m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00316)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
LILRB4
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Browse Drug
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | Mouse liver | Mus musculus |
|
Treatment: FTO knockout mouse liver tissue
Control: Wild type mouse liver tissue
|
GSE125785 | |
| Regulation |
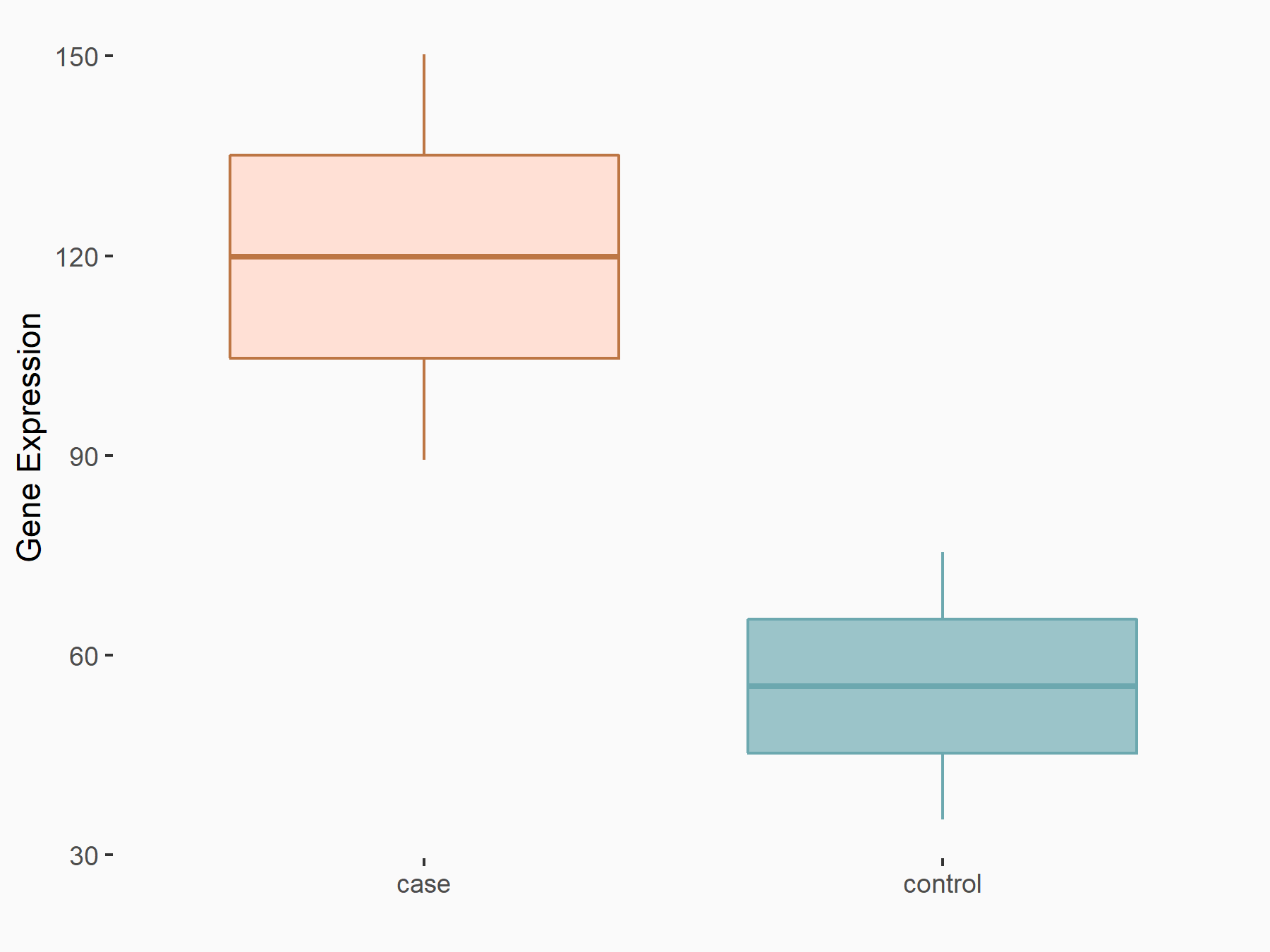 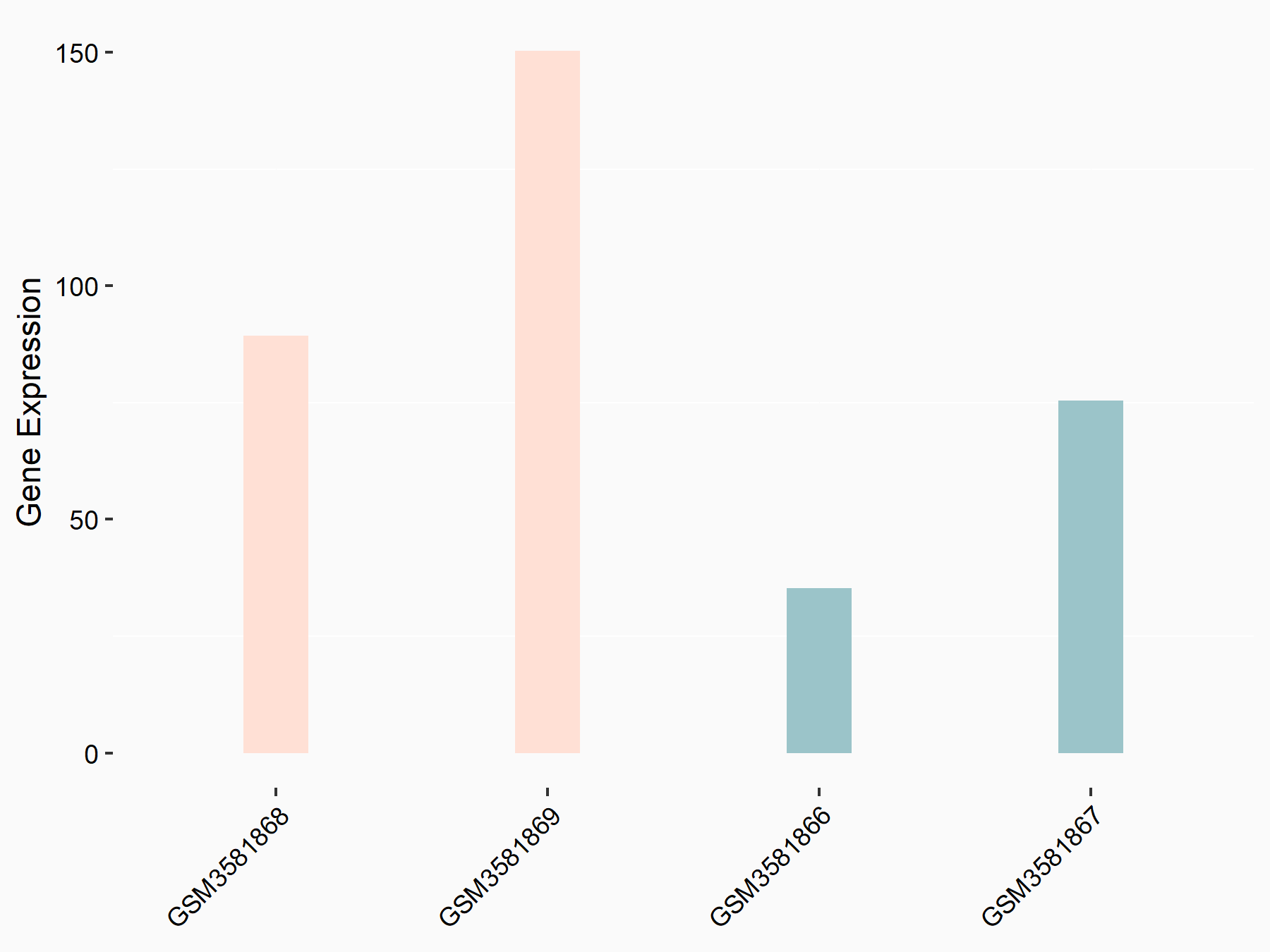 |
logFC: 1.12E+00 p-value: 2.09E-02 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 7 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2A60 | ||
| Responsed Drug | Meclofenamic acid | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2A60 | ||
| Responsed Drug | R-2HG | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2A60 | ||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
| Experiment 4 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2A60 | ||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
| Experiment 5 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2A60 | ||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
| Experiment 6 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2A60 | ||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
| Experiment 7 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2A60 | ||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60]
| In total 7 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | Meclofenamic acid | Approved | ||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | R-2HG | Investigative | ||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
| Experiment 4 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
| Experiment 5 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
| Experiment 6 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
| Experiment 7 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
Meclofenamic acid
[Approved]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2A60 | ||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
R-2HG
[Investigative]
| In total 1 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | Genetic depletion and pharmacological inhibition of FTO dramatically attenuate leukemia stem/initiating cell self-renewal and reprogram immune response by suppressing expression of immune checkpoint genes, especially Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 (LILRB4). FTO inhibitors, such as rhein, meclofenamic acid (MA), MO-I-500, fluorescein, and R-2HG, can inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell viability. CS1 and CS2 displayed a much higher efficacy in inhibiting AML cell viability. | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute myeloid leukaemia | ICD-11: 2A60 | ||
| Pathway Response | B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | ||
| Cell Process | Immune Evasion | |||
| In-vitro Model | MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For each experiment, 6- to 8-week-old mice were used and randomly allocated to each group. For xenograft mouse, 0.1 × 106 MA9.3ITD cells were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously. Drug treatment was started from 10 days after transplantation. CS2 was administered through intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection at 5mg/kg/day, every other day. CS1 dissolved in saturated Beta-cyclodextrin (C0926, Sigma-Aldrich) solution was delivered by intravenous injection (i.v.). Successful engraftment was observed following 4 weeks post inoculation displaying a level of about 5% human CD33+ cells in peripheral. To generate PDX mouse models, 1 × 106 AML patient derived BMMNCs were transplanted into NRGS recipient mice intravenously, and drug treatment was started from 7 days later. CS2, FB23-2, and free CS1 were administered through i.p. injection at 5 mg/kg/day, while Micelle (900661, Sigma-Aldrich) packaged CS1 was delivered by i.v. injection at 5mg/kg/day. Both CS1 and CS2 were injected every other day for a total of ten times. | |||
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00316)
| In total 2 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: A2ISITE009297 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:54656710-54656711:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | TGGCTTATTTCACTGACCATAATGACCTCCAGTTCCAACTA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000270452.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_72926 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE009298 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:54656730-54656731:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | AATGACCTCCAGTTCCAACTATGTTGCTGTAAATGTCAGGA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000270452.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_72927 | ||
References