m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT03011
|
[1] | |||
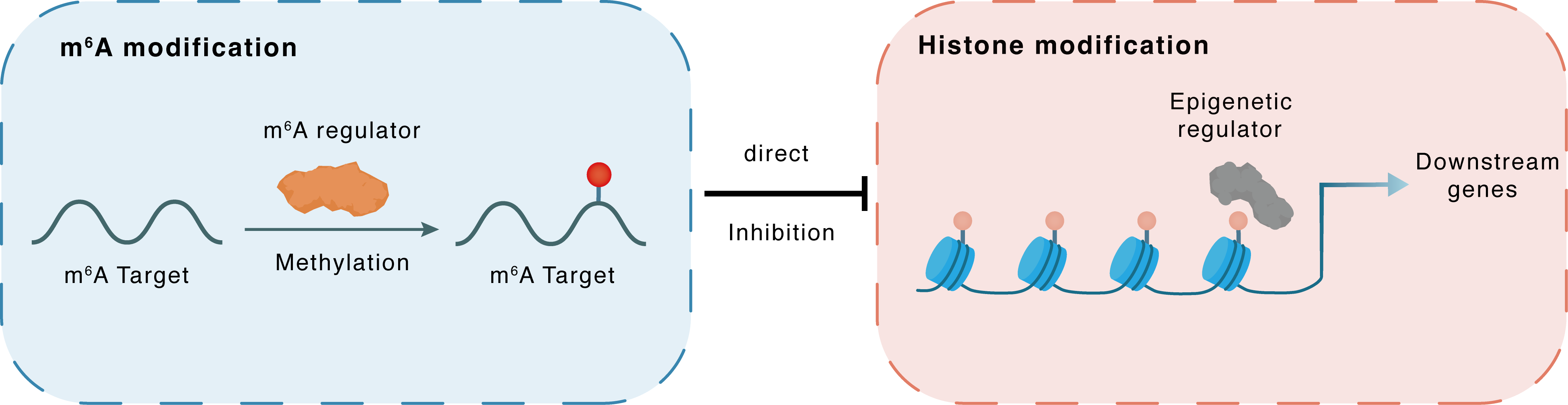 m6A modification
CBP
CBP
METTL14
Methylation
m6A modification
CBP
CBP
METTL14
Methylation
 : m6A sites
Direct
Inhibition
Histone modification
H3K27me3
CBP
Downstream Gene : m6A sites
Direct
Inhibition
Histone modification
H3K27me3
CBP
Downstream Gene
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | |||
| m6A Target | Phosphoprotein associated with glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains 1 (CBP) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Histone modification (HistMod) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) | WRITER | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | m6A → Histone modification | Inhibition | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | m6A modification impacts directly histone modification through modulating the expression level of histone-associated enzymes | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | The downregulation of Phosphoprotein associated with glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains 1 (CBP) and p300 by METTL14 serves as a regulatory mechanism for the modulation of specific histone modifications, namely Histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3), H3K27ac, and H3K4me3. This regulatory action underscores the role of METTL14 in epigenetic control through the influence of m6A RNA methylation on histone modification patterns. | ||||
| In-vivo Model | Positive ES clones were used for injection into c57 blastocysts and generation of chimerical mice. To produce Mettl14f/+ mice, the chimeras were crossed with wild-type c57 for germ line transmission and then crossed with Atcb-Flpe transgenic mice (The Jackson Laboratory, # 003800) to remove FRT flanked selection cassette. Male Mettl14f/+ mice were crossed to female EIIa-Cre transgenic mice (The Jackson Laboratory, # 003724) to obtain Mettl14+/mice, and Mettl14+/ mice were intercrossed to obtain Mettl18-conventional knockout mice. Sex of embryos was determined. | ||||
Full List of Potential Compound(s) Related to This m6A-centered Crosstalk
| CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) | 8 Compound(s) Regulating the Target | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| PRI-724 | Phase 1/2 | [2] | ||
| MOA | Modulator | |||
| External Link | ||||
| C 82 | Phase 1/2 | [3] | ||
| Synonyms |
N-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2H-triazol-4-amine; SCHEMBL15831502; C82
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| External Link | ||||
| CCS1477 | Phase 1/2 | [4] | ||
| Synonyms |
CCS-1477; CBP-IN-1; 2222941-37-7; (S)-1-(3,4-Difluorophenyl)-6-(5-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-1-((1r,4S)-4-methoxycyclohexyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)piperidin-2-one; SCHEMBL20094038; SCHEMBL21515367; SCHEMBL22134021; EX-A3687; NSC818619; NSC-818619; HY-111784; CS-0091862; (S)-1-(3,4-Difluorophenyl)-6-(5-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-1-(trans-4-methoxycyclohexyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)piperidin-2-one
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| External Link | ||||
| FT-7051 | Phase 1 | [5] | ||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| External Link | ||||
| Pyrrolo-pyrrolone derivative 6 | Patented | [6] | ||
| Synonyms |
PMID26924192-Compound-39
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 < 91 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
| ischemin | Investigative | [7] | ||
| Synonyms |
MS120
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 = 5000 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
| SGC-CBP30 | Investigative | [8] | ||
| Synonyms |
1613695-14-9; (s)-4-(1-(2-(3-chloro-4-methoxyphenethyl)-5-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-1h-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)propan-2-yl)morpholine; 2-[2-(3-chloro-4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]-5-(dimethyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl)-1-[(2S)-2-(morpholin-4-yl)propyl]-1H-1,3-benzodiazole; 2-[2-(3-Chloro-4-Methoxyphenyl)ethyl]-5-(3,5-Dimethyl-1,2-Oxazol-4-Yl)-1-[(2s)-2-(Morpholin-4-Yl)propyl]-1h-Benzimidazole; 2LO; C28H33ClN4O3; GTPL7529; SCHEMBL17512896; CHEMBL3622373; AOB4800; MolPort-035-395-859; BDBM188519; EX-A2159; ZINC96170456; s7256
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 = 30 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
| I-CBP112 | Investigative | [9] | ||
| Synonyms |
1640282-31-0; I-CBP 112; CHEMBL3774655; 1-[7-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-9-[[(3S)-1-methylpiperidin-3-yl]methoxy]-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1,4-benzoxazepin-4-yl]propan-1-one; 1-[7-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-9-{[(3S)-1-methylpiperidin-3-yl]methoxy}-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1,4-benzoxazepin-4-yl]propan-1-one; GTPL8236; SCHEMBL17620385; MolPort-035-765-871; EX-A2474; ZINC96024493; BDBM50151663; AKOS024458402; CS-6146; NCGC00350526-04; HY-19541; I-CBP112, >
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 = 440 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
References