m6A Regulator Information
General Information of the m6A Regulator (ID: REG00029)
| Regulator Name | Synaptic functional regulator FMR1 (FMR1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
FMR1; Fragile X mental retardation protein 1; FMRP; Protein FMR-1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene Name | FMR1 | ||||
| Sequence |
MEELVVEVRGSNGAFYKAFVKDVHEDSITVAFENNWQPDRQIPFHDVRFPPPVGYNKDIN
ESDEVEVYSRANEKEPCCWWLAKVRMIKGEFYVIEYAACDATYNEIVTIERLRSVNPNKP ATKDTFHKIKLDVPEDLRQMCAKEAAHKDFKKAVGAFSVTYDPENYQLVILSINEVTSKR AHMLIDMHFRSLRTKLSLIMRNEEASKQLESSRQLASRFHEQFIVREDLMGLAIGTHGAN IQQARKVPGVTAIDLDEDTCTFHIYGEDQDAVKKARSFLEFAEDVIQVPRNLVGKVIGKN GKLIQEIVDKSGVVRVRIEAENEKNVPQEEEIMPPNSLPSNNSRVGPNAPEEKKHLDIKE NSTHFSQPNSTKVQRVLVASSVVAGESQKPELKAWQGMVPFVFVGTKDSIANATVLLDYH LNYLKEVDQLRLERLQIDEQLRQIGASSRPPPNRTDKEKSYVTDDGQGMGRGSRPYRNRG HGRRGPGYTSGTNSEASNASETESDHRDELSDWSLAPTEEERESFLRRGDGRRRGGGGRG QGGRGRGGGFKGNDDHSRTDNRPRNPREAKGRTTDGSLQIRVDCNNERSVHTKTLQNTSS EGSRLRTGKDRNQKKEKPDSVDGQQPLVNGVP Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Family | FMR1 family | ||||
| Function |
Multifunctional polyribosome-associated RNA-binding protein that plays a central role in neuronal development and synaptic plasticity through the regulation of alternative mRNA splicing, mRNA stability, mRNA dendritic transport and postsynaptic local protein synthesis of a subset of mRNAs. Plays a role in the alternative splicing of its own mRNA. Plays a role in mRNA nuclear export (By similarity). Together with export factor NXF2, is involved in the regulation of the NXF1 mRNA stability in neurons (By similarity). Stabilizes the scaffolding postsynaptic density protein DLG4/PSD-95 and the myelin basic protein (MBP) mRNAs in hippocampal neurons and glial cells, respectively; this stabilization is further increased in response to metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR) stimulation (By similarity). Plays a role in selective delivery of a subset of dendritic mRNAs to synaptic sites in response to mGluR activation in a kinesin-dependent manner (By similarity). Plays a role as a repressor of mRNA translation during the transport of dendritic mRNAs to postsynaptic dendritic spines. Component of the CYFIP1-EIF4E-FMR1 complex which blocks cap-dependent mRNA translation initiation (By similarity). Represses mRNA translation by stalling ribosomal translocation during elongation (By similarity). Reports are contradictory with regards to its ability to mediate translation inhibition of MBP mRNA in oligodendrocytes. Also involved in the recruitment of the RNA helicase MOV10 to a subset of mRNAs and hence regulates microRNA (miRNA)-mediated translational repression by AGO2. Plays also a role as an activator of mRNA translation of a subset of dendritic mRNAs at synapses . In response to mGluR stimulation, FMR1-target mRNAs are rapidly derepressed, allowing for local translation at synapses (By similarity). Binds to a large subset of dendritic mRNAs that encode a myriad of proteins involved in pre- and postsynaptic functions. Binds to 5'-ACU[GU]-3' and/or 5'-[AU]GGA-3' RNA consensus sequences within mRNA targets, mainly at coding sequence (CDS) and 3'-untranslated region (UTR) and less frequently at 5'-UTR. Binds to intramolecular G-quadruplex structures in the 5'- or 3'-UTRs of mRNA targets. Binds also to RNA ligands harboring a kissing complex (kc) structure; this binding may mediate the association of FMR1 with polyribosomes. Binds mRNAs containing U-rich target sequences. Binds to a triple stem-loop RNA structure, called Sod1 stem loop interacting with FMRP (SoSLIP), in the 5'-UTR region of superoxide dismutase SOD1 mRNA. Binds to the dendritic, small non-coding brain cytoplasmic RNA 1 (BC1); which may increase the association of the CYFIP1-EIF4E-FMR1 complex to FMR1 target mRNAs at synapses (By similarity). Associates with export factor NXF1 mRNA-containing ribonucleoprotein particles (mRNPs) in a NXF2-dependent manner (By similarity). Binds to a subset of miRNAs in the brain ). May associate with nascent transcripts in a nuclear protein NXF1-dependent manner. In vitro, binds to RNA homomer; preferentially on poly(G) and to a lesser extent on poly(U), but not on poly(A) or poly(C). Moreover, plays a role in the modulation of the sodium-activated potassium channel KCNT1 gating activity. Negatively regulates the voltage-dependent calcium channel current density in soma and presynaptic terminals of dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons, and hence regulates synaptic vesicle exocytosis (By similarity). Modulates the voltage-dependent calcium channel CACNA1B expression at the plasma membrane by targeting the channels for proteosomal degradation (By similarity). Plays a role in regulation of MAP1B-dependent microtubule dynamics during neuronal development (By similarity). Recently, has been shown to play a translation-independent role in the modulation of presynaptic action potential (AP) duration and neurotransmitter release via large-conductance calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels in hippocampal and cortical excitatory neurons. Finally, FMR1 may be involved in the control of DNA damage response (DDR) mechanisms through the regulation of ATR-dependent signaling pathways such as histone H2AX/H2A.x and BRCA1 phosphorylations; FUNCTION: [Isoform 10]: Binds to RNA homomer; preferentially on poly(G) and to a lesser extent on poly(U), but not on poly(A) or poly(C). May bind to RNA in Cajal bodies: Binds to RNA homomer; preferentially on poly(G) and to a lesser extent on poly(U), but not on poly(A) or poly(C). May bind to RNA in Cajal bodies; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a positive regulator of influenza A virus (IAV) replication. Required for the assembly and nuclear export of the viral ribonucleoprotein (vRNP) components.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Gene ID | 2332 | ||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Regulator Type | WRITER ERASER READER | ||||
| Mechanism Diagram | Click to View the Original Diagram | ||||
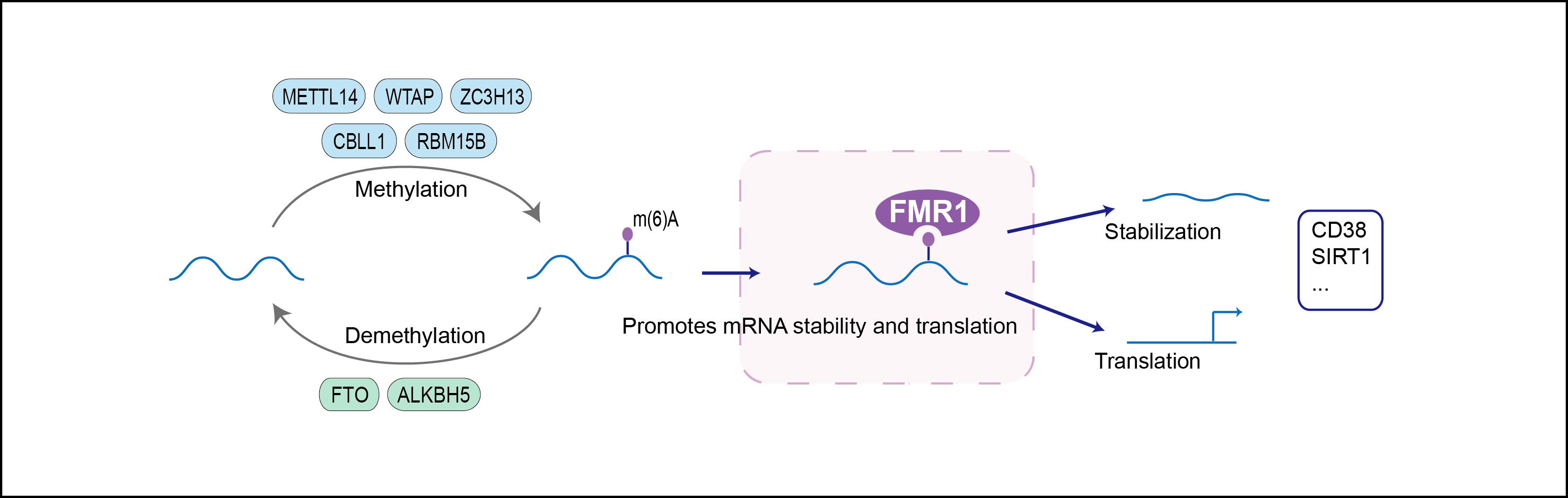
|
|||||
Full List of Target Gene(s) of This m6A Regulator and Corresponding Disease/Drug Response(s)
FMR1 can regulate the m6A methylation of following target genes, and result in corresponding disease/drug response(s). You can browse corresponding disease or drug response(s) resulted from the regulation of certain target gene.
Browse Target Gene related Disease
Putative C->U-editing enzyme APOBEC-4 (APOBEC4)
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
In-vitro Model |
HEY | Ovarian serous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0297 |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0006 | |
| Response Summary | Putative C->U-editing enzyme APOBEC-4 (APOBEC4) was found to be significantly correlated with m6A regulators such as WTAP, METTL14, ZC3H13, RBM15B, and FMR1. APOBEC3A was identified as a protective factor from comprehensive analyses based on the immune microenvironment and genomic instability of ovarian cancer. APOBEC3A had the potential to serve as a promising prognostic biomarker for foretelling the survival and immunotherapy response of ovarian cancer patients. | |||
Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 8 (ADAM8)
Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [2] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoarthritis [ICD-11: FA05] | |||
| Target Regulation | Up regulation | |||
Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase GPX4 (GPX4)
Acute kidney failure [ICD-11: GB60]
| In total 1 item(s) under this disease | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the m6A-centered Disease Response of This Target Gene | [3] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Acute kidney failure [ICD-11: GB60] | |||
| Target Regulation | Down regulation | |||
In-vitro Model |
HK-2 [Human kidney] | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0302 |
| In-vivo Model | All rats were housed under a 12 h light/dark cycle with constant temperature about 25 °C and relative humidity approximating 55%. The rats had free access to food and water for 10 days prior to the experiment. After that, the renal ischemia-reperfusion injury rat model was established. SD rats were anesthetized with an intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital sodium (25 mg/kg). Then an incision was made in the rat abdomen, and the right kidney was removed for nephrectomy. The left kidney was exposed after a midline incision, the renal artery was clamped for 45 min with a nontraumatic clamp, and renal blood flow was then restored. | |||
Full List of Crosstalk(s) between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation Related to This Regulator
DNA modification
m6A Target: Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase GPX4 (GPX4)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT02053 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) | |
| Regulated Target | Fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein 1 (FMR1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | DNA modification → m6A | |
| Disease | Acute kidney failure | |
Non-coding RNA
m6A Target: Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 8 (ADAM8)
| In total 1 item(s) under this m6A target | ||
| Crosstalk ID: M6ACROT05084 | ||
| Epigenetic Regulator | FAS antisense RNA 1 (FAS-AS1) | |
| Regulated Target | Fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein 1 (FMR1) | |
| Crosstalk relationship | ncRNA → m6A | |
| Disease | Osteoarthritis | |
Xenobiotics Compound(s) Regulating the m6A Methylation Regulator
| Compound Name | Donepezil | Investigative |
|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
donepezil; 120014-06-4; Aricept; 2-((1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-one; donepezilo; 2-[(1-benzyl-4-piperidyl)methyl]-5,6-dimethoxy-2,3-dihydroinden-1-one; 2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl]-5,6-dimethoxy-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-one; HSDB 7743; CHEMBL502; (S)-E2020 (free base); 142057-79-2; C24H29NO3; CHEBI:53289; 2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl]-5,6-dimethoxy-2,3-dihydroinden-1-one; Donepezil [INN:BAN]; (RS)-2-[(1-BENZYL-4-PIPERIDYL)METHYL]-5,6-DIMETHOXYINDAN-1-ONE; 1H-Inden-1-one, 2,3-dihydro-5,6-dimethoxy-2-((1-(phenylmethyl)-4-piperidinyl)methyl)-; 1H-Inden-1-one, 2,3-dihydro-5,6-dimethoxy-2-[[1-(phenylmethyl)-4-piperidinyl]methyl]-; 142057-80-5; NSC 737535; NSC 758882; NCGC00167537-01; donepezilum; Domepezil; Donaz; Donepezil (INN); Donaz (TN); Spectrum_001664; Spectrum5_001662; SCHEMBL2149; Oprea1_188452; KBioSS_002144; BDBM8960; GTPL6599; SCHEMBL8265876; DTXSID8048317; KBio2_002144; KBio2_004712; KBio2_007280; AMY8939; CHEBI:145499; BCPP000253; HMS3886M11; BCP07590; MFCD00912833; s5073; STK003905; AKOS000277311; AKOS016842349; AC-6969; BCP9000622; CCG-268401; DB00843; MRF-0000323; HY-14566; I903; SBI-0206789.P001; D-797; FT-0601545; D07869; AB00640013-07; AB00640013-08; AB00640013_09; AB00640013_10; 014D064; Q415081; Q-100098; BRD-A49160188-003-04-4; Z1741977105; 2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl]-5,6-dimethoxyindan-1-one; (+/-)-2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl]-5,6-dimethoxy-indan-1-one; 2-[(1-benzyl-4-piperidyl)methyl]- 5,6-dimethoxy-2,3-dihydroinden-1-one; 2,3-dihydro-5,6-dimethoxy-2 [[1-(phenyl methyl)-4-piperidinyl]methyl]-1H-inden-1-one; 2,3-dihydro-5,6-dimethoxy-2[[1-(phenyl methyl)-4-piperidinyl]methyl]-1H-inden-1-one; 5,6-dimethoxy-2-[[1-(phenylmethyl)piperidin-4-yl]methyl]-2,3-dihydroinden-1-one
Click to Show/Hide
|
|
| External link | ||
| Description |
Treatment of AIE-exposed adult rats with donepezil reversed both the dendritic spine adaptations and epigenetic modifications and expression of Fmr1.
|
[4] |
References