m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00292)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
IKBKB
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | HeLa cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: METTL3 knockdown HeLa cells
Control: HeLa cells
|
GSE70061 | |
| Regulation |
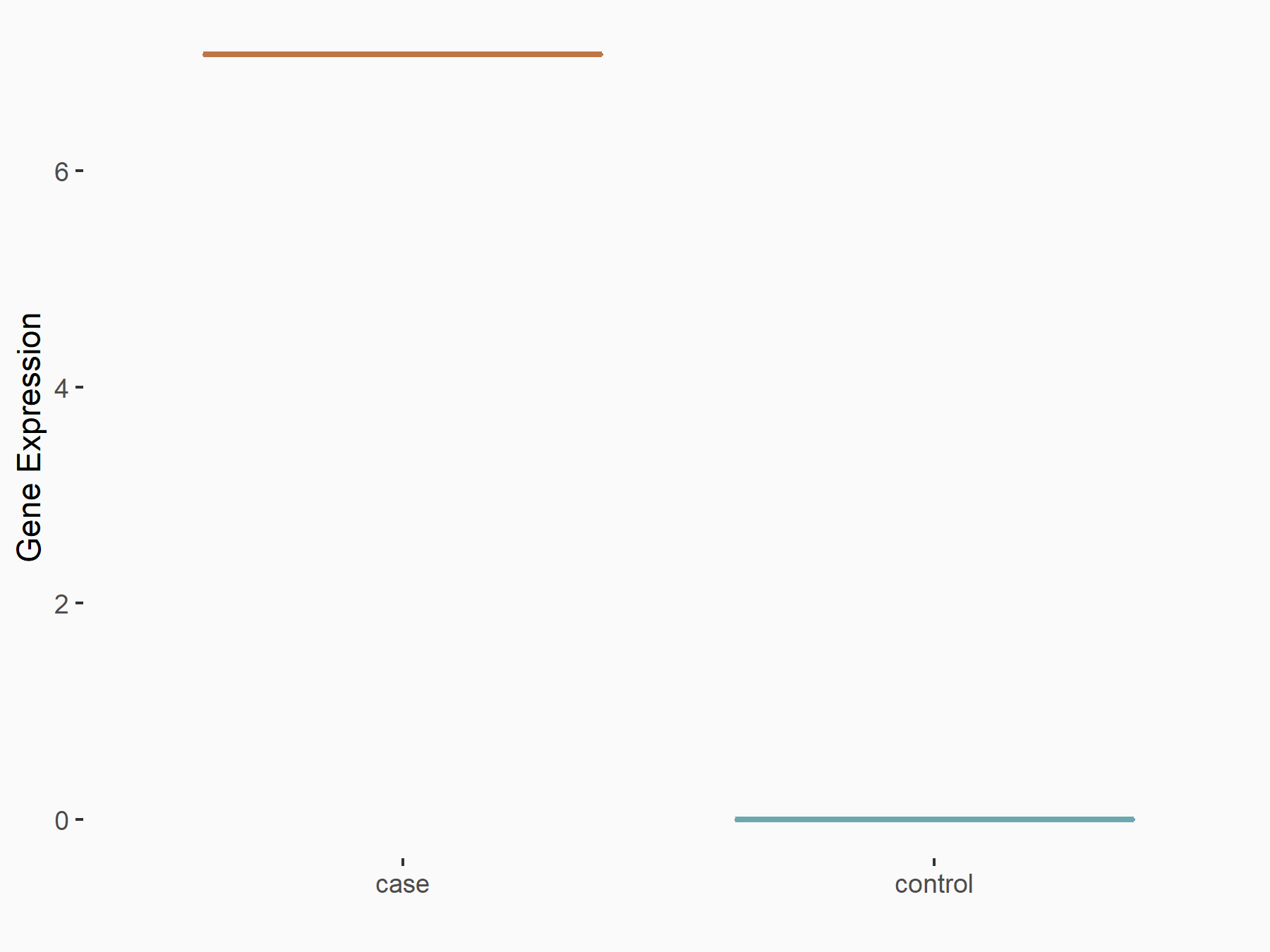  |
logFC: 3.01E+00 p-value: 5.15E-06 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | AF4/FMR2 family member 4 (AFF4), two key regulators of NF-Kappa-B pathway (Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta (IKBKB) and RELA) and MYC were further identified as direct targets of METTL3-mediated m6A modification.overexpression of METTL3 significantly promoted Bladder cancer cell growth and invasion. | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer | ICD-11: 2C94 | ||
| Cell Process | Glucose metabolism | |||
Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | AF4/FMR2 family member 4 (AFF4), two key regulators of NF-Kappa-B pathway (Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta (IKBKB) and RELA) and MYC were further identified as direct targets of METTL3-mediated m6A modification.overexpression of METTL3 significantly promoted Bladder cancer cell growth and invasion. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Glucose metabolism | |||
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00292)
| In total 36 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002588 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42273268-42273269:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | TCTACTAAAAATACAAAATTAGCTGGTGTGGTGGTGCATGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520835.7; rmsk_2501192; ENST00000522147.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130627 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002589 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42273666-42273667:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CTTCCCGTCTTTGCCTCCCAAAATGTTTGGATTACAGGCCT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000523105.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130628 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002590 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42273667-42273668:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | TTCCCGTCTTTGCCTCCCAAAATGTTTGGATTACAGGCCTG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000519735.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130629 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002591 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42273668-42273669:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | TCCCGTCTTTGCCTCCCAAAATGTTTGGATTACAGGCCTGA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000342222.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130630 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002592 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42273734-42273735:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | GTTTTTTTTTTATTTTTTGTAGTGATGGTGGTCTCACAATG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000517917.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130631 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002593 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42274159-42274160:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CCTGCCTCAGCCTCCTGAGTACCTGGAATTACAGGTGTGCA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000518679.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130632 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002594 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42274169-42274170:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CCTCCTGAGTACCTGGAATTACAGGTGTGCACCACCATGCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000518647.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130633 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002595 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42274194-42274195:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | TGTGCACCACCATGCCAGCTAATTTTTGTATTTTTAGTAGA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520655.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130634 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002596 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42274229-42274230:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | AGTAGAAATGGGGTTTCACCATGTAGGCCATGCCGGTCTCA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000521661.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130635 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002597 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42274249-42274250:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | ATGTAGGCCATGCCGGTCTCAAACTCCTGACCTCAGGTGAT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520655.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130636 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002598 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42275326-42275327:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | CCTCCTGAGTAGCTGGGACTACAGGTGTGCGTTGCCATGCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000518679.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130637 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002599 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42276006-42276007:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | CATGCCACCATACCCGGCTAATTTTTATGTTTTCAGCAGAG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000517388.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130638 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002600 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42279676-42279677:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | AGCTCGCAAGCAAAGAGGCTAGGATTGGAACCTGCGTCTGT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000523105.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130639 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002601 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42282213-42282214:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | ATTTTTTGAGACAGGGTCTCACTCCAGTAGTCCACGCTGGA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000519733.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130640 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002602 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42285417-42285418:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | ATAAAAAAAATTAGCTGGACACAATGACACATGCTTGTAAT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520201.5; rmsk_2501220; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000517388.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130641 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002603 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42285441-42285442:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | TGACACATGCTTGTAATCCCAGCTACTTGAAGCTGAGGTGG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000518679.5; rmsk_2501220; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000517890.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130642 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002604 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42286604-42286605:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CCTCCTGAGTGGCTAAGACTACAGGTGCATGGCACCACACC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520201.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130643 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002605 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42287646-42287647:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | CCCTGCTCTGCAGGGTTACTAATACCTGCTAGAGGCTTGTT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520835.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130644 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002606 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42288265-42288266:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | GTGTGGTTGCGCATGCCTGTAATCCCAGCTACTCAGGAGGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000520320.5; rmsk_2501225; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000523105.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130645 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002607 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42288266-42288267:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | TGTGGTTGCGCATGCCTGTAATCCCAGCTACTCAGGAGGCT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000629753.1; rmsk_2501225; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000517890.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130646 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002608 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42288828-42288829:+ | [4] | |
| Sequence | GTGCGTGGCTCACGCCTGTAATCCTAGCACTTTGGAAGGCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000523105.5; rmsk_2501226; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000342222.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130647 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002609 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42289139-42289140:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | CAGGAGAATGGCGTGAACCCAGGAGGCGGAGCTTGCAGTGA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520835.7; rmsk_2501227; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000416505.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130648 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002610 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42300435-42300436:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGGAATGTAGCTCAAACAAAAATGTTCTGAAGGGAACTTAG | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520810.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130649 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002611 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42300902-42300903:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | CTTGCTCTGTTGTCCGGGCTAGAGTGCAGTGGCACGATCAT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000523517.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130650 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002612 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42300983-42300984:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | CTCACCTCAGTCTCCCACGTAGCTGGGATGAAGGCATGCGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000519733.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130651 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002613 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42301039-42301040:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | ATTAAAATTTTTTTTTTTGTAGAGACAGGGTCTTGCTATAT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000517917.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130652 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002614 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42301045-42301046:+ | [5] | |
| Sequence | ATTTTTTTTTTTGTAGAGACAGGGTCTTGCTATATTGCCCA | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000520835.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130653 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002615 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42309498-42309499:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTACAGTGGCTCACTCCTGTAATCCCAGCACTTTGGGAGGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000342222.6; rmsk_2501257; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000519735.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130654 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002616 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42309499-42309500:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TACAGTGGCTCACTCCTGTAATCCCAGCACTTTGGGAGGCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000518679.5; rmsk_2501257; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000629753.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130655 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002617 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42309504-42309505:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGGCTCACTCCTGTAATCCCAGCACTTTGGGAGGCCGAGGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520201.5; rmsk_2501257; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000629753.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130656 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002618 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42309627-42309628:+ | [6] | |
| Sequence | GTGTGGTGGCGGGCGCCTGTAATCCCAGCTACTCGGAAGGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520810.6; rmsk_2501257; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000517890.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130657 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002619 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42321647-42321648:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CCTCCCATCTCAGCCTCCCAAGTAACCGGGACTACAGGCGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000518679.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130658 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002620 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42321734-42321735:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | GCACAGTGGATCACATCTGTAATCCCAGCACCTTGGGATGC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000523517.5; rmsk_2501277; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000522147.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130659 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002621 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42321735-42321736:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CACAGTGGATCACATCTGTAATCCCAGCACCTTGGGATGCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520201.5; rmsk_2501277; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000416505.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130660 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002622 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42327222-42327223:+ | [2] | |
| Sequence | CTTAATTTTCTCTTGGCTGTATGGCACGCGCTTGTAATCCT | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000523018.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000521225.3; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000649612.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130661 | ||
| mod ID: A2ISITE002623 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42327238-42327239:+ | [3] | |
| Sequence | CTGTATGGCACGCGCTTGTAATCCTAGCACTTTGGGAGGCC | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000521225.3; ENST00000519938.5; rmsk_2501288; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000523018.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520201.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: RNA-editing_site_130662 | ||
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 77 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084776 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42272320-42272321:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTGGCTTTGGTCATCTTGGGACAGTGAATAGGGGGACTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000518983.1; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000520655.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795674 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084777 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42272335-42272336:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTGGGACAGTGAATAGGGGGACTGGGAAGAGGGCTTCAGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000518983.1; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000517890.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795675 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084778 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42288636-42288637:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTGTGCTGTTTCTGTAGGAAACAGGTGAGCAGATTGCCATC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD4T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000523105.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795676 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084779 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42288688-42288689:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GCAGGAGCTCAGCCCCCGGAACCGAGAGCGGTGGTGCCTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD4T; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000523105.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795677 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084780 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42290208-42290209:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGTCCCTGAGGGGATGCAGAACTTGGCGCCCAATGACCTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; endometrial; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000518679.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795678 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084781 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42293449-42293450:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ACTTTCTTGACAGTACCTGAACCAGTTTGAGAACTGCTGTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000517890.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795679 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084782 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42293461-42293462:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GTACCTGAACCAGTTTGAGAACTGCTGTGGTCTGCGGGAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000517917.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795680 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084783 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42298039-42298040:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | AGCAGCTGGAAATGATATGGACTGCCACGTAATGTGACCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000342222.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795681 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084784 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42305213-42305214:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | GCTTAGATACCTTCATGAAAACAGAATCATCCATCGGGATC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000517812.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000523517.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795682 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084785 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42305246-42305247:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | TCGGGATCTAAAGCCAGAAAACATCGTCCTGCAGCAAGGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000517917.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795683 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084786 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42305268-42305269:+ | [9] | |
| Sequence | ATCGTCCTGCAGCAAGGAGAACAGAGGGTAAGTGACCTCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520320.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000519735.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795684 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084787 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42306402-42306403:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGGATCAGGGCAGTCTTTGCACATCATTCGTGGGGACCCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000342222.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795685 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084788 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42306417-42306418:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTTGCACATCATTCGTGGGGACCCTGCAGTACCTGGTAAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000342222.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795686 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084789 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42308928-42308929:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCTACTGGAGCAGCAGAAGTACACAGTGACCGTCGACTACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.856142857 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000519733.5; ENST00000519735.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000517388.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000518679.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795687 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084790 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42314353-42314354:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | GCGGCAGAAGAGTGAGGTGGACATTGTTGTTAGCGAAGACT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000522545.1; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000629753.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795688 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084791 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42316725-42316726:+ | [11] | |
| Sequence | GCAGCTGGTTCATATCTTGAACATGGTCACGGGCACCATCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520201.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795689 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084792 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42316806-42316807:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GAAGGCCAGAATCCAACAGGACACGGGCATCCCAGAGGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T; MT4; MM6; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000517917.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795690 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084793 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42316827-42316828:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CACGGGCATCCCAGAGGAGGACCAGGAGCTGCTGCAGGAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4; MM6; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520655.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795691 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084794 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42316960-42316961:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTGGCTGTGCCTCCTGGGAAACTCAACACACTTTCAGATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000518647.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000522147.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795692 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084795 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42317669-42317670:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TTTGCAGTTAAATGAGGGCCACACATTGGACATGGATCTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000517502.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000517917.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795693 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084796 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42318625-42318626:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGGTCTGGCACAGCATCCAGACCCTGAAGGAAGATTGCAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD4T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000517502.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000522785.1; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520810.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795694 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084797 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42318660-42318661:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGCAACCGGCTGCAGCAGGGACAGCGAGCCGCCATGTAGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; CD4T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517502.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000522785.1; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520655.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795695 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084798 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42318700-42318701:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GTGCCAGGCTTTTTTTTTAAACTTAATTTATTTAAAATTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; Huh7; CD4T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000517502.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000522785.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795696 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084799 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42318759-42318760:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGGAGGTGGTTGAGGCAGGGACCCAGAAGCAACCGTTATGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000522785.1; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000517502.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000522147.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795697 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084800 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42318794-42318795:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTATGAGCAACAAAAGGAAGACACTGGTTTGGATGGACGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000522785.1; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000517502.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000523105.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795698 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084801 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42318834-42318835:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GAAGCGGTTGGGTGGGCTGGACTGACGGAGGCCCCTTTAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000522785.1; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000517502.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000521661.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795699 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084802 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42318854-42318855:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ACTGACGGAGGCCCCTTTAGACCTGGCGAGGTGAGTGTGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000522785.1; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000517502.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000523517.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795700 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084803 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42319174-42319175:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGATAATAATTATAGCAGGGACCTCCCTTGACATTTGAGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; MT4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000522785.1; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000517502.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000416505.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795701 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084804 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42319286-42319287:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | CAGGATGAATCTCCTCCGAAACAACAGCTGCCTCTCCAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD4T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000517502.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000522785.1; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000649751.1; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000416505.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795702 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084805 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42319366-42319367:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | CCAAGTTGGATTTCTTCAAAACCAGCATCCAGATTGACCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD4T; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517502.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000522785.1; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000649751.1; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000521661.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795703 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084806 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42319405-42319406:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | TGGAGAAGTACAGCGAGCAAACCGAGTTTGGGATCAGTGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD4T; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000649751.1; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000522785.1; ENST00000517502.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000648136.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795704 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084807 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42319451-42319452:+ | [12] | |
| Sequence | ACTTTGCAATGAGTTTAAAGACACCATTTTTTTTTCTTTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD4T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649751.1; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000517502.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000522785.1; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520810.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795705 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084808 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42319594-42319595:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTTTTTTCAGCATCAGATAAACTGCTGCTGGCCTGGAGGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000522785.1; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000517502.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000649751.1; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000523105.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795706 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084809 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42319653-42319654:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GCTCTGTGGGCGGGTAGGAGACTCATTTTGGGTTTCGGAAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000522785.1; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000517502.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000649751.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795707 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084810 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42319672-42319673:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GACTCATTTTGGGTTTCGGAACTTACCAAGGGGGTGAGATT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000649751.1; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000517502.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000522785.1; ENST00000517890.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795708 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084811 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42319723-42319724:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ACTTTTCACTTTCTCATCAAACACTGGGTCGATCTCTGTCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000522785.1; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000517502.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000517917.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000649751.1; ENST00000517890.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795709 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084812 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42320748-42320749:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CATTAGGAGAACGAAGTGAAACTCCTGGTAGAACGGATGAT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; U2OS; Huh7; endometrial; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000519938.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795710 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084813 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42320779-42320780:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AACGGATGATGGCTCTGCAGACCGACATTGTGGACTTACAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; U2OS; MM6; Huh7; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000523105.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795711 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084814 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42320792-42320793:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCTGCAGACCGACATTGTGGACTTACAGAGGAGCCCCATGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; U2OS; MM6; Huh7; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000519938.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795712 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084815 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42320887-42320888:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCTGTGCCCAGCACACACAGACAGCCCTGGAGCTTCGGTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; U2OS; MM6; Huh7; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000523599.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795713 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084816 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42320941-42320942:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ACCCTCAGTGGCTGTGCGGGACCATTCTCTAGAGCATGCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000649612.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795714 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084817 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42321871-42321872:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ATATTTGACCTCAAGTCTAGACAGAACTTCTTTGTATATTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; U2OS; Huh7; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000522147.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795715 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084818 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42321876-42321877:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGACCTCAAGTCTAGACAGAACTTCTTTGTATATTTTAGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; U2OS; Huh7; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial; NB4; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000522147.4 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795716 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084819 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42321925-42321926:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GCAAGGGAGCTGTACAGGAGACTAAGGGAAAAACCTCGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; U2OS; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000520655.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795717 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084820 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42321937-42321938:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TACAGGAGACTAAGGGAAAAACCTCGAGGTAAGTGGGGTTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; U2OS; HEK293T; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000518679.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795718 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084821 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42322061-42322062:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCCTCTCTCCAGACCAGCGAACTGAGGGTGACAGTCAGGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; U2OS; HEK293T; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; endometrial; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000648136.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795719 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084822 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42322187-42322188:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTTCCTGCTCTGGAGGAAGGACTGGGAGATGCAGGTATGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD4T; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000520835.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795720 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084823 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42322240-42322241:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CCTCCTCTCTGATTCGCTGGACCTCATGAAGAGAGTTTCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000648136.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795721 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084824 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42322350-42322351:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGTTTATTCTTTGCAGTAAAACTGTGGTTTGCAAGCAGAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; LCLs; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000519938.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795722 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084825 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42322379-42322380:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGCAAGCAGAAGGCGCTGGAACTGTTGCCCAAGGTGGAAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; LCLs; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000648136.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795723 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084826 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42322431-42322432:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TAATGAATGAGGATGAGAAGACTGTTGTCCGGCTGCAGGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; LCLs; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000523105.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000522133.1; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000416505.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795724 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084827 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42329129-42329130:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ATCATTTTCTTTAGTGAAGAACTGGTGGCTGAAGCACATAA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MT4; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000521225.3; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000523018.5; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000629753.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795725 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084828 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42329182-42329183:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GCTAGAAAATGCCATACAGGACACTGTGAGGGAACAAGACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; MT4; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000523018.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000521225.3; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000517890.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795726 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084829 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42329195-42329196:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ATACAGGACACTGTGAGGGAACAAGACCAGAGTTTCACGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; MT4; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000523018.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520201.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795727 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084830 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42329200-42329201:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGACACTGTGAGGGAACAAGACCAGAGTTTCACGGTAACAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; CD34; HepG2; HEK293T; MT4; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000523018.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000521661.5; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000416505.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795728 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084831 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42329231-42329232:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ACGGTAACAGCTTGTGTGAGACTCCTGCGATTCCATGTCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; MT4; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; TREX; endometrial | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000523018.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000523517.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795729 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084832 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42330920-42330921:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TGTTGACTTTCAGGCCCTAGACTGGAGCTGGTTACAGACGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000342222.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795730 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084833 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42330988-42330989:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGGCCTCATGATGTGGGGGGACTCGACCCCCTGACATGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000520835.7 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795731 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084834 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42331001-42331002:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGGGGGGACTCGACCCCCTGACATGGGGCAGCCCATAGCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000648136.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795732 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084835 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42331040-42331041:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGGCCTTGTGCAGTGGGGGGACTCGACCCCCTGACATGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000520810.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795733 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084836 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42331053-42331054:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGGGGGGACTCGACCCCCTGACATGGGGCTGCCTGGAGCAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000517890.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000523517.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520835.7; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000520655.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795734 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084837 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42331187-42331188:+ | [8] | |
| Sequence | TCGCTTCCTCAGCAGCTGTGACTTTCACCCAGGACCCAGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.28175 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000342222.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795735 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084838 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42331200-42331201:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | AGCTGTGACTTTCACCCAGGACCCAGGACGCAGCCCTCCGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hNPCs; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520201.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795736 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084839 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42331366-42331367:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGCTTGGAGTACGGTTTGCCACACACGTGACTGGACAGTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000523599.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795737 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084840 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42331380-42331381:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | TTTGCCACACACGTGACTGGACAGTGTCCAATTCAAATCTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000416505.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795738 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084841 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42331485-42331486:+ | [13] | |
| Sequence | TCCCTGTCCTCTCTCACTTTACAGCTTGTGTTTCTTCTGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | kidney | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000523599.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795739 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084842 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42331521-42331522:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTGGATTCAGCTTCTCCTAAACAGACAGTTTAATTATAGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; H1A; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; GM12878; LCLs; Huh7; Jurkat; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000629753.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795740 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084843 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42331525-42331526:+ | [10] | |
| Sequence | ATTCAGCTTCTCCTAAACAGACAGTTTAATTATAGTTGCGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000519938.5; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000648136.1; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000649612.2 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795741 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084844 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42331770-42331771:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | GTGATTGTCACAGAGGAGGGACAGAAAGGGTATCTGCTGAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; H1B; hESCs; GM12878; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; TREX | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000522147.4; ENST00000522103.3; ENST00000520655.5; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000518679.5; ENST00000520810.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795742 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084845 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42332081-42332082:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | CTTCTTCAACATTTCACAGAACTTCTCTTTTATATAAAGGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000629753.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795743 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084846 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42332108-42332109:+ | [14] | |
| Sequence | TTTTATATAAAGGCAAGAGCACAAAATGAGTTCAGATGATC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000629753.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795744 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084847 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42332133-42332134:+ | [7] | |
| Sequence | ATGAGTTCAGATGATCACAAACAGGTGAGTTTTGTTGGAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000523599.2; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000342222.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795745 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084848 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42332335-42332336:+ | [15] | |
| Sequence | AGGCTTAACTTTGTGTAAGAACACTGTTTATCAATGTCATT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000342222.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795746 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084849 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42332367-42332368:+ | [15] | |
| Sequence | AATGTCATTTGGCTATAGAAACATTTTCTCCTGCTGATTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000342222.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795747 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084850 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42332397-42332398:+ | [15] | |
| Sequence | CTGCTGATTGTGTGTGTGAAACATGTATTAACATTCCAATG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520810.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795748 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084851 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42332419-42332420:+ | [15] | |
| Sequence | ATGTATTAACATTCCAATGAACTAGCATTTAATAAAGCACA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000520201.5; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000416505.6 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795749 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE084852 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr8:42332449-42332450:+ | [15] | |
| Sequence | AATAAAGCACAATTTTGGAAACCCTGGTAAATGACAGTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000649612.2; ENST00000629753.1; ENST00000342222.6; ENST00000520810.6; ENST00000416505.6; ENST00000520201.5 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_795750 | ||
References