m6A Target Gene Information
General Information of the m6A Target Gene (ID: M6ATAR00215)
Full List of m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
CEBPA
can be regulated by the following regulator(s), and cause disease/drug response(s). You can browse detail information of regulator(s) or disease/drug response(s).
Browse Regulator
Browse Disease
Browse Drug
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) [ERASER]
| Representative RNA-seq result indicating the expression of this target gene regulated by FTO | ||
| Cell Line | NB4 cell line | Homo sapiens |
|
Treatment: shFTO NB4 cells
Control: shNS NB4 cells
|
GSE103494 | |
| Regulation |
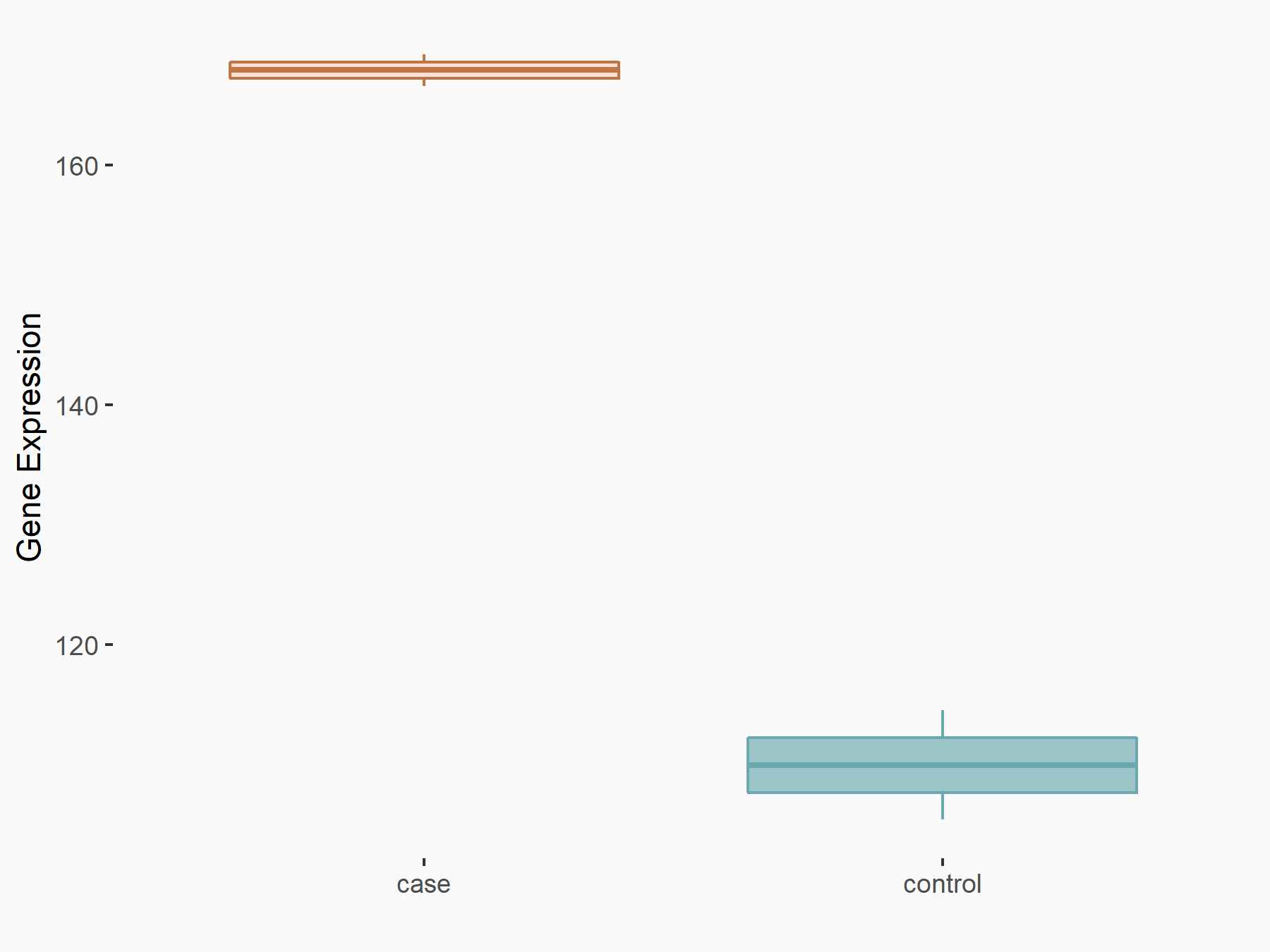  |
logFC: 6.07E-01 p-value: 3.92E-03 |
| More Results | Click to View More RNA-seq Results | |
| In total 2 item(s) under this regulator | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | This work demonstrates anti-tumor effects of 2HG in inhibiting proliferation/survival of FTO-high cancer cells via targeting FTO/m6A/MYC/CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA) signaling.High levels of FTO sensitize leukemia cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. R-2HG also displays anti-tumor activity in glioma. High levels of FTO sensitize leukemic cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma | ICD-11: 2A00.0 | ||
| Responsed Drug | R-2HG | Investigative | ||
| Cell Process | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 8-MG-BA | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1052 |
| A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
| DK-MG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1173 | |
| GaMG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1226 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| Jurkat | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0065 | |
| KOCL-45 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3993 | |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| KOCL-50 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6866 | |
| KOCL-51 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6865 | |
| KOCL-69 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3995 | |
| KOPN-1 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3937 | |
| LN-18 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0392 | |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| MA9.3 (MA9.3) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| MA9.6 (MLL-AF9) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| ME-1 [Human leukemia] | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2110 | |
| ML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1418 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| NOMO-1 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1609 | |
| PL21 | Familial adenomatous polyposis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_JM48 | |
| T98G | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0556 | |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For R-2HG injection mouse models, sensitive (NOMO-1 and MA9.3ITD) or resistant (MA9.3RAS) cells were injected into NSGS or NRGS intravenously, and then R-2HG (6mg/kg body weight) or PBS were injected once daily through tail vein for 12 consecutive days starting from day 11 post xeno-transplantation. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A Methylation Regulator of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | This work demonstrates anti-tumor effects of 2HG in inhibiting proliferation/survival of FTO-high cancer cells via targeting FTO/m6A/MYC/CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA) signaling.High levels of FTO sensitize leukemia cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. R-2HG also displays anti-tumor activity in glioma. High levels of FTO sensitize leukemic cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Leukaemia | ICD-11: 2B33.4 | ||
| Responsed Drug | R-2HG | Investigative | ||
| Cell Process | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 8-MG-BA | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1052 |
| A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
| DK-MG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1173 | |
| GaMG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1226 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| Jurkat | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0065 | |
| KOCL-45 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3993 | |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| KOCL-50 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6866 | |
| KOCL-51 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6865 | |
| KOCL-69 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3995 | |
| KOPN-1 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3937 | |
| LN-18 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0392 | |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| MA9.3 (MA9.3) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| MA9.6 (MLL-AF9) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| ME-1 [Human leukemia] | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2110 | |
| ML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1418 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| NOMO-1 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1609 | |
| PL21 | Familial adenomatous polyposis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_JM48 | |
| T98G | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0556 | |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For R-2HG injection mouse models, sensitive (NOMO-1 and MA9.3ITD) or resistant (MA9.3RAS) cells were injected into NSGS or NRGS intravenously, and then R-2HG (6mg/kg body weight) or PBS were injected once daily through tail vein for 12 consecutive days starting from day 11 post xeno-transplantation. | |||
Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | This work demonstrates anti-tumor effects of 2HG in inhibiting proliferation/survival of FTO-high cancer cells via targeting FTO/m6A/MYC/CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA) signaling.High levels of FTO sensitize leukemia cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. R-2HG also displays anti-tumor activity in glioma. High levels of FTO sensitize leukemic cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.0] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | R-2HG | Investigative | ||
| Cell Process | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 8-MG-BA | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1052 |
| A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
| DK-MG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1173 | |
| GaMG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1226 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| Jurkat | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0065 | |
| KOCL-45 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3993 | |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| KOCL-50 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6866 | |
| KOCL-51 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6865 | |
| KOCL-69 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3995 | |
| KOPN-1 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3937 | |
| LN-18 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0392 | |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| MA9.3 (MA9.3) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| MA9.6 (MLL-AF9) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| ME-1 [Human leukemia] | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2110 | |
| ML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1418 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| NOMO-1 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1609 | |
| PL21 | Familial adenomatous polyposis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_JM48 | |
| T98G | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0556 | |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For R-2HG injection mouse models, sensitive (NOMO-1 and MA9.3ITD) or resistant (MA9.3RAS) cells were injected into NSGS or NRGS intravenously, and then R-2HG (6mg/kg body weight) or PBS were injected once daily through tail vein for 12 consecutive days starting from day 11 post xeno-transplantation. | |||
Malignant haematopoietic neoplasm [ICD-11: 2B33]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | This work demonstrates anti-tumor effects of 2HG in inhibiting proliferation/survival of FTO-high cancer cells via targeting FTO/m6A/MYC/CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA) signaling.High levels of FTO sensitize leukemia cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. R-2HG also displays anti-tumor activity in glioma. High levels of FTO sensitize leukemic cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. | |||
| Responsed Disease | Leukaemia [ICD-11: 2B33.4] | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Drug | R-2HG | Investigative | ||
| Cell Process | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 8-MG-BA | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1052 |
| A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
| DK-MG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1173 | |
| GaMG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1226 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| Jurkat | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0065 | |
| KOCL-45 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3993 | |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| KOCL-50 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6866 | |
| KOCL-51 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6865 | |
| KOCL-69 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3995 | |
| KOPN-1 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3937 | |
| LN-18 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0392 | |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| MA9.3 (MA9.3) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| MA9.6 (MLL-AF9) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| ME-1 [Human leukemia] | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2110 | |
| ML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1418 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| NOMO-1 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1609 | |
| PL21 | Familial adenomatous polyposis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_JM48 | |
| T98G | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0556 | |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For R-2HG injection mouse models, sensitive (NOMO-1 and MA9.3ITD) or resistant (MA9.3RAS) cells were injected into NSGS or NRGS intravenously, and then R-2HG (6mg/kg body weight) or PBS were injected once daily through tail vein for 12 consecutive days starting from day 11 post xeno-transplantation. | |||
R-2HG
[Investigative]
| In total 2 item(s) under this drug | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | This work demonstrates anti-tumor effects of 2HG in inhibiting proliferation/survival of FTO-high cancer cells via targeting FTO/m6A/MYC/CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA) signaling.High levels of FTO sensitize leukemia cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. R-2HG also displays anti-tumor activity in glioma. High levels of FTO sensitize leukemic cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Glioma | ICD-11: 2A00.0 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 8-MG-BA | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1052 |
| A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
| DK-MG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1173 | |
| GaMG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1226 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| Jurkat | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0065 | |
| KOCL-45 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3993 | |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| KOCL-50 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6866 | |
| KOCL-51 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6865 | |
| KOCL-69 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3995 | |
| KOPN-1 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3937 | |
| LN-18 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0392 | |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| MA9.3 (MA9.3) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| MA9.6 (MLL-AF9) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| ME-1 [Human leukemia] | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2110 | |
| ML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1418 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| NOMO-1 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1609 | |
| PL21 | Familial adenomatous polyposis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_JM48 | |
| T98G | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0556 | |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For R-2HG injection mouse models, sensitive (NOMO-1 and MA9.3ITD) or resistant (MA9.3RAS) cells were injected into NSGS or NRGS intravenously, and then R-2HG (6mg/kg body weight) or PBS were injected once daily through tail vein for 12 consecutive days starting from day 11 post xeno-transplantation. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the m6A-centered Drug Response | [1] | |||
| Response Summary | This work demonstrates anti-tumor effects of 2HG in inhibiting proliferation/survival of FTO-high cancer cells via targeting FTO/m6A/MYC/CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA) signaling.High levels of FTO sensitize leukemia cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. R-2HG also displays anti-tumor activity in glioma. High levels of FTO sensitize leukemic cells to R-2HG, whereas hyperactivation of MYC signaling confers resistance that can be reversed by the inhibition of MYC signaling. | |||
| Target Regulator | Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) | ERASER | ||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
| Responsed Disease | Leukaemia | ICD-11: 2B33.4 | ||
| Cell Process | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| In-vitro Model | 8-MG-BA | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1052 |
| A-172 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0131 | |
| DK-MG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1173 | |
| GaMG | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1226 | |
| HEL | Erythroleukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0001 | |
| Jurkat | T acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0065 | |
| KOCL-45 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3993 | |
| KOCL-48 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6867 | |
| KOCL-50 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6866 | |
| KOCL-51 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_6865 | |
| KOCL-69 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3995 | |
| KOPN-1 | B acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_3937 | |
| LN-18 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0392 | |
| LN-229 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0393 | |
| MA9.3 (MA9.3) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| MA9.6 (MLL-AF9) | ||||
| MA9.6ITD (MLL-AF9 plus FLT3-ITD) | ||||
| MA9.6RAS (MLL-AF9 plus NRasG12D) | ||||
| ME-1 [Human leukemia] | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2110 | |
| ML-2 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1418 | |
| MV4-11 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0064 | |
| NB4 | Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0005 | |
| NOMO-1 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1609 | |
| PL21 | Familial adenomatous polyposis | Homo sapiens | CVCL_JM48 | |
| T98G | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0556 | |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0022 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0007 | |
| In-vivo Model | For R-2HG injection mouse models, sensitive (NOMO-1 and MA9.3ITD) or resistant (MA9.3RAS) cells were injected into NSGS or NRGS intravenously, and then R-2HG (6mg/kg body weight) or PBS were injected once daily through tail vein for 12 consecutive days starting from day 11 post xeno-transplantation. | |||
RNA Modification Sequencing Data Associated with the Target (ID: M6ATAR00215)
| In total 1 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M1ASITE000068 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33302533-33302534:- | [2] | |
| Sequence | GGGCCGGCGCGGGCCGGGCCATTCGCGACCCGGAGGTGCGC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m1A-MAP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m1A_site_547 | ||
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
| In total 15 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001889 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301598-33301599:- | ||
| Sequence | AGTGGCGGCAGCGGCGCGGGCAAGGCCAAGAAGTCGGTGGA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_23911 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001890 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301602-33301603:- | ||
| Sequence | CGCGAGTGGCGGCAGCGGCGCGGGCAAGGCCAAGAAGTCGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_23912 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001891 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301604-33301605:- | ||
| Sequence | CGCGCGAGTGGCGGCAGCGGCGCGGGCAAGGCCAAGAAGTC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_23913 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001892 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301607-33301608:- | ||
| Sequence | CTCCGCGCGAGTGGCGGCAGCGGCGCGGGCAAGGCCAAGAA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_23914 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001893 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301610-33301611:- | ||
| Sequence | GACCTCCGCGCGAGTGGCGGCAGCGGCGCGGGCAAGGCCAA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_23915 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001894 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301613-33301614:- | ||
| Sequence | CCCGACCTCCGCGCGAGTGGCGGCAGCGGCGCGGGCAAGGC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_23916 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001895 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301682-33301683:- | ||
| Sequence | GCGCCCGCGCTCGGTGCCGCCGGCCTGCCGGGCCCTGGCAG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_23917 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001896 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301683-33301684:- | ||
| Sequence | CGCGCCCGCGCTCGGTGCCGCCGGCCTGCCGGGCCCTGGCA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_23918 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001897 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301685-33301686:- | ||
| Sequence | CCCGCGCCCGCGCTCGGTGCCGCCGGCCTGCCGGGCCCTGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_23919 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001898 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33302102-33302103:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | ACGGGCGGCGGCGGCGGCGGCGACTTTGACTACCCGGGCGC | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_23920 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001899 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33302105-33302106:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | CCCACGGGCGGCGGCGGCGGCGGCGACTTTGACTACCCGGG | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_23921 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001900 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33302108-33302109:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GGCCCCACGGGCGGCGGCGGCGGCGGCGACTTTGACTACCC | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_23922 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001901 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33302111-33302112:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GTGGGCCCCACGGGCGGCGGCGGCGGCGGCGACTTTGACTA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_23923 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001902 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33302114-33302115:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GCCGTGGGCCCCACGGGCGGCGGCGGCGGCGGCGACTTTGA | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_23924 | ||
| mod ID: M5CSITE001903 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33302117-33302118:- | [3] | |
| Sequence | GCGGCCGTGGGCCCCACGGGCGGCGGCGGCGGCGGCGACTT | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | T24 | ||
| Seq Type List | Bisulfite-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m5C_site_23925 | ||
N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
| In total 36 m6A sequence/site(s) in this target gene | |||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040796 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300180-33300181:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | ATTACTTTTGATCCTGGGGGACCAATGAGGTGAGGGGGGTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433387 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040797 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300224-33300225:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AGCTGGGGGAAGGGTCTGAGACTCCCTTTCCTTTTGGTTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433389 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040798 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300257-33300258:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CGGATACTTGCCAAAATGAGACTCTCCGTCGGCAGCTGGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.319380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433391 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040799 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300272-33300273:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | TGTTTTGGTTTTGCTCGGATACTTGCCAAAATGAGACTCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.53247619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433392 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040800 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300385-33300386:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | TGCTTTATCAGCCGATATCAACACTTGTATCTGGCCTCTGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.173910714 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433393 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040801 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300424-33300425:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CCAGAGGGACCGGAGTTATGACAAGCTTTCCAAATATTTTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433394 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040802 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300436-33300437:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GATCAGTCCATCCCAGAGGGACCGGAGTTATGACAAGCTTT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; A549; HEK293A-TOA; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433395 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040803 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300467-33300468:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GCCTTCAGCATTGCCTAGGAACACGAAGCACGATCAGTCCA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; hESC-HEK293T; A549; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433397 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040804 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300512-33300513:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GGGGGTGAAGGGCCACTGGGACCCTCAGCCTTGTTTGTACT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HEK293T; A549; Huh7; HEK293A-TOA | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433398 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040805 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300562-33300563:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | ACCCCTGGTGGGAGAGGGAGACCTAGAGATCTGGCTGTGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; Huh7; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433399 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040806 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300676-33300677:- | [7] | |
| Sequence | GGGCTTCCCCTTGGGGCGGAACTCACTGCGATGGGGGTCAC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | Huh7; peripheral-blood; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | MeRIP-seq; m6A-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433400 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040807 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300725-33300726:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CCTCTCCCACCTCCCTCCGCACACACCCCACCCCAGCCTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.830589286 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433401 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040808 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300775-33300776:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | AAGGTTGTTCCCCTAGTTCTACATGAAGGTGGAGGGTCTCT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.078666667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433402 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040809 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300799-33300800:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | ATAGGGACTTGGGGCTTGGAACCTAAGGTTGTTCCCCTAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 2.930744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; HeLa; MM6; Huh7; peripheral-blood; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433403 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040810 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300813-33300814:- | [8] | |
| Sequence | AAAGGGGTGGAAACATAGGGACTTGGGGCTTGGAACCTAAG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; HeLa; MM6; Huh7; peripheral-blood; HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433404 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040811 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300821-33300822:- | [9] | |
| Sequence | GTCCTTAGAAAGGGGTGGAAACATAGGGACTTGGGGCTTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.20572619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HepG2; hESC-HEK293T; HeLa; MM6; Huh7; peripheral-blood | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MAZTER-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433405 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040812 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300876-33300877:- | [5] | |
| Sequence | CTCAGGGAGCTGAGATCCCGACAAGCCCGCCAGCCCCAGCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HEK293T; hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | DART-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433406 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040813 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33300942-33300943:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCTTCCCGAGGCTACAGCAGACCCCCATGAGAGAAGGAGGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; MM6; Huh7; HEK293T; iSLK | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433407 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040814 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301036-33301037:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CTTGTGCCTTGGAAATGCAAACTCACCGCTCCAATGCCTAC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.627720238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1B; MM6; Huh7; peripheral-blood; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TREX; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433408 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040815 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301164-33301165:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCTCCCTTCCTCTGCGCCGGACTTGGTGCGTCTAAGATGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1A; H1B; hESCs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433409 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040816 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301233-33301234:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CCCGAGCCGTGCGAGCCAGGACTAGGAGATTCCGGTGCCTC | ||
| Motif Score | 4.065041667 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1A; H1B; hESCs; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433410 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040817 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301293-33301294:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | TGGGCCAGCCTCCGGCGGGGACCCAGGGAGTGGTTTGGGGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1A; H1B; hESCs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433412 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040818 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301320-33301321:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GTGAGGCGCGCGGCTGTGGGACCGCCCTGGGCCAGCCTCCG | ||
| Motif Score | 3.622404762 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1A; H1B; hESCs; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433413 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040819 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301407-33301408:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | ACAGCTGAGCCGCGAACTGGACACGCTGCGGGGCATCTTCC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; liver; A549; hESC-HEK293T; H1A; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; MT4; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433414 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040820 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301412-33301413:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | GTGGAACAGCTGAGCCGCGAACTGGACACGCTGCGGGGCAT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; H1A; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; MT4; H1299; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433415 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040821 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301427-33301428:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CGCCTGCGCAAGCGGGTGGAACAGCTGAGCCGCGAACTGGA | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; H1A; H1B; hESCs; fibroblasts; MT4; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; MSC; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433416 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040822 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301449-33301450:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | GGAGCTGACCAGTGACAATGACCGCCTGCGCAAGCGGGTGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.839113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433417 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040823 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301455-33301456:- | [11] | |
| Sequence | GGTGCTGGAGCTGACCAGTGACAATGACCGCCTGCGCAAGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.859755952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | liver; hESC-HEK293T; A549; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-REF-seq; MAZTER-seq; m6A-CLIP/IP; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433418 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040824 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301462-33301463:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | AGCAGAAGGTGCTGGAGCTGACCAGTGACAATGACCGCCTG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.839113095 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | CD8T; A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433419 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040825 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301486-33301487:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | CCAAGCAGCGCAACGTGGAGACGCAGCAGAAGGTGCTGGAG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.871321429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433420 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040826 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301494-33301495:- | [10] | |
| Sequence | CGACAAGGCCAAGCAGCGCAACGTGGAGACGCAGCAGAAGG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.147845238 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | A549 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-CLIP/IP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433421 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040827 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301512-33301513:- | [6] | |
| Sequence | CGCGGTGCGCAAGAGCCGCGACAAGGCCAAGCAGCGCAACG | ||
| Motif Score | 2.865571429 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | hESC-HEK293T | ||
| Seq Type List | MAZTER-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433422 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040828 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301572-33301573:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CAAGAAGTCGGTGGACAAGAACAGCAACGAGTACCGGGTGC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.951386905 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; HEK293T; A549; hESC-HEK293T; H1A; H1B; hESCs; MT4; MM6; Huh7; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TREX; endometrial; HEC-1-A; GSCs; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433423 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040829 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301578-33301579:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | CAAGGCCAAGAAGTCGGTGGACAAGAACAGCAACGAGTACC | ||
| Motif Score | 3.643047619 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; hESC-HEK293T; H1A; hESCs; MT4; MM6; Jurkat; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TREX; endometrial; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; MAZTER-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433424 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040830 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33301768-33301769:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AGATCGCGCACTGCGGCCAGACCACCATGCACCTGCAGCCC | ||
| Motif Score | 2.876744048 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; MT4; MM6; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; TREX; NB4 | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433425 | ||
| mod ID: M6ASITE040831 | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| mod site | chr19:33302427-33302428:- | [4] | |
| Sequence | AGGCTCGCCATGCCGGGAGAACTCTAACTCCCCCATGGAGT | ||
| Motif Score | 3.373380952 | ||
| Cell/Tissue List | HeLa; HepG2; A549; MM6; CD4T; peripheral-blood; GSC-11; HEK293T; HEK293A-TOA; iSLK; NB4; AML | ||
| Seq Type List | m6A-seq; MeRIP-seq; miCLIP | ||
| Transcript ID List | ENST00000498907.3 | ||
| External Link | RMBase: m6A_site_433426 | ||
References