m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00365)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
PTGS2
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | MOLM-13 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL3 MOLM13 cells
Control: MOLM13 cells
|
GSE98623 | |
| Regulation |
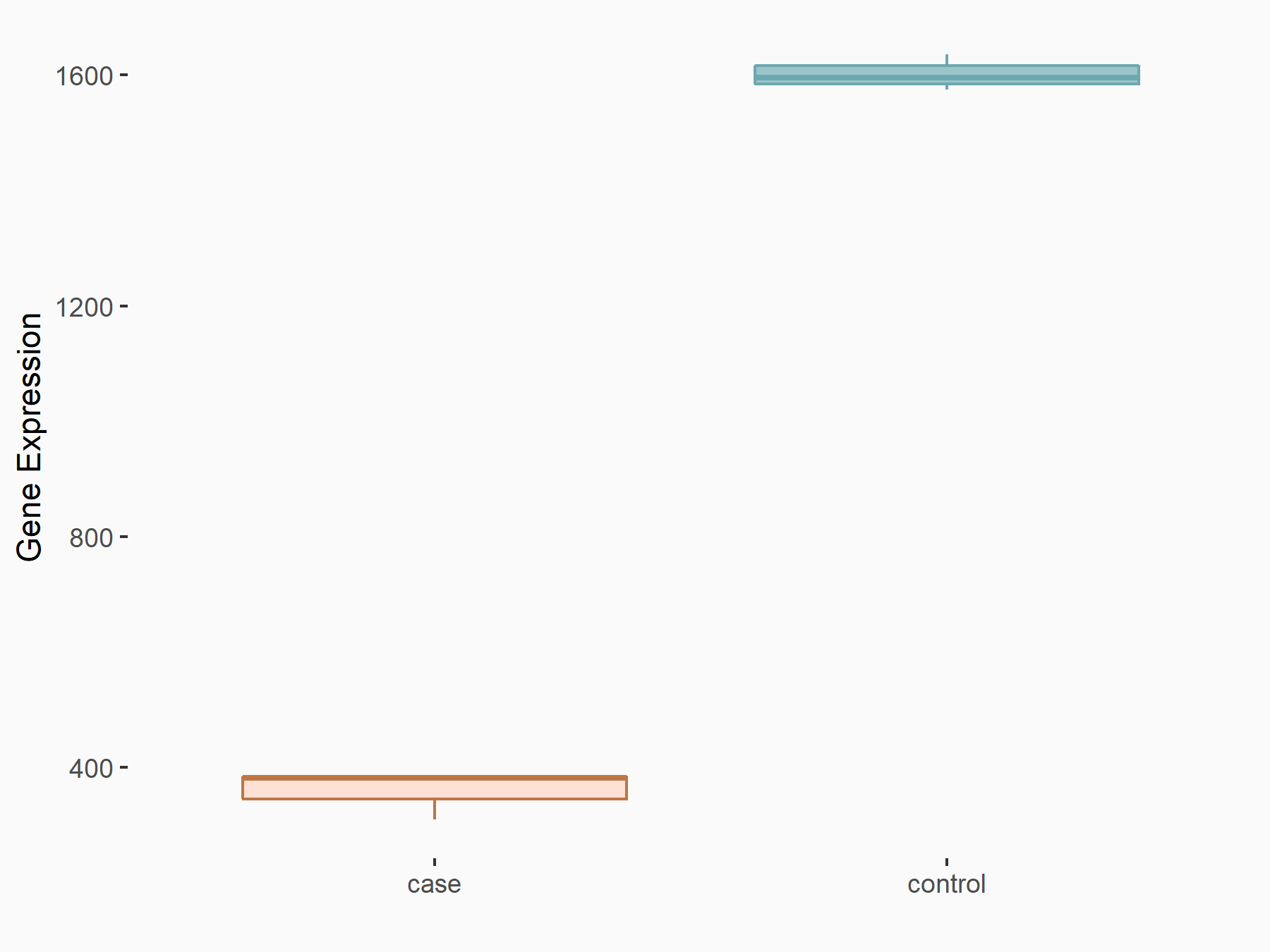 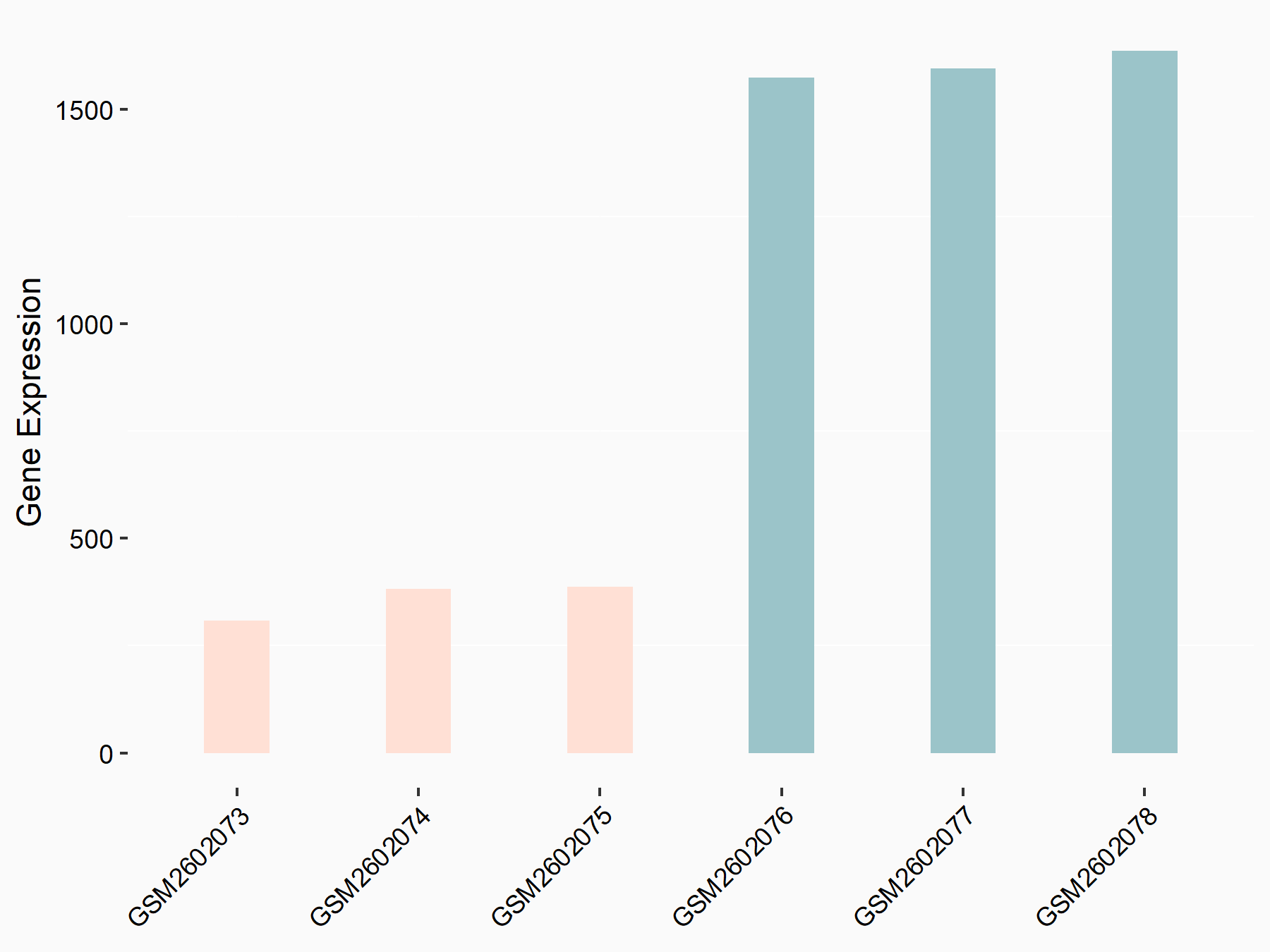 |
logFC: -2.16E+00 p-value: 5.15E-154 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 has a functional role in mediates osteoarthritis progression by regulating NF-Kappa-B signaling and ECM synthesis in chondrocytes that shed insight on developing preventive and curative strategies for OA by focusing on METTL3 and mRNA methylation. Silencing of METTL3 promotes degradation of extracellular matrix (ECM) by reducing the expression of MMP-13 and Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 (Coll X/PTGS2), elevating the expression of Aggrecan and Coll II. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoarthritis | ICD-11: FA05 | ||
| Cell Process | Inflammatory response and apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | ATDC-5 | Mouse teratocarcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_3894 |
| In-vivo Model | The right knee joint of each OA mouse was injected with 1U of type VII collagenase over two consecutive days to obtain experimental OA joint, and the control mice received the equal volume of physiological saline. | |||
Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 has a functional role in mediates osteoarthritis progression by regulating NF-Kappa-B signaling and ECM synthesis in chondrocytes that shed insight on developing preventive and curative strategies for OA by focusing on METTL3 and mRNA methylation. Silencing of METTL3 promotes degradation of extracellular matrix (ECM) by reducing the expression of MMP-13 and Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 (Coll X/PTGS2), elevating the expression of Aggrecan and Coll II. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Inflammatory response and apoptosis | |||
| In-vitro Model | ATDC-5 | Mouse teratocarcinoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_3894 |
| In-vivo Model | The right knee joint of each OA mouse was injected with 1U of type VII collagenase over two consecutive days to obtain experimental OA joint, and the control mice received the equal volume of physiological saline. | |||
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00365)
| In total 12 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE072597 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:186674276-186674277:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | TTTAATAATATTTATATTAAACTCCTTATGTTACTTAACAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000367468.10; ENST00000490885.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_69607 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE072598 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:186674318-186674319:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | ATATTTATTTATTTATATGAACCATGTCTATTAATTTAATT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | fibroblasts; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000490885.6; ENST00000367468.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_69608 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE072599 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:186674358-186674359:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | CTAAAAGAACGTTCGACTGAACTGTAGAAGTCTAATGATCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | fibroblasts; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559627.1; ENST00000367468.10; ENST00000490885.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_69609 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE072600 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:186674363-186674364:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TACTACTAAAAGAACGTTCGACTGAACTGTAGAAGTCTAAT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.287565476 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559627.1; ENST00000490885.6; ENST00000367468.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_69610 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE072601 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:186674370-186674371:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCCACAGTACTACTAAAAGAACGTTCGACTGAACTGTAGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.925321429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559627.1; ENST00000367468.10; ENST00000490885.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_69611 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE072602 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:186674406-186674407:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GCAAGTTCTTCCCGCTCCGGACTAGATGATATCAATCCCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000490885.6; ENST00000367468.10; ENST00000559627.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_69612 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE072603 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:186674441-186674442:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CAGATCCAGAGCTCATTAAAACAGTCACCATCAATGCAAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq; m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559627.1; ENST00000367468.10; ENST00000490885.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_69613 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE072604 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:186674610-186674611:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GCACCATTCTCCTTGAAAGGACTTATGGGTAATGTTATATG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000490885.6; ENST00000466691.1; ENST00000559627.1; ENST00000367468.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_69614 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE072605 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:186674648-186674649:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | CAGATGCCATCTTTGGTGAAACCATGGTAGAAGTTGGAGCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000466691.1; ENST00000490885.6; ENST00000367468.10; ENST00000559627.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_69615 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE072606 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:186679407-186679408:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CTGTTCCCACCCATGTCAAAACCGAGGTGTATGTATGAGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000490885.6; ENST00000559800.1; ENST00000559627.1; ENST00000367468.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_69616 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE072607 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:186680332-186680333:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCACAGCCAGACGCCCTCAGACAGCAAAGCCTACCCCCGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; fibroblasts; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000367468.10; ENST00000490885.6; ENST00000559800.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_69617 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE072608 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr1:186680378-186680379:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGTCAGGAGCACGTCCAGGAACTCCTCAGCAGCGCCTCCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549; fibroblasts; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000559800.1; ENST00000490885.6; ENST00000367468.10 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_69618 | ||
References