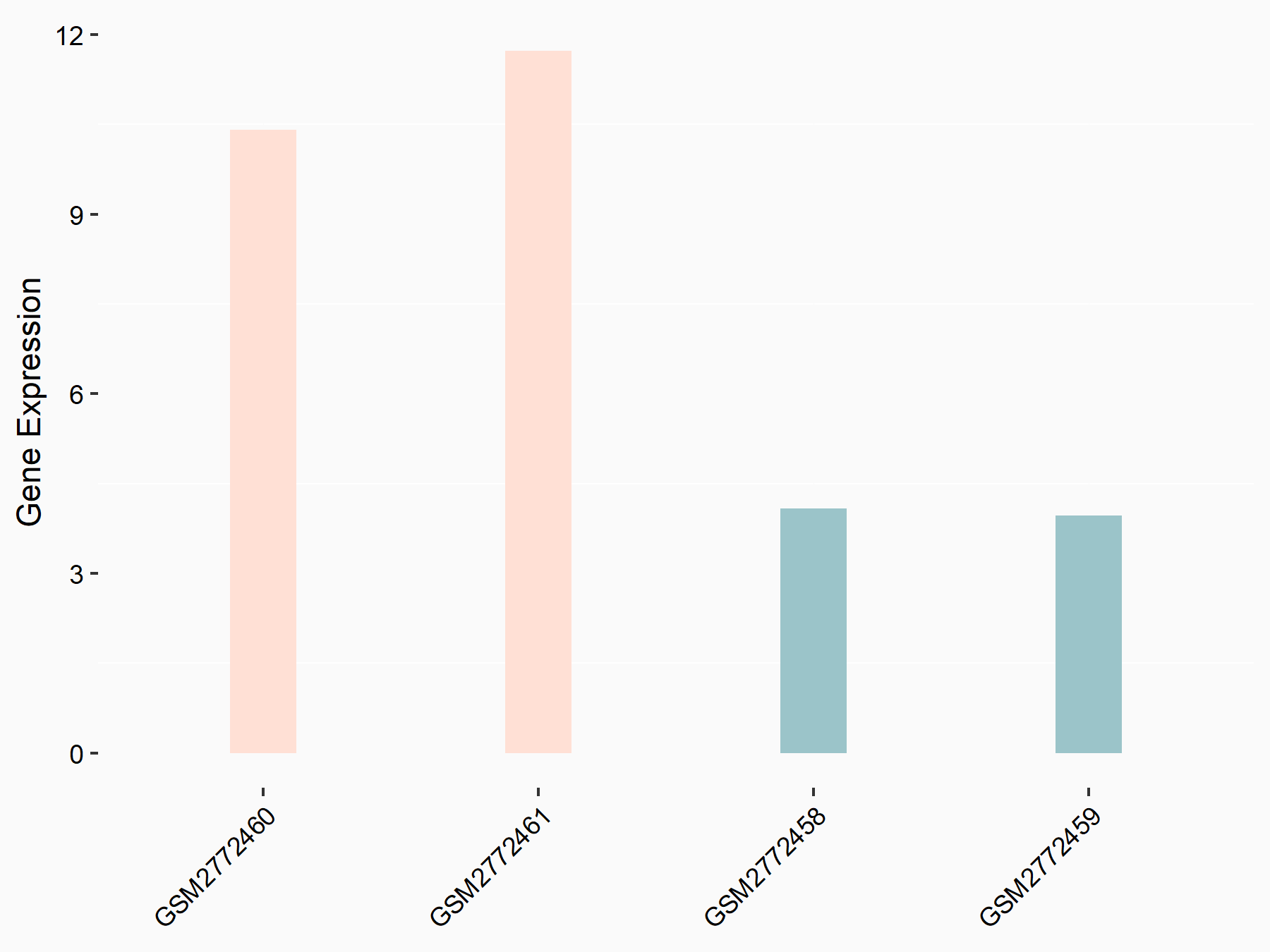 |
logFC: 1.26E+00 p-value: 1.34E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | FTO acts as a tumor suppressor to inhibit tumor glycolysis in Papillary thyroid cancer(PTC). FTO/Apolipoprotein E (APOE) axis inhibits PTC glycolysis by modulating IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Papillary thyroid cancer | ICD-11: 2D10.1 | ||
| Pathway Response | JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | ||
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | hsa00010 | |||
| Cell Process | Glycolysis | |||
| In-vitro Model | TPC-1 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6298 |
| Nthy-ori 3-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2659 | |
| K1 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2537 | |
| IHH-4 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2960 | |
| B-CPAP | Thyroid gland carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0153 | |
Thyroid Cancer [ICD-11: 2D10]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | FTO acts as a tumor suppressor to inhibit tumor glycolysis in Papillary thyroid cancer(PTC). FTO/Apolipoprotein E (APOE) axis inhibits PTC glycolysis by modulating IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Papillary thyroid cancer [ICD-11: 2D10.1] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | ||
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | hsa00010 | |||
| Cell Process | Glycolysis | |||
| In-vitro Model | TPC-1 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6298 |
| Nthy-ori 3-1 | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2659 | |
| K1 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2537 | |
| IHH-4 | Thyroid gland papillary carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2960 | |
| B-CPAP | Thyroid gland carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0153 | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00582)
| In total 23 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041485 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44905899-44905900:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | GGCCTCTAGAAAGAGCTGGGACCCTGGGAACCCCTGGCCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1A; H1B; MM6; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000434152.5; ENST00000485628.2; ENST00000252486.9; ENST00000446996.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443389 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041486 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44905908-44905909:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | AAAGAGCTGGGACCCTGGGAACCCCTGGCCTCCAGGTAGTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1A; H1B; MM6; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000485628.2; ENST00000446996.5; ENST00000434152.5; ENST00000252486.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443390 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041487 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44906420-44906421:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | GGATGGGGAGATAAGAGAAGACCAGGAGGGAGTTAAATAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MM6; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000446996.5; ENST00000425718.1; ENST00000434152.5; ENST00000485628.2; ENST00000252486.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443391 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041488 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44906601-44906602:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | GACAGTTTCTCCTTCCCCAGACTGGCCAATCACAGGCAGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1A; MM6; Huh7; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial; HEC-1-A | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000252486.9; ENST00000425718.1; ENST00000485628.2; ENST00000446996.5; ENST00000434152.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443392 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041489 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44906654-44906655:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | TGTGGGCTGCGTTGCTGGTCACATTCCTGGCAGGTATGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.047297619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000252486.9; ENST00000446996.5; ENST00000425718.1; ENST00000434152.5; ENST00000485628.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443393 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041490 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44906748-44906749:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | TCCTGGCCCCATTCAGGCAGACCCTGGGCCCCCTCTTCTGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MM6; Huh7; CD4T; GSC-11; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000434152.5; ENST00000425718.1; ENST00000252486.9; ENST00000446996.5; rmsk_5009161; ENST00000485628.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443394 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041491 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44907294-44907295:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | CCTGCCTGGGGCACACAAGGACACTCAATACATGCTTTTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MM6; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000425718.1; ENST00000485628.2; ENST00000446996.5; ENST00000434152.5; ENST00000252486.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443395 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041492 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44907791-44907792:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | AGGTGGAGCAAGCGGTGGAGACAGAGCCGGAGCCCGAGCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; brain; MM6; Huh7; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; m6A-REF-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000425718.1; ENST00000252486.9; ENST00000446996.5; ENST00000434152.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443396 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041493 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44907821-44907822:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | AGCCCGAGCTGCGCCAGCAGACCGAGTGGCAGAGCGGCCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MM6; Huh7; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000425718.1; ENST00000434152.5; ENST00000252486.9; ENST00000446996.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443397 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041494 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44907850-44907851:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | CAGAGCGGCCAGCGCTGGGAACTGGCACTGGGTCGCTTTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; MM6; Huh7; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000425718.1; ENST00000434152.5; ENST00000446996.5; ENST00000252486.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443398 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041495 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44907893-44907894:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | ATTACCTGCGCTGGGTGCAGACACTGTCTGAGCAGGTGCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; MM6; Huh7; CD4T; GSC-11; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000446996.5; ENST00000425718.1; ENST00000434152.5; ENST00000252486.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443399 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041496 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44907946-44907947:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | AGCTCCCAGGTCACCCAGGAACTGAGGTGAGTGTCCCCATC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1A; MM6; Huh7; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293T; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000446996.5; ENST00000425718.1; ENST00000252486.9; ENST00000434152.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443400 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041497 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44908548-44908549:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | GCAGGGCGCTGATGGACGAGACCATGAAGGAGTTGAAGGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1A; H1B; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293T; MSC; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000252486.9; ENST00000446996.5; ENST00000434152.5; ENST00000425718.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443401 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041498 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44908570-44908571:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CATGAAGGAGTTGAAGGCCTACAAATCGGAACTGGAGGAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000434152.5; ENST00000446996.5; ENST00000252486.9; ENST00000425718.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443402 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041499 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44908580-44908581:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | TTGAAGGCCTACAAATCGGAACTGGAGGAACAACTGACCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293T; MSC; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000446996.5; ENST00000252486.9; ENST00000434152.5; ENST00000425718.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443403 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041500 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44908589-44908590:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | TACAAATCGGAACTGGAGGAACAACTGACCCCGGTGGCGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; A549; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; GSC-11; MSC; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000425718.1; ENST00000446996.5; ENST00000434152.5; ENST00000252486.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443404 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041501 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44908669-44908670:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | GCAGGCCCGGCTGGGCGCGGACATGGAGGACGTGTGCGGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; Brain; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; A549; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; GSC-11; MSC; iSLK; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000446996.5; ENST00000434152.5; ENST00000425718.1; ENST00000252486.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443405 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041502 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44908907-44908908:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | CGCCTGGGGCCCCTGGTGGAACAGGGCCGCGTGCGGGCCGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; H1A; H1B; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293T; iSLK; MSC; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000434152.5; ENST00000446996.5; ENST00000252486.9; ENST00000425718.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443406 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041503 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44909022-44909023:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | TGGAGGAGATGGGCAGCCGGACCCGCGACCGCCTGGACGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1A; H1B; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293T; MSC; iSLK; TIME; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000252486.9; ENST00000434152.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443407 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041504 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44909161-44909162:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | GTTCGAGCCCCTGGTGGAAGACATGCAGCGCCAGTGGGCCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; H1A; H1B; MT4; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; GSC-11; MSC; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000252486.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443408 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041505 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44909239-44909240:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CGCCGCCCCTGTGCCCAGCGACAATCACTGAACGCCGAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000252486.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443409 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041506 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44909322-44909323:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | CGCGCAGCCTGCAGCGGGAGACCCTGTCCCCGCCCCAGCCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1A; H1B; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293T; MSC; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000252486.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443410 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE041507 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:44909357-44909358:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | CAGCCGTCCTCCTGGGGTGGACCCTAGTTTAATAAAGATTC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; H1A; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; GSC-11; HEK293T; MSC; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000252486.9 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_443411 | ||
References