m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00257)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
FOXD1
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) [WRITER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by METTL3 | ||
| Cell Line | LX2 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shMETTL3 LX2 cells
Control: shLuc LX2 cells
|
GSE207909 | |
| Regulation |
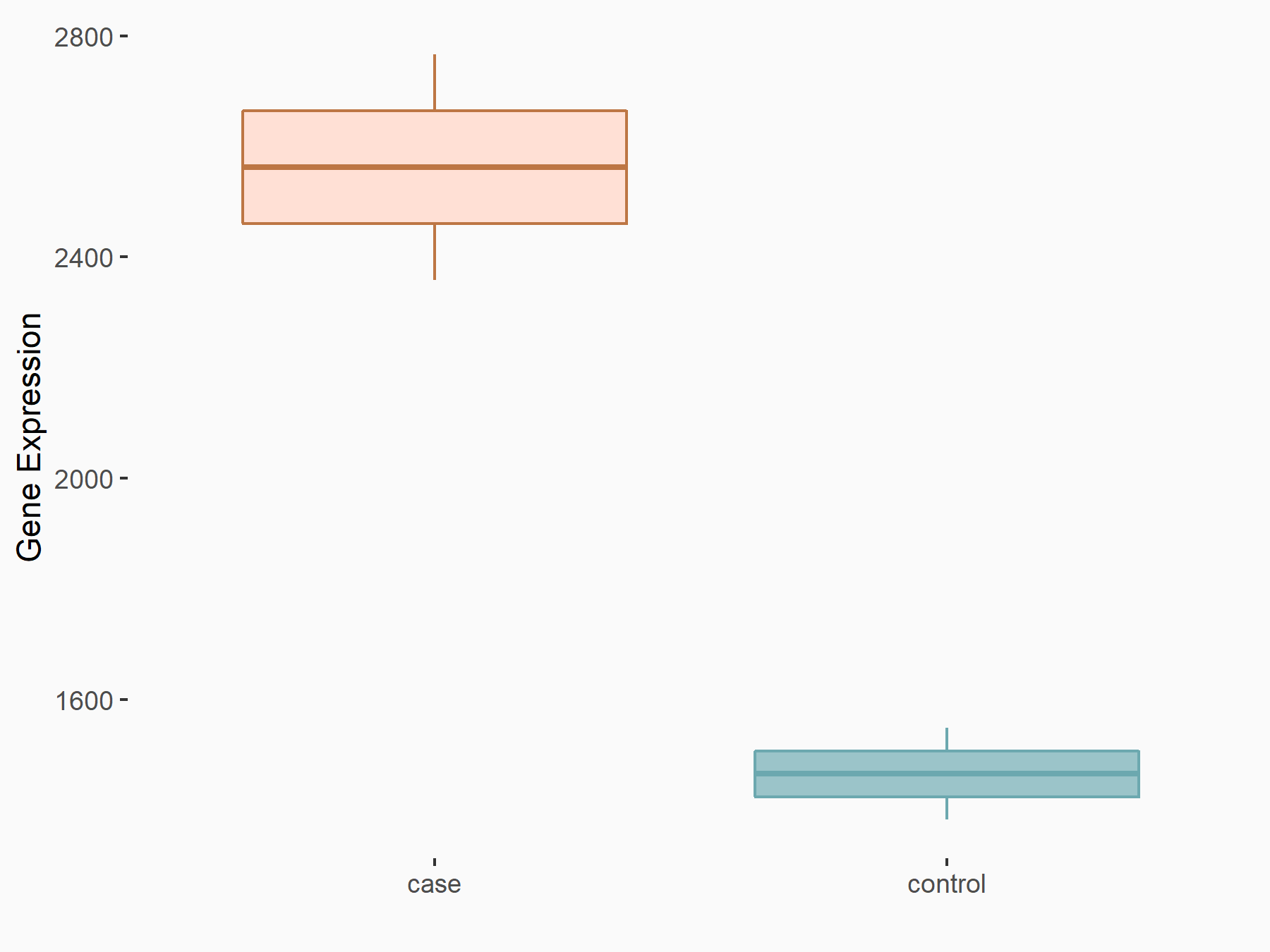  |
logFC: 8.07E-01 p-value: 2.88E-13 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| Representative RIP-seq result supporting the interaction between FOXD1 and the regulator | ||
| Cell Line | MDA-MB-231 | Homo sapiens |
| Regulation | logFC: 6.40E+00 | GSE60213 |
| In total 1 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 contributes to renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating Forkhead box protein D1 (FOXD1) methylation. When METTL3 was inhibited, m6A levels were accordingly decreased and cell apoptosis was suppressed in the H/R in vitro model. Based on MeRIP sequencing, transcription factor activating enhancer binding protein 2-alpha (tfap2a), cytochrome P-450 1B1 (cyp1b1), and forkhead box D1 (foxd1) were significantly differentially expressed, as was m6A, which is involved in the negative regulation of cell proliferation and kidney development. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Injury of kidney | ICD-11: NB92.0 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | NRK-52E | Normal | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0468 |
| In-vivo Model | Rats were anesthetized and incised through the midline of the abdomen, and the left renal vertebral arch and arteries were blocked for 45 min, thereby resulting in left kidney ischemia. At the same time, the right kidney was removed, further aggravating the degree of left kidney injury. | |||
Urinary/pelvic organs injury [ICD-11: NB92]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | METTL3 contributes to renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating Forkhead box protein D1 (FOXD1) methylation. When METTL3 was inhibited, m6A levels were accordingly decreased and cell apoptosis was suppressed in the H/R in vitro model. Based on MeRIP sequencing, transcription factor activating enhancer binding protein 2-alpha (tfap2a), cytochrome P-450 1B1 (cyp1b1), and forkhead box D1 (foxd1) were significantly differentially expressed, as was m6A, which is involved in the negative regulation of cell proliferation and kidney development. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Injury of kidney [ICD-11: NB92.0] | |||
| Target Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) | WRITER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Cell Process | Cell proliferation | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | NRK-52E | Normal | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0468 |
| In-vivo Model | Rats were anesthetized and incised through the midline of the abdomen, and the left renal vertebral arch and arteries were blocked for 45 min, thereby resulting in left kidney ischemia. At the same time, the right kidney was removed, further aggravating the degree of left kidney injury. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
RNA modification
m6A Regulator: Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO)
| In total 4 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00033 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | tRNA-Gln (anticodon TTG) 1-1 (TRQ-TTG1-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00035 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | tRNA-Arg (anticodon CCG) 1-1 (TRR-CCG1-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00037 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | tRNA-Thr (anticodon CGT) 1-1 (TRT-CGT1-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00046 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | Forkhead box protein D1 (FOXD1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
m6A Regulator: YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2)
| In total 3 item(s) under this m6A regulator | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00034 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | tRNA-Gln (anticodon TTG) 1-1 (TRQ-TTG1-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00036 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | tRNA-Arg (anticodon CCG) 1-1 (TRR-CCG1-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT00038 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | tRNA methyltransferase 10 homolog A (TRMT10A) | |
| Regulated Target | tRNA-Thr (anticodon CGT) 1-1 (TRT-CGT1-1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | m1G → m6A | |
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00257)
| In total 9 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003464 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73447070-73447071:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | ATCCCTCGTGGCCGCCGCGGCCGCCGCCGCCTCCTCAGTCT | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_35249 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003465 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73447075-73447076:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | ACCCGATCCCTCGTGGCCGCCGCGGCCGCCGCCGCCTCCTC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_35250 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003466 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73447102-73447103:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GCGGCCGTGGGCCCGGCGGCCGCGCTCACCCGATCCCTCGT | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_35251 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003467 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73447103-73447104:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GGCGGCCGTGGGCCCGGCGGCCGCGCTCACCCGATCCCTCG | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_35252 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003468 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73447106-73447107:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GCAGGCGGCCGTGGGCCCGGCGGCCGCGCTCACCCGATCCC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_35253 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003469 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73447109-73447110:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GGCGCAGGCGGCCGTGGGCCCGGCGGCCGCGCTCACCCGAT | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_35254 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003470 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73447110-73447111:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | CGGCGCAGGCGGCCGTGGGCCCGGCGGCCGCGCTCACCCGA | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_35255 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003471 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73447111-73447112:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GCGGCGCAGGCGGCCGTGGGCCCGGCGGCCGCGCTCACCCG | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_35256 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE003472 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73447258-73447259:- | ||
| Sequence | TTCTCCATCGAGAGCATCATCGGGGGCAGCTTGGGCCCGGC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | testis | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_35257 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 35 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069362 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73444902-73444903:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GCGGAATCCAAACGGCACAGACACTGCTGGCGCGCCTGGTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.897386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; H1299; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000513595.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672598 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069363 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73444959-73444960:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TTGAACCCGAGAACGTCCGGACTCCACGCGCCGCCCCGGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; H1299; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000513595.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672599 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069364 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73444975-73444976:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TAAGAGAGAGGAGTCATTGAACCCGAGAACGTCCGGACTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; H1299; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000513595.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672600 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069365 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73445038-73445039:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | ACAAATTGAAATACTGTTAGACCAAAGTCTTATATACAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000513595.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672601 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069366 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73445080-73445081:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TTAAACCCTCTCACTCTCAAACTTACCACTAAATCTATAGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; H1299; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000513595.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672602 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069367 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73445096-73445097:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAATGTTTGGAGGAGGTTAAACCCTCTCACTCTCAAACTTA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.185083333 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; H1299; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000513595.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672603 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069368 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73445165-73445166:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | TCTTTTTAGGGAGAAAACGGACTCTCACGGGCTCAAATGAA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; fibroblasts; A549; H1299; MM6; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000513595.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672604 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069369 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73446305-73446306:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | ATTCTAAATGTAAGATTTTTACACTTTTTCAGAAATAAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000513595.1; ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672605 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069370 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73446367-73446368:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GTACTTACTGCGTATTCTTTACAAGGAGTATTGTAAATTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.07285119 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3; ENST00000513595.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672606 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069371 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73446385-73446386:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | AGACGTGTGGATTTTTTTGTACTTACTGCGTATTCTTTACA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.278136905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3; ENST00000513595.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672607 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069372 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73446460-73446461:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | AAAATGGTTAACATGTTTACACAAGAAAAAAAGTCAAAATT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.084928571 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3; ENST00000513595.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672609 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069373 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73446470-73446471:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | ATGAAAAGGAAAAATGGTTAACATGTTTACACAAGAAAAAA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.168095238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3; ENST00000513595.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672611 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069374 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73446513-73446514:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CAATTCTTTTTTATTTGAGGACACTTGTCTGGTGTACTTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T; fibroblasts; A549; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3; ENST00000513595.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672613 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069375 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73446570-73446571:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | ATAATGGTCAAAAGAATAATACAAAAATAGTAAAGGTCTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.110482143 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000513595.1; ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672615 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069376 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73446641-73446642:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | TGACGTTTGGCAGATGAAAAACAACTAAGCCTTTTTGAGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; U2OS; fibroblasts; H1299; MM6; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3; ENST00000513595.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672617 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069377 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73446659-73446660:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | AGGCACTAGAGGCTCCCTTGACGTTTGGCAGATGAAAAACA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.833690476 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3; ENST00000513595.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672618 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069378 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73446729-73446730:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | CTACAGCCCCCCAACCCCCGACCTGGGGTAGGGAGGAAGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.844928571 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000513595.1; ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672621 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069379 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73446816-73446817:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GCTGCGAATTCTCGGACAAAACTGTCAACAGCCCGGGCGCG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; U2OS; fibroblasts; H1299; MM6; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000513595.1; ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672622 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069380 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73446821-73446822:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TCGCCGCTGCGAATTCTCGGACAAAACTGTCAACAGCCCGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; U2OS; fibroblasts; H1299; MM6; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000513595.1; ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672623 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069381 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73446858-73446859:- | [12] | |
| Sequence | TCCAGGCGCGGCCCCTCTCGACCTCGCGCGCCCATTTTCGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.844928571 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3; ENST00000513595.1 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672624 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069382 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73446987-73446988:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | TGTCCAGTGTCGAGAACTTTACTGCTAGGATTTCCAATTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.494845238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000513595.1; ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672625 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069383 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73446992-73446993:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TGCCCTGTCCAGTGTCGAGAACTTTACTGCTAGGATTTCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; U2OS; hESCs; fibroblasts; H1299; MM6; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672626 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069384 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73447014-73447015:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TGGGGACTCTGCACCAAGGGACTGCCCTGTCCAGTGTCGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; U2OS; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; H1299; MM6; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672627 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069385 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73447029-73447030:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCTCGTCCGCCGCCTTGGGGACTCTGCACCAAGGGACTGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; U2OS; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; H1299; MM6; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672628 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069386 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73447389-73447390:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | CGGCCGCCGAGCTGGCCCGGACCGCCTTCGGCTACCGGCCG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | U2OS; H1299; GSC-11; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672629 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069387 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73447742-73447743:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | GCTGGACCCGGAGTCCGCCGACATGTTCGACAACGGCAGCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672630 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069388 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73447757-73447758:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GGGCAACTACTGGACGCTGGACCCGGAGTCCGCCGACATGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; HepG2; U2OS; fibroblasts; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672631 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069389 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73447838-73447839:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | CTGGCAGAACAGCATCCGCCACAACCTCTCGCTCAACGACT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.053113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672632 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069390 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73447850-73447851:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GAAGTTCCCCGCCTGGCAGAACAGCATCCGCCACAACCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; U2OS; fibroblasts; H1299; MM6; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672633 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069391 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73448000-73448001:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | CGCGGGTAGCGGCGCCAAGAACCCGCTGGTGAAGCCGCCCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | U2OS; H1299; MM6; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672634 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069392 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73448313-73448314:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCTCTGGCCTCGCCGAGGAAACAGACATCGACGTGGTGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; U2OS; H1B; H1A; HEK293T; H1299; MM6; Jurkat; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TIME; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672635 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069393 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73448436-73448437:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | GGCCGGGCCTGCCGCCCGGGACCCGGGCTGGGGCGCAGAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | U2OS; H1299; GSC-11; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; MM6 | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672636 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069394 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73448530-73448531:- | [13] | |
| Sequence | TTATAAAGTCGGCGCGCGAGACTCCGCCGCCACCCGGCAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | U2OS; H1299; MM6; GSC-11; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; MSC; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672637 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069395 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73448740-73448741:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TCGCCGAGCTCTGTTCTTAGACTCTCACCCGTCCCGCACGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; MM6; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672638 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE069396 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr5:73448774-73448775:- | [14] | |
| Sequence | GAAGGTCCGCCCTCTCCTGGACTCAGCCCTGGCCTCGCCGA | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | MM6; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000615637.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_672639 | ||
References