m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT03099
|
[1] | |||
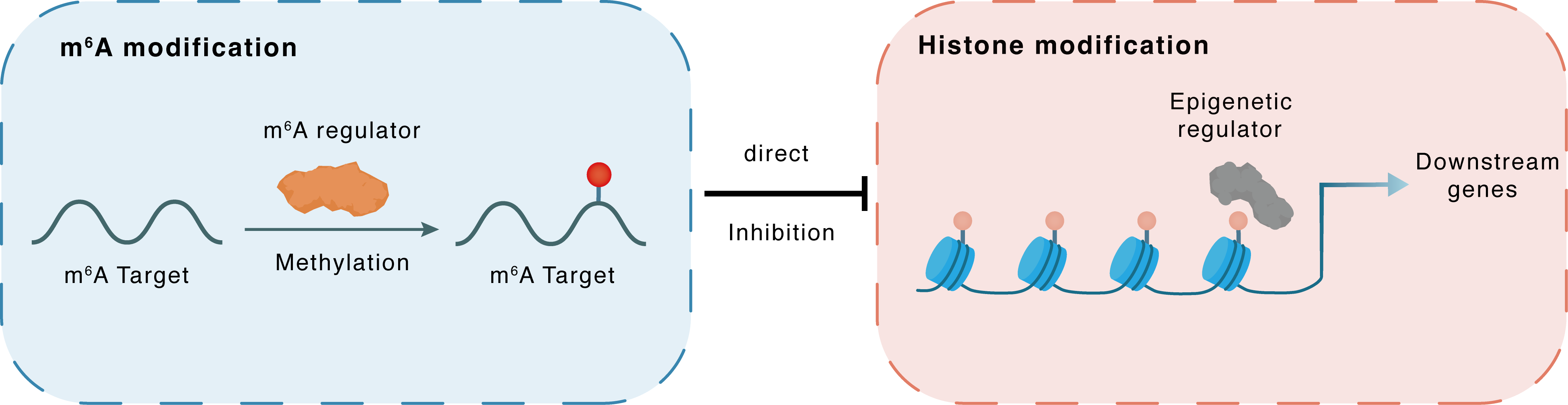 m6A modification
pri-rRNA
pri-rRNA
METTL14
Methylation
m6A modification
pri-rRNA
pri-rRNA
METTL14
Methylation
 : m6A sites
Direct
Inhibition
Histone modification
H3K9me3
SUV39H2
Downstream Gene : m6A sites
Direct
Inhibition
Histone modification
H3K9me3
SUV39H2
Downstream Gene
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | |||
| m6A Target | pri-rRNA | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Histone modification (HistMod) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV39H2 (SUV39H2) | WRITER | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | m6A → Histone modification | Inhibition | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | m6A modification directly impacts histone modification through recruiting histone-associated enzymes | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | SUV39H1/H2 protein, the methyltransferases catalyzing Histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) were dramatically elevated in METTL3/METTL14 deficient cells, which causes an accumulation and infiltration of H3K9me3 across the whole nucleolus and impairs the LLPS. Mechanistically, METTL3/METTL14 complex serves as an essential adapter for CRL4 E3 ubiquitin ligase targeting SUV39H1/SUV39H2 for polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation and therefore prevents H3K9me3 accumulation in nucleoli. | ||||