m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT05151
|
[1], [2] | |||
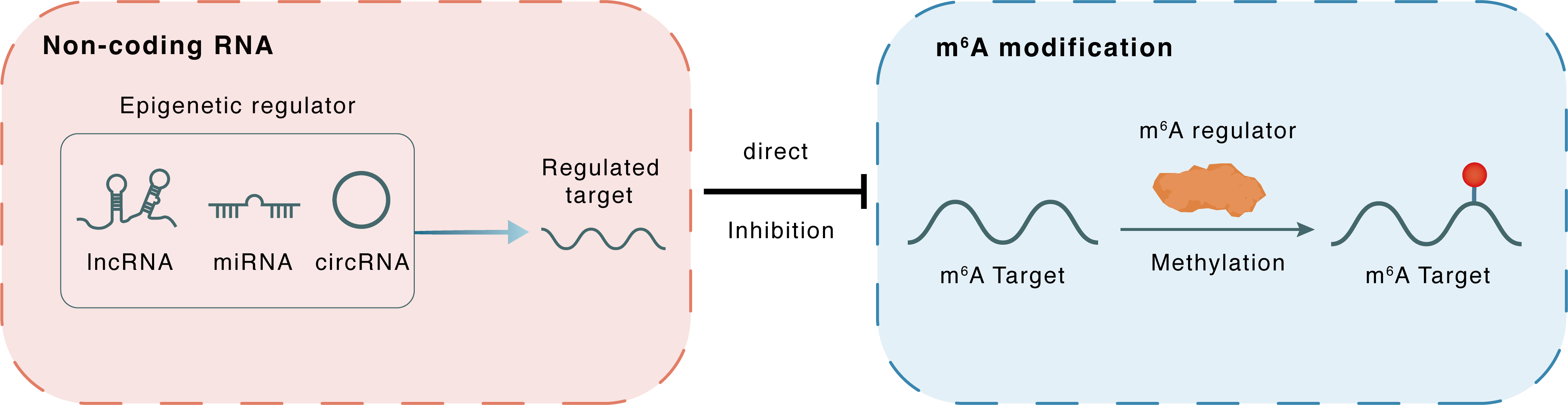 Non-coding RNA
miR-103-3p
METTL14
lncRNA miRNA circRNA
Direct
Inhibition
m6A modification
NFATC1
NFATC1
METTL14
Methylation
Non-coding RNA
miR-103-3p
METTL14
lncRNA miRNA circRNA
Direct
Inhibition
m6A modification
NFATC1
NFATC1
METTL14
Methylation
 : m6A sites : m6A sites
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | |||
| m6A Target | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1 (NFATC1) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | hsa-miR-103-3p | microRNA | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | ncRNA → m6A | Inhibition | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | ncRNAs directly impacts m6A modification through modulating the expression level of m6A regulator | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | hsa-miR-103-3p targets the m6 A methyltransferase METTL14 to inhibit osteoblastic bone formation.METTL14 released by exosomes can increase the m6A methylation level of Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1 (NFATC1) to inhibit osteoclasts, help postmenopausal osteoporosis patients preserve bone mass, and avoid triggering osteonecrosis of the jaw, thus becoming a new bioactive molecule for the treatment of osteoporosis. | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Osteoporosis | ICD-11: FB83.1 | |||
In-vitro Model |
RAW 264.7 | Mouse leukemia | Mus musculus | CVCL_0493 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0409 | ||
References