m6A-centered Crosstalk Information
Mechanism of Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Epigenetic Regulation
| Crosstalk ID |
M6ACROT03009
|
[1] | |||
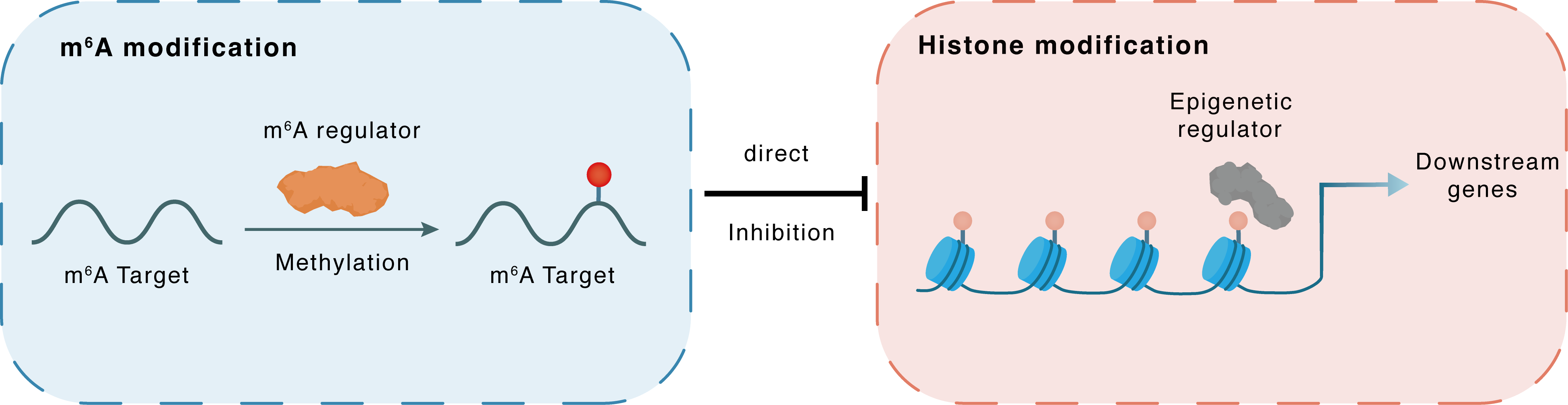 m6A modification
CBP
CBP
METTL14
Methylation
m6A modification
CBP
CBP
METTL14
Methylation
 : m6A sites
Direct
Inhibition
Histone modification
H3K4me3
CBP
Downstream Gene : m6A sites
Direct
Inhibition
Histone modification
H3K4me3
CBP
Downstream Gene
|
|||||
| m6A Modification: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m6A Regulator | Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) | WRITER | |||
| m6A Target | Phosphoprotein associated with glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains 1 (CBP) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulation that have Cross-talk with This m6A Modification: | |||||
| Epigenetic Regulation Type | Histone modification (HistMod) | ||||
| Epigenetic Regulator | CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) | WRITER | View Details | ||
| Regulated Target | Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) | View Details | |||
| Crosstalk Relationship | m6A → Histone modification | Inhibition | |||
| Crosstalk Mechanism | m6A modification impacts directly histone modification through modulating the expression level of histone-associated enzymes | ||||
| Crosstalk Summary | The downregulation of Phosphoprotein associated with glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains 1 (CBP) and p300 by METTL14 serves as a regulatory mechanism for the modulation of specific histone modifications, namely H3K27me3, H3K27ac, and Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3). This regulatory action underscores the role of METTL14 in epigenetic control through the influence of m6A RNA methylation on histone modification patterns. | ||||
| In-vivo Model | Positive ES clones were used for injection into c57 blastocysts and generation of chimerical mice. To produce Mettl14f/+ mice, the chimeras were crossed with wild-type c57 for germ line transmission and then crossed with Atcb-Flpe transgenic mice (The Jackson Laboratory, # 003800) to remove FRT flanked selection cassette. Male Mettl14f/+ mice were crossed to female EIIa-Cre transgenic mice (The Jackson Laboratory, # 003724) to obtain Mettl14+/mice, and Mettl14+/ mice were intercrossed to obtain Mettl16-conventional knockout mice. Sex of embryos was determined. | ||||
Full List of Potential Compound(s) Related to This m6A-centered Crosstalk
| CREB-binding protein (CREBBP) | 8 Compound(s) Regulating the Target | Click to Show/Hide the Full List | ||
| PRI-724 | Phase 1/2 | [2] | ||
| MOA | Modulator | |||
| External Link | ||||
| C 82 | Phase 1/2 | [3] | ||
| Synonyms |
N-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2H-triazol-4-amine; SCHEMBL15831502; C82
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| External Link | ||||
| CCS1477 | Phase 1/2 | [4] | ||
| Synonyms |
CCS-1477; CBP-IN-1; 2222941-37-7; (S)-1-(3,4-Difluorophenyl)-6-(5-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-1-((1r,4S)-4-methoxycyclohexyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)piperidin-2-one; SCHEMBL20094038; SCHEMBL21515367; SCHEMBL22134021; EX-A3687; NSC818619; NSC-818619; HY-111784; CS-0091862; (S)-1-(3,4-Difluorophenyl)-6-(5-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-1-(trans-4-methoxycyclohexyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)piperidin-2-one
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| External Link | ||||
| FT-7051 | Phase 1 | [5] | ||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| External Link | ||||
| Pyrrolo-pyrrolone derivative 6 | Patented | [6] | ||
| Synonyms |
PMID26924192-Compound-39
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 < 91 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
| ischemin | Investigative | [7] | ||
| Synonyms |
MS120
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 = 5000 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
| SGC-CBP30 | Investigative | [8] | ||
| Synonyms |
1613695-14-9; (s)-4-(1-(2-(3-chloro-4-methoxyphenethyl)-5-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-1h-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)propan-2-yl)morpholine; 2-[2-(3-chloro-4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]-5-(dimethyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl)-1-[(2S)-2-(morpholin-4-yl)propyl]-1H-1,3-benzodiazole; 2-[2-(3-Chloro-4-Methoxyphenyl)ethyl]-5-(3,5-Dimethyl-1,2-Oxazol-4-Yl)-1-[(2s)-2-(Morpholin-4-Yl)propyl]-1h-Benzimidazole; 2LO; C28H33ClN4O3; GTPL7529; SCHEMBL17512896; CHEMBL3622373; AOB4800; MolPort-035-395-859; BDBM188519; EX-A2159; ZINC96170456; s7256
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 = 30 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
| I-CBP112 | Investigative | [9] | ||
| Synonyms |
1640282-31-0; I-CBP 112; CHEMBL3774655; 1-[7-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-9-[[(3S)-1-methylpiperidin-3-yl]methoxy]-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1,4-benzoxazepin-4-yl]propan-1-one; 1-[7-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-9-{[(3S)-1-methylpiperidin-3-yl]methoxy}-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1,4-benzoxazepin-4-yl]propan-1-one; GTPL8236; SCHEMBL17620385; MolPort-035-765-871; EX-A2474; ZINC96024493; BDBM50151663; AKOS024458402; CS-6146; NCGC00350526-04; HY-19541; I-CBP112, >
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| MOA | Inhibitor | |||
| Activity | IC50 = 440 nM | |||
| External Link | ||||
References